Spring Boot中如何优雅地实现异步调用?
前言
SpringBoot想必大家都用过,但是大家平时使用发布的接口大都是同步的,那么你知道如何优雅的实现异步呢?
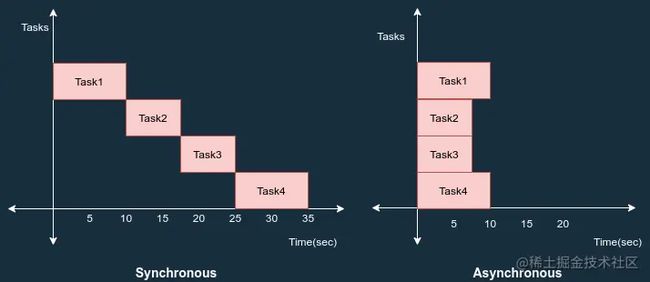
这篇文章就是关于如何在Spring Boot中实现异步行为的。但首先,让我们看看同步和异步之间的区别。
- 同步编程:在同步编程中,任务一次执行一个,只有当一个任务完成时,下一个任务才会被解除阻塞。
- 异步编程:在异步编程中,可以同时执行多个任务。您可以在上一个任务完成之前转到另一个任务。
在Spring Boot中,我们可以使用@Async注解来实现异步行为。
实现步骤
- 定义一个异步服务接口
AsyncService.java
public interface AsyncService {
void asyncMethod() throws InterruptedException;
Future futureMethod() throws InterruptedException;
} - 实现定义的接口
AsyncServiceImpl.java
@Service
@Slf4j
public class AsyncServiceImpl implements AsyncService {
@Async
@Override
public void asyncMethod() throws InterruptedException {
Thread.sleep(3000);
log.info("Thread: [{}], Calling other service..", Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
@Async
@Override
public Future futureMethod() throws InterruptedException {
Thread.sleep(5000);
log.info("Thread: [{}], Calling other service..", Thread.currentThread().getName());
return new AsyncResult<>("task Done");
}
} AsyncServiceImpl是一个spring管理的bean。- 您的异步方法必须是公共的,而且是被
@Async注解修饰。 - 返回类型被限制为
void或Future。
- 定义一个控制器
AsyncController.java
@EnableAsync
@RestController
@Slf4j
public class AsyncController {
@Autowired
AsyncService asyncService;
@GetMapping("/async")
public String asyncCallerMethod() throws InterruptedException {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
log.info("call async method, thread name: [{}]", Thread.currentThread().getName());
asyncService.asyncMethod();
String response = "task completes in :" + (System.currentTimeMillis() - start) + "milliseconds";
return response;
}
@GetMapping("/asyncFuture")
public String asyncFuture() throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
log.info("call async method, thread name: [{}]", Thread.currentThread().getName());
Future future = asyncService.futureMethod(); // 阻塞获取结果
String taskResult = future.get();
String response = taskResult + "task completes in :" + (System.currentTimeMillis() - start) + "milliseconds";
return response;
}
} - 关键点,需要添加启用异步的注解
@EnableAsync,当然这个注解加在其他地方也ok得。 - 当外部调用该接口时,
asyncMethod()将由默认任务执行程序创建的另一个线程执行,主线程不需要等待完成异步方法执行。
- 运行一下
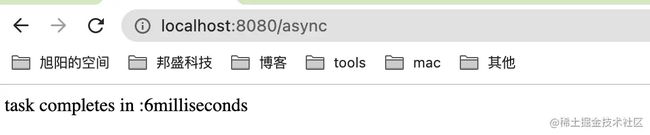
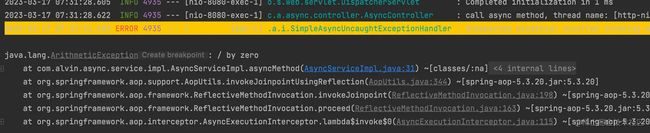
现在我们运行一下看看,是不是异步返回的。
- 可以看到调用
/async接口,最终一步调用了方法。
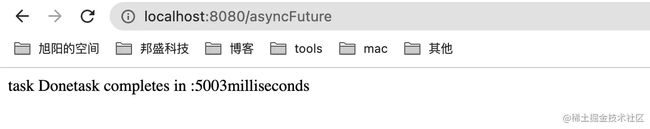
- 调用
/asyncFuture,发现返回5秒多,难道不是异步的吗?其实也是异步的,看日志可以看出来,只不过我们返回的是Future,调用Futrue.get()是阻塞的。
自定义异步任务执行器和异常处理
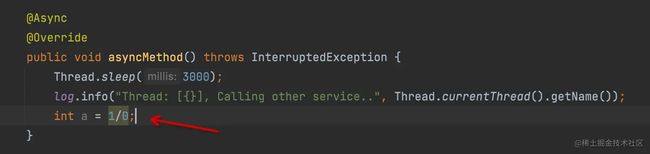
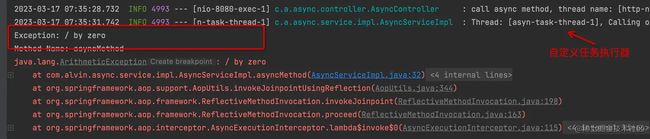
我们现在看看如果异常方法中报错了会怎么样?修改异步代码如下所示,会抛运行时异常:
再次执行异步接口,如下所示,会使用默认的线程池和异常处理。
我们也可以自定义异步方法的处理异常和异步任务执行器,我们需要配置 AsyncUncaughtExceptionHandler,如下代码所示:
@Configuration
public class AsynConfiguration extends AsyncConfigurerSupport {
@Override
public Executor getAsyncExecutor() {
ThreadPoolTaskExecutor executor = new ThreadPoolTaskExecutor();
executor.setCorePoolSize(3);
executor.setMaxPoolSize(4);
executor.setThreadNamePrefix("asyn-task-thread-");
executor.setWaitForTasksToCompleteOnShutdown(true);
executor.initialize();
return executor;
}
@Override
public AsyncUncaughtExceptionHandler getAsyncUncaughtExceptionHandler() {
return new AsyncUncaughtExceptionHandler() {
@Override
public void handleUncaughtException(Throwable ex, Method method, Object... params) {
System.out.println("Exception: " + ex.getMessage());
System.out.println("Method Name: " + method.getName());
ex.printStackTrace();
}
};
}
}再次运行,得到的结果如下:
@Async如何工作的?
必须通过使用 @EnableAsync注解注解主应用程序类或任何直接或间接异步方法调用程序类来启用异步支持。主要通过代理模式实现,默认模式是 Proxy,另一种是 AspectJ。代理模式只允许通过代理拦截调用。永远不要从定义它的同一个类调用异步方法,它不会起作用。
当使用 @Async对方法进行注解时,它会根据“proxyTargetClass”属性为该对象创建一个代理。当 spring 执行这个方法时,默认情况下它会搜索关联的线程池定义。上下文中唯一的 spring 框架 TaskExecutor bean 或名为“taskExecutor”的 Executor bean。如果这两者都不可解析,默认会使用spring框架SimpleAsyncTaskExecutor来处理异步方法的执行。
其他调用async的方法
@GetMapping("/gettest")
public String b() throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {
Future future1 = asyncInvokeService.exec1("张三");
Future future2 = asyncInvokeService.exec2("15618881888");
List> futureList = new ArrayList<>();
futureList.add(future1);
futureList.add(future2);
System.out.println(new Date());
//while (!sendMessage3.isDone() || !sendMessage4.isDone()){
// Thread.sleep(50);
// result += sendMessage3.get();
// result += sendMessage4.get();
//}
//查询任务执行的结果
for (Future future : futureList) {
while (true) {//CPU高速轮询:每个future都并发轮循,判断完成状态然后获取结果,这一行,是本实现方案的精髓所在。即有10个future在高速轮询,完成一个future的获取结果,就关闭一个轮询
if (future.isDone() && !future.isCancelled()) { //获取future成功完成状态,如果想要限制每个任务的超时时间,取消本行的状态判断+future.get(1000*1, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS)+catch超时异常使用即可。
Boolean result = future.get();//获取结果
System.out.println("任务i=" + i + "获取完成!" + new Date());
list.add(result);
break;//当前future获取结果完毕,跳出while
} else {
Thread.sleep(1);//每次轮询休息1毫秒(CPU纳秒级),避免CPU高速轮循耗空CPU---》新手别忘记这个
}
System.out.println(new Date());
}
}
System.out.println(new Date());
return "执行成功!!";
} 方法三(CountDownLatch)
public class StatsDemo {
final static SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat(
"yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
final static String startTime = sdf.format(new Date());
/**
* IO密集型任务 = 一般为2*CPU核心数(常出现于线程中:数据库数据交互、文件上传下载、网络数据传输等等)
* CPU密集型任务 = 一般为CPU核心数+1(常出现于线程中:复杂算法)
* 混合型任务 = 视机器配置和复杂度自测而定
*/
private static int corePoolSize = Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors();
/**
* public ThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize,int maximumPoolSize,long keepAliveTime,
* TimeUnit unit,BlockingQueue workQueue)
* corePoolSize用于指定核心线程数量
* maximumPoolSize指定最大线程数
* keepAliveTime和TimeUnit指定线程空闲后的最大存活时间
* workQueue则是线程池的缓冲队列,还未执行的线程会在队列中等待
* 监控队列长度,确保队列有界
* 不当的线程池大小会使得处理速度变慢,稳定性下降,并且导致内存泄露。如果配置的线程过少,则队列会持续变大,消耗过多内存。
* 而过多的线程又会 由于频繁的上下文切换导致整个系统的速度变缓——殊途而同归。队列的长度至关重要,它必须得是有界的,这样如果线程池不堪重负了它可以暂时拒绝掉新的请求。
* ExecutorService 默认的实现是一个无界的 LinkedBlockingQueue。
*/
private static ThreadPoolExecutor executor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(corePoolSize, corePoolSize+1, 10l, TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue(1000));
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch(5);
//使用execute方法
executor.execute(new Stats("任务A", 1000, latch));
executor.execute(new Stats("任务B", 1000, latch));
executor.execute(new Stats("任务C", 1000, latch));
executor.execute(new Stats("任务D", 1000, latch));
executor.execute(new Stats("任务E", 1000, latch));
latch.await();// 等待所有人任务结束
System.out.println("所有的统计任务执行完成:" + sdf.format(new Date()));
}
static class Stats implements Runnable {
String statsName;
int runTime;
CountDownLatch latch;
public Stats(String statsName, int runTime, CountDownLatch latch) {
this.statsName = statsName;
this.runTime = runTime;
this.latch = latch;
}
public void run() {
try {
System.out.println(statsName+ " do stats begin at "+ startTime);
//模拟任务执行时间
Thread.sleep(runTime);
System.out.println(statsName + " do stats complete at "+ sdf.format(new Date()));
latch.countDown();//单次任务结束,计数器减一
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
作者:jeffrey_hjf
链接:https://www.jianshu.com/p/a8592c7b3e83
来源:简书
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
总结
在本文中,我们演示了在 spring boot 中如何使用 @Async 注解和异步方法中的异常处理实现异步行为。我们可以在一个接口中,需要访问不同的资源,比如异步调用各个其他服务的接口,可以使用@Async,然后将结果通过Future的方式阻塞汇总,不失为一个提高性能的好方法。