DBA技术栈MongoDB: 索引和查询优化
2.1 批量插入数据
单条数据插入
db.collection.insertOne()
多条数据插入
db.collection.insertMany()
db.inventory.insertMany( [
{ item: "journal", qty: 25, size: { h: 14, w: 21, uom: "cm" }, status: "A" },
{ item: "notebook", qty: 50, size: { h: 8.5, w: 11, uom: "in" }, status: "A" },
{ item: "paper", qty: 100, size: { h: 8.5, w: 11, uom: "in" }, status: "D" },
{ item: "planner", qty: 75, size: { h: 22.85, w: 30, uom: "cm" }, status: "D" },
{ item: "postcard", qty: 45, size: { h: 10, w: 15.25, uom: "cm" }, status: "A" }
]);
插入数据
use testdb
for(var i =1; i<10; i++) db.users.insert({id:i,name: "zhangsan"+i,age: 100+i})
2.2 查询选择器
2.2.1 常规查询方式
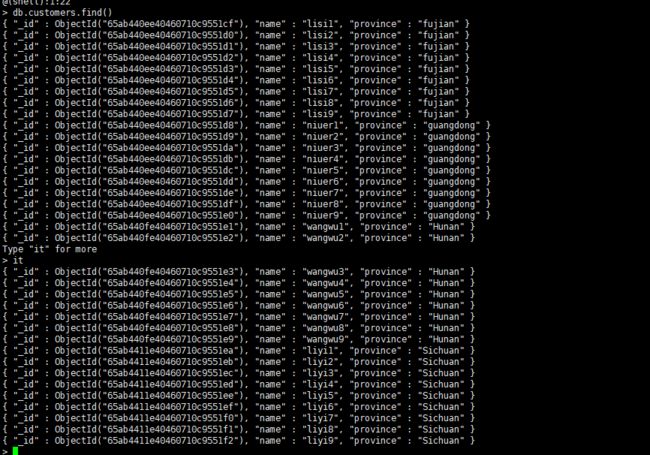
最简单的查询语句为:db.customers.find(),按照插入的顺序返回前20个文档,如果 记录总数比20大,则我们可以通过命令“it”获取更多文档。
> db.users.find({id:9})
精确匹配选择器,返回包含键值对id:9的文档。
> db.users.find({name:"xiaoming",age:101})
精确匹配选择器,但查询条件是要返回同时匹配键值对{name:"xiaoming",age:101}的文档。
> db.users.find({age:{$lt:102}})
$lt表示的是小于
> db.users.find({age:{$lte:102}})
$lte表示的小于或等于
> db.users.find({age:{$gt:105}})
$gt表示的是大于
> db.users.find({age:{$gte:105}})
$gte表示的是大于或等于
> db.users.find({age:{$lt:120,$gte:105}})
范围选择器,age:{$lt:120,$gte:119}表示的是小于120,大于或等于119
> db.users.find({id:{$in:[1,2]}})
表示返回key的值在某些value范围内
> db.users.find({id:{$nin:[1,2]}})
$nin表示返回key的值不在某些value范围内,$nin是一种比较低效的査询选择器,它会进行全表扫描,因此最好不要单独使用$nin
> db.users.find({id:{$ne:1}})
$ne表示不等于。单独使用$ne,它也不会利用索引的优势,反而会进行全表扫描,我们最好与其他查询选择器配合使用。
> db.users.find({$or:[{id:11},{age:109}] })
$or表示或运算的选择器,主要用于对两个不同key对应的文档进行连接。
> db.users.find({$and:[{id:1},{age:109}]})
$and表示与运算的选择器,对于两个不同的key,要同时满足条件。
> db.users.find({id:{$exists:ture}})
$exists与关系数据库中的exists不一样,因为MongoDB的表结构不是固定的,有的时候需要返回包含有某个字段的所有记录或者不包含某个字段的所有记录。
2.2.2 索引和查询优化
索引是个与数据存储和査询相关的古老话题,目的只有一个:“提高数据获取的性能”。我们知道一本书的前面几页肯定会有一个目录,这个目录式的索引能使我们快速査询想看的内容。索引保存在哪里,是个什么样的数据结构,计算机领域的索引无外乎也是这两个主题。
数据库保存记录的机制是建立在文件系统上的,索引也是以文件的形式存储在磁盘上,在数据库中用到的最多的索引结构就是B树。尽管索引在数据库领域是不可缺少的,但是对一个表建立过多的索引也会带来一些问题,索引的建立要花费系统时间,同时索引文件也会占用磁盘空间。
**索引通常能够极大的提高查询的效率,如果没有索引,MongoDB在读取数据时必须扫描集合中的每个文件并选取那些符合查询条件的记录。**扫描全集合的查询效率是非常低的,特别在处理大量的数据时,查询可以要花费几十秒甚至几分钟,这对网站的性能是非常致命的。
索引是特殊的数据结构,索引存储在一个易于遍历读取的数据集合中,索引是对数据库表中一列或多列的值进行排序的一种结构。
MongoDB索引的数据结构也是B+树,它能存储一小部分集合的数据,具体来说就是存储集合中建有索引的一个或多个字段的值,而且按照值的升序或降序排列。对于一个查询来说,如果存在合适的索引,MongoDB能够利用这个索引减少文档的扫描数量。
如图所示查询低于30岁的用户,不用去扫描全部文档,通过索引快速返回结果,这样查询的效率是很高的。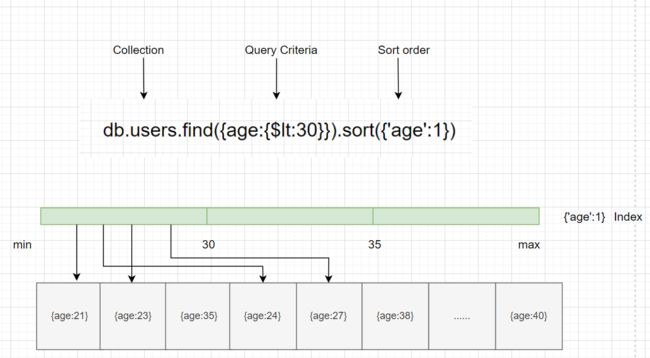
单字段索引
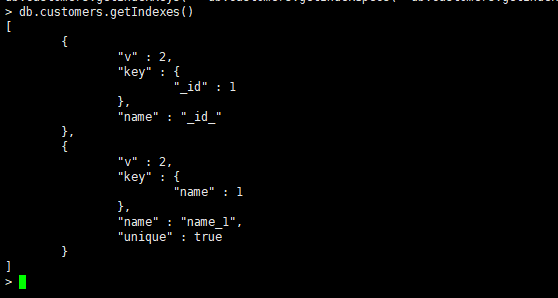
MongoDB默认为所有集合都创建了一个_id字段的单字段索引,而且这个索引是唯一的,不能被删除,_id字段作为一个集合的主键,值是唯一的,对于一个集合来说,也可以在其他字段上创建单字段的唯一索引。
创建单一键索引:db.collection.createIndex( { : } ),其中 是你要创建索引的字段名, 是索引类型,例如:1(升序)或 -1(降序)。
插入数据
for(var i = 1;i < 10;i++) db.custoners.insert({name:"zhangsan"+i,province:"liaoning"})
for(var i = 1;i < 10;i++) db.customers.insert({name:"lisi"+i,province:"fujian"})
for(var i = 1;i < 10;i++) db.customers.insert({name:"niuer"+i,province:"guangdong"})
for(var i = 1;i < 10;i++) db.customers.insert({name:"wangwu"+i,province:"Hunan"})
for(var i = 1;i < 10;i++) db.customers.insert({name:"liyi"+i,province:"Sichuan"})
创建索引
建立单字段唯一索引或者去掉{unique:true}选项就是一个普通的单字段索引
db.customers.createIndex({name:1},{unique:true})
1表示升序创建索引,-1表示降序创建索引。
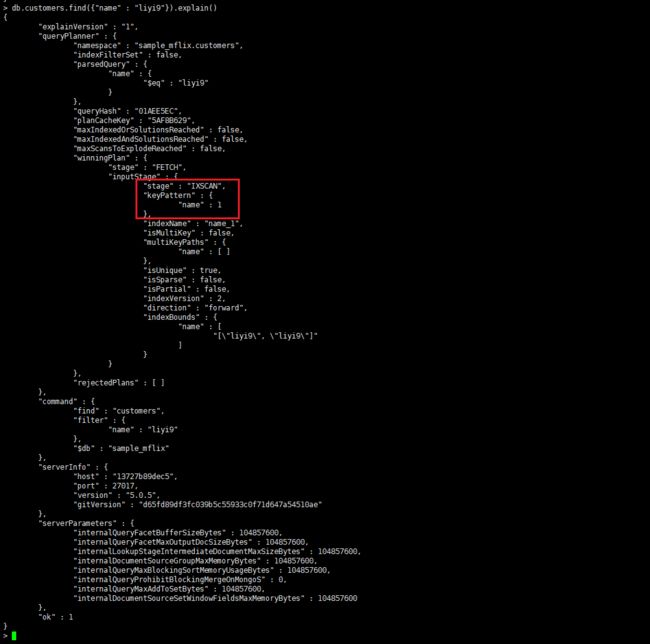
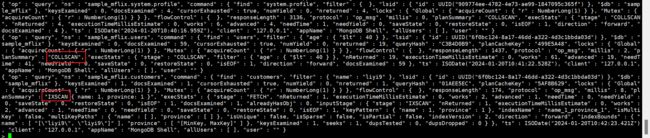
通过explain查看执行计划
MongoDB中的explain()方法用于显示查询执行计划,它可以帮助我们了解MongoDB如何执行一个查询。
执行explain()方法后,MongoDB将返回一个对象,该对象描述了查询执行的过程,包括查询的阶段、输入输出、使用的索引等信息。
这个对象通常包含以下字段:
- stages:查询执行的阶段列表,每个阶段描述了查询的一部分执行过程。
- input:查询输入的文档数量。
- output:查询输出的文档数量。
- millis:查询执行的时间(毫秒)。
- executionStats:更详细的执行统计信息。
其中,stages字段是最重要的,它描述了查询从开始到结束的所有阶段。每个阶段都有一个type字段,描述了这个阶段的类型,比如:
- COLLSCAN:扫描整个集合。
- IXSCAN:扫描索引。
- SHARD_MERGE:合并从多个分片返回的结果。
通过查看stages字段,我们可以了解查询使用了哪些索引,是否有更好的优化方案等。
需要注意的是,explain()方法返回的结果包含了大量的详细信息,对于普通用户来说可能比较难以理解。通常我们只需要关注stages字段,以及其中的type值为IXSCAN的阶段,因为这是查询执行的关键阶段。
没走索引查询,查询使用了COLLSCAN阶段扫描了整个集合,但是并没有使用到索引。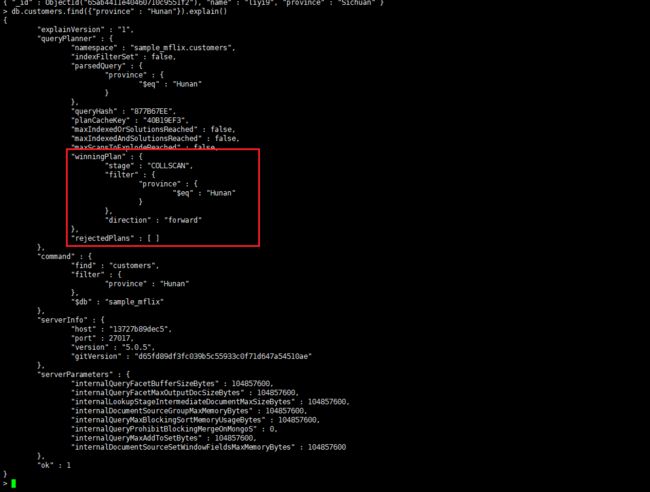
复合索引
创建复合索引:db.collection.createIndex( { : , : } ),其中 和 是你要创建索引的字段名, 和 是索引类型,
例如:1(升序)或 -1(降序)。
请注意,创建索引可能需要一些时间,具体取决于你的数据量及系统性能。同时,创建过多的索引可能会对写入性能产生负面影响,因此需要谨慎考虑。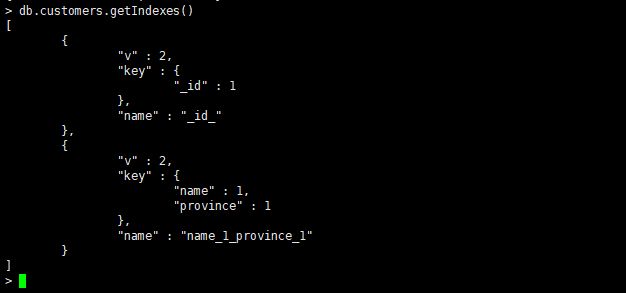
> db.customers.find({"name" : "liyi6", "province" : "Sichuan"}).explain()
{
"explainVersion" : "1",
"queryPlanner" : {
"namespace" : "sample_mflix.customers",
"indexFilterSet" : false,
"parsedQuery" : {
"$and" : [
{
"name" : {
"$eq" : "liyi6"
}
},
{
"province" : {
"$eq" : "Sichuan"
}
}
]
},
"queryHash" : "AE1EB7A5",
"planCacheKey" : "C0AA3338",
"maxIndexedOrSolutionsReached" : false,
"maxIndexedAndSolutionsReached" : false,
"maxScansToExplodeReached" : false,
"winningPlan" : {
"stage" : "FETCH",
"inputStage" : {
"stage" : "IXSCAN",
"keyPattern" : {
"name" : 1,
"province" : 1
},
"indexName" : "name_1_province_1",
"isMultiKey" : false,
"multiKeyPaths" : {
"name" : [ ],
"province" : [ ]
},
"isUnique" : false,
"isSparse" : false,
"isPartial" : false,
"indexVersion" : 2,
"direction" : "forward",
"indexBounds" : {
"name" : [
"[\"liyi6\", \"liyi6\"]"
],
"province" : [
"[\"Sichuan\", \"Sichuan\"]"
]
}
}
},
"rejectedPlans" : [ ]
},
"command" : {
"find" : "customers",
"filter" : {
"name" : "liyi6",
"province" : "Sichuan"
},
"$db" : "sample_mflix"
},
"serverInfo" : {
"host" : "13727b89dec5",
"port" : 27017,
"version" : "5.0.5",
"gitVersion" : "d65fd89df3fc039b5c55933c0f71d647a54510ae"
},
"serverParameters" : {
"internalQueryFacetBufferSizeBytes" : 104857600,
"internalQueryFacetMaxOutputDocSizeBytes" : 104857600,
"internalLookupStageIntermediateDocumentMaxSizeBytes" : 104857600,
"internalDocumentSourceGroupMaxMemoryBytes" : 104857600,
"internalQueryMaxBlockingSortMemoryUsageBytes" : 104857600,
"internalQueryProhibitBlockingMergeOnMongoS" : 0,
"internalQueryMaxAddToSetBytes" : 104857600,
"internalDocumentSourceSetWindowFieldsMaxMemoryBytes" : 104857600
},
"ok" : 1
}
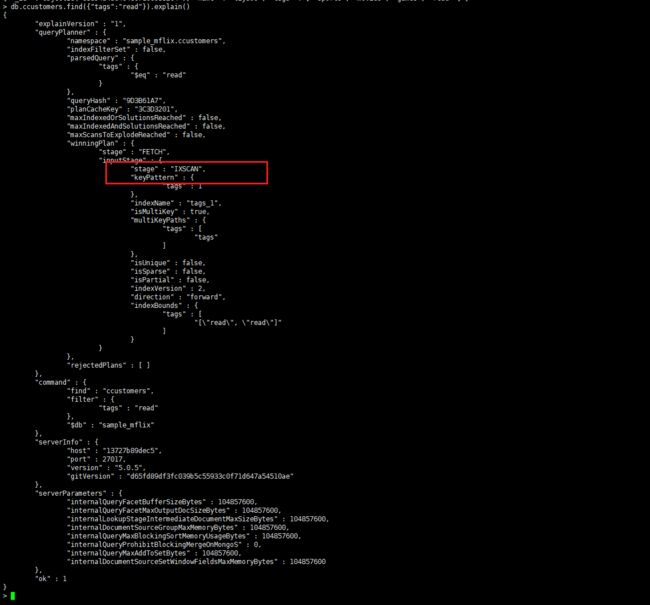
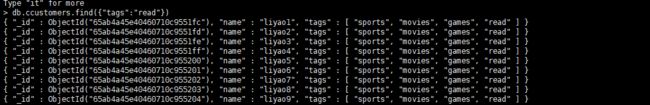
数组的多键索引
注意,创建索引可能需要一些时间,具体取决于你的数据量和系统性能。同时,创建过多的索引可能会对写入性能产生负面影响,因此需要谨慎考虑。
tags 的数组字段为例,展示多键索
> for(var i = 1;i < 10;i++) db.ccustomers.insert({name:"liyi"+i,"tags": ["sports", "music", "movies"]})
WriteResult({ "nInserted" : 1 })
> for(var i = 1;i < 10;i++) db.ccustomers.insert({name:"liyao"+i,"tags": ["sports", "movies","games","read"]})
WriteResult({ "nInserted" : 1 })
> for(var i = 1;i < 10;i++) db.ccustomers.insert({name:"lisi"+i,"tags": ["sports", "music", "movies"]})
WriteResult({ "nInserted" : 1 })
> for(var i = 1;i < 10;i++) db.ccustomers.insert({name:"liyiyi"+i,"tags": ["sports", "movies","write"]})
WriteResult({ "nInserted" : 1 })
> db.ccustomers.createIndex({"tags":1})
{
"numIndexesBefore" : 1,
"numIndexesAfter" : 2,
"createdCollectionAutomatically" : false,
"ok" : 1
}
查询优化
MongoDB查询优化的方法主要有以下几点:
- 用合适的索引:索引是提高查询性能的关键。MongoDB支持多种索引类型,如单一键索引、复合索引、文本索引、地理空间索引等。在设计数据库时,应根据数据的特性和查询需求选择合适的索引类型。同时,也要注意索引的使用,尽量使用已经创建的索引,避免全集合扫描。
- 优化查询语句:查询语句的设计也会影响查询性能。应尽量避免使用不等于操作符、模运算符等导致全集合扫描的操作符。同时,应使用投影查询,减少返回的字段,减少数据传输和处理的开销。
- 批量操作:批量操作可以减少IO操作次数,提高性能。例如批量插入、批量更新、批量删除等。
- 使用缓存:使用缓存可以避免重复查询,提高查询性能。
- 优化数据结构:数据结构的设计也会影响查询性能。应尽量选择合适的数据类型,避免使用嵌套文档和数组,提高查询效率。
- 调整系统参数:根据系统性能和硬件配置调整MongoDB的配置参数,例如内存、磁盘、网络等参数。
- 使用分析工具:使用MongoDB提供的分析工具,如explain()、profile()等,可以了解查询性能,找出优化点。
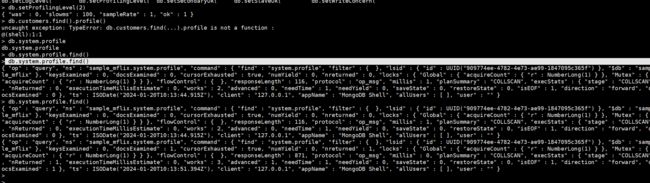
位慢查询的方法是打开数据库的监视功能,它默认是关闭的,我们可以通过下面的命令打开。
db.setProfilingLevel(level,[ slowms])
参数:
level是监视级别。
值为0表示关闭数据库的监视功能
值为1表示只记录慢查询
值为2表示记录所有的操作
slowms为可选参数,设定慢查询的阈值。
所有监视的结果都将保存到一个特殊的集合system.profile中。
> db.setProfilingLevel(2)
{ "was" : 0, "slowms" : 100, "sampleRate" : 1, "ok" : 1 }
> db.system.profile.find()
2.3 总结
MongoDB可以在一个集合上建立一个或多个索引,而且必须为在字段_id建立一个索引,建索引的目的与关系数据库一样,就是为了提高对数据库的查询效率;
一旦索引创建好,MongoDB会自动地根据数据的变化维护索引,如果索引太大而不能全部保存在内存中,将被移到磁盘文件上,这样会影响查询性能,因此要时刻监控索引的大小,保证合适的索引在内存中;
监控一个查询是否用到索引,可以在查询语句后用explain命令或profile()方式进行监控。并不是所有的字段都要建立索引,我们应该根据自己业务所涉及的查询,建立合适的索引;
如果系统有大量的写操作,由于需要维护索引的变化,会导致系统性能降低。我们在对大数据建立索引时最好在后台进行,否则会导致数据库停止响应。要注意虽然我们在某些字段上建了索引,但是查询时可能用不上索引,如使用 n e 和 ne和 ne和nin表达式等。