Hadoop -- Hive
文章目录
- 1. 什么是hive?
-
- 1.1 基本思想
- 1.2 为什么使用hive?
- 1.3 hive创建表与查询原理
- 2. hive安装
-
- 2.1.mysql安装
- 2.2.hive的元数据库配置
- 3. hive使用方式
-
- 3.1 最基本使用方式
- 3.2 启动hive服务使用
- 3.3 脚本化运行
- 4. 建库建表与数据导入
-
- 4.1 建库
- 4.2 建表
-
- 4.2.1 基本建表语句
- 4.2.2 删除表
- 4.2.3 内部表与外部表
- 4.2.4 分区表
- 4.2.5 外部分区表
- 4.3 数据导入导出
-
- 4.3.1 将数据导入到hive的表
- 4.3.2 将hive表中的数据导出到指定路径的文件
- 4.4 修改字段名
- 5. 数据类型
-
- 5.1 数字
- 5.2 日期
- 5.3 字符串类型
- 5.4 混杂类型
- 5.5 复合类型
-
- 5.5.1 array数组类型
- 5.5.2 map类型
- 5.5.3 struct类型
- 6. 某些函数的使用
-
- 6.1 row_number() over() —— 分组TOPN
- 6.2 sum() over()
-
- 传统做法
- sum() over()
- 7. springboot 结合 hive
1. 什么是hive?
1.1 基本思想
hive是基于Hadoop的一个数据仓库工具,用来进行数据提取、转化、加载,这是一种可以存储、查询和分析存储在Hadoop中的大规模数据的机制。hive数据仓库工具能将结构化的数据文件映射为一张数据库表,并提供SQL查询功能,能将SQL语句转变成MapReduce任务来执行,所以hive的底层还是执行MapReduce任务,只不过提供了一个非常方便的sql接口来实现MapReduce任务。
1.2 为什么使用hive?
-
直接使用hadoop所面临的问题
人员学习成本太高
项目周期要求太短
MapReduce实现复杂查询逻辑开发难度太大 -
为什么要使用Hive
操作接口采用类SQL语法,提供快速开发的能力。
避免了去写MapReduce,减少开发人员的学习成本。
功能扩展很方便。
但是并不是说我们不用去写MapReduce了,MapReduce也有他的应用场景,例如当数据文件的数据结构很复杂,这时写MapReduce就方便很多。
1.3 hive创建表与查询原理
-
根据HDFS上数据格式,创建hive表
-
通过映射关系将HDFS数据导入到表中,分为内部表和外部表
创建表时:
内部表会移动数据到指定位置 ,将数据文件移动到默认位置,一般都是/usr/hive/warehouse/ 目录下
外部表不会移动数据,数据在哪就是哪
删除表时:
内部表删除,元数据和数据一起删除
外部表不会删除数据,只清楚元数据 -
此时hive表对应的元数据信息记录到 mysql 中
-
在执行查询操作时 ,先从元数据库中找到 对应表对应的文件位置,再通过 hive 的 解析器、编译器、优化器 执行器 将 sql 语句 转换成 MR 程序,运行在 Yarn 上,最终得到结果。
2. hive安装
2.1.mysql安装
将mysql作为元数据库
① 上传mysql安装包
② 解压:
tar -xvf MySQL-5.6.26-1.linux_glibc2.5.x86_64.rpm-bundle.tar
③ 安装mysql的server包
rpm -ivh MySQL-server-5.6.26-1.linux_glibc2.5.x86_64.rpm
若依赖报错:缺perl
yum install perl
(可以配置一个本地yum源进行安装:
1、先在vmware中给这台虚拟机连接一个光盘镜像
2、挂在光驱到一个指定目录:mount -t iso9660 -o loop /dev/cdrom /mnt/cdrom
3、将yum的配置文件中baseURL指向/mnt/cdrom
)
安装完perl后 ,继续重新安装mysql-server
rpm -ivh MySQL-server-5.6.26-1.linux_glibc2.5.x86_64.rpm
又出错:包冲突conflict with
移除老版本的冲突包:mysql-libs-5.1.73-3.el6_5.x86_64
rpm -e mysql-libs-5.1.73-3.el6_5.x86_64 --nodeps
继续重新安装mysql-server
rpm -ivh MySQL-server-5.6.26-1.linux_glibc2.5.x86_64.rpm
成功后,注意提示:里面有初始密码及如何改密码的信息
初始密码:/root/.mysql_secret
改密码脚本:/usr/bin/mysql_secure_installation
④ 安装mysql的客户端包:
rpm -ivh MySQL-client-5.6.26-1.linux_glibc2.5.x86_64.rpm
⑤ 启动mysql的服务端:
service mysql start
Starting MySQL. SUCCESS!
⑥ 修改root的初始密码:
/usr/bin/mysql_secure_installation 按提示
⑦ 测试:
用mysql命令行客户端登陆mysql服务器看能否成功
mysql -uroot -proot
mysql> show databases;
⑧ 给root用户授予从任何机器上登陆mysql服务器的权限:
mysql> grant all privileges on *.* to 'root'@'%' identified by '你的密码' with grant option;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> flush privileges;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
注意点:要让mysql可以远程登录访问
最直接测试方法:从windows上用Navicat去连接,能连,则可以,不能连,则要去mysql的机器上用命令行客户端进行授权:
在mysql的机器上,启动命令行客户端:
mysql -uroot -proot
mysql>grant all privileges on *.* to 'root'@'%' identified by 'root的密码' with grant option;
mysql>flush privileges;
2.2.hive的元数据库配置
准备工作:安装hive的机器上应该有HADOOP环境(安装目录,HADOOP_HOME环境变量)
安装:直接解压一个hive安装包即可
1、到hive解压目录下修改xml文件
vi conf/hive-site.xml
<configuration>
<property>
<name>javax.jdo.option.ConnectionURL</name>
<value>jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/hive?createDatabaseIfNotExist=true</value>
<description>JDBC connect string for a JDBC metastore</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>javax.jdo.option.ConnectionDriverName</name>
<value>com.mysql.jdbc.Driver</value>
<description>Driver class name for a JDBC metastore</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>javax.jdo.option.ConnectionUserName</name>
<value>root</value>
<description>username to use against metastore database</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>javax.jdo.option.ConnectionPassword</name>
<value>root</value>
<description>password to use against metastore database</description>
</property>
</configuration>
2、上传一个mysql的驱动jar包到hive的安装目录的lib中
3、配置HADOOP_HOME 和HIVE_HOME到系统环境变量中:/etc/profile
4、source /etc/profile
5、hive启动测试
用命令启动hive交互界面:
[root@hadoop100 ~]# hive
3. hive使用方式
3.1 最基本使用方式
cd 到hive的安装目录中启动一个hive交互shell
[root@hadoop100 hive-1.2.1]# bin/hive
设置一些基本参数,让hive使用起来更便捷,比如:
1、让提示符显示当前库:
hive>set hive.cli.print.current.db=true;
2、显示查询结果时显示字段名称:
hive>set hive.cli.print.header=true;
但是这样设置只对当前会话有效,重启hive会话后就失效,解决办法:
在linux的当前用户目录中,编辑一个 .hiverc 文件(注意有个点. ,是隐藏文件),将参数写入其中:
vi .hiverc
set hive.cli.print.header=true;
set hive.cli.print.current.db=true;
3.2 启动hive服务使用
启动hive的服务:
[root@hadoop100 hive-1.2.1]# bin/hiveserver2 -hiveconf hive.root.logger=DEBUG,console
上述启动,会将这个服务启动在前台,如果要启动在后台,则命令如下:
nohup bin/hiveserver2 1>/dev/null 2>&1 &
启动成功后,可以在别的节点上用beeline去连接
[root@hadoop101 hive-1.2.1]# bin/beeline -u jdbc:hive2://hadoop100:10000 -n root
(hadoop100是hiveserver2所启动的那台主机名,端口默认是10000)
#注意:
启动thrift
hive --service metastore
3.3 脚本化运行
大量的hive查询任务,如果用交互式shell来进行输入的话,显然效率及其低下,因此,生产中更多的是使用脚本化运行机制:
该机制的核心点是:hive可以用一次性命令的方式来执行给定的hql语句
可以将命令写入shell脚本中,以便于脚本化运行hive任务,并控制、调度众多hive任务,示例如下:
vi t_order_etl.sh
#!/bin/bash
hql1=hive -e "select * from db_order.t_order"
hive -e "$hql1"
hql2=hive -e "select * from default.t_user"
hive -e "$hql2"
hql3="create table default.t_bash as select * from db_order.t_order"
hive -e "$hql3"
然后运行该t_order_etl.sh
sh t_order_etl.sh
如果要执行的hql语句特别复杂,那么,可以把hql语句写入一个文件:
vi x.hql
select * from db_order.t_order;
select count(1) from db_order.t_user;
然后,用hive -f /root/x.hql来执行
4. 建库建表与数据导入
4.1 建库
hive中有一个默认的库:
库名: default
库目录:hdfs://hadoop100:9000/user/hive/warehouse
新建库:
create database db_order;
库建好后,在hdfs中会生成一个库目录:
hdfs:/hadoop100:9000/user/hive/warehouse/db_order.db
4.2 建表
4.2.1 基本建表语句
use db_order;
create table t_order(id string,create_time string,amount float,uid string);
表建好后,会在所属的库目录中生成一个表目录
/user/hive/warehouse/db_order.db/t_order
只是,这样建表的话,hive会认为表数据文件中的字段分隔符为 ^A
正确的建表语句为:
create table t_order(id string,create_time string,amount float,uid string)
row format delimited fields terminated by ',';
这样就指定了,我们的表数据文件中的字段分隔符为 “,”
4.2.2 删除表
drop table t_order;
删除表的效果是:
hive会从元数据库中清除关于这个表的信息;
hive还会从hdfs中删除这个表的表目录;
4.2.3 内部表与外部表
内部表(MANAGED_TABLE):表目录按照hive的规范来部署,位于hive的仓库目录/user/hive/warehouse中
外部表(EXTERNAL_TABLE):表目录由建表用户自己指定
create external table t_access(ip string,url string,access_time string)
row format delimited
fields terminated by ','
location '/access/log';
外部表和内部表的特性差别:
1、内部表的目录在hive的仓库目录中 VS 外部表的目录由用户指定(例如日志采集系统中日志文件存放的目录)
2、drop一个内部表时:hive会清除相关元数据,并删除表数据目录
3、drop一个外部表时:hive只会清除相关元数据;
一个hive的数据仓库,最底层的表,一定是来自于外部系统,为了不影响外部系统的工作逻辑,在hive中可建external表来映射这些外部系统产生的数据目录。
4.2.4 分区表
分区表的实质是:在表目录中为数据文件创建分区子目录,以便于在查询时,MR程序可以针对分区子目录中的数据进行处理,缩减读取数据的范围。
比如,网站每天产生的浏览记录,浏览记录应该建一个表来存放,但是,有时候,我们可能只需要对某一天的浏览记录进行分析
这时,就可以将这个表建为分区表,每天的数据导入其中的一个分区;
当然,每日的分区目录,应该有一个目录名(分区字段)
示例如下:
1、创建带分区的表
create table t_access(ip string,url string,access_time string)
partitioned by(dt string)
row format delimited
fields terminated by ',';
注意:分区字段不能是表定义中的已存在字段
2、向分区中导入数据
load data local inpath '/root/access.log.2017-08-04.log' into table t_access partition(dt='20170804');
load data local inpath '/root/access.log.2017-08-05.log' into table t_access partition(dt='20170805');
3、针对分区数据进行查询
a、统计8月4号的总PV:
select count(*) from t_access where dt='20170804';
实质:就是将分区字段当成表字段来用,就可以使用where子句指定分区了
b、统计表中所有数据总的PV:
select count(*) from t_access;
实质:不指定分区条件即可
多个分区字段示例
建表:
create table t_partition(id int,name string,age int)
partitioned by(department string,sex string,howold int)
row format delimited fields terminated by ',';
导数据:
load data local inpath '/root/p1.dat' into table t_partition partition(department='xiangsheng',sex='male',howold=20);
4.2.5 外部分区表
假如外部表location 中有数据,而在hive中查不到数据,例如locarion中:
/user/hive/warehouse/test/dt=2021-12-21/part-38e562d9-efb4-4fe4-b956-eecbbffd3677-0-0
可尝试 add partition
alter table test add partition(dt='2021-12-21') location 'hdfs://localhost:9000/user/hive/warehouse/test/dt=2021-12-21'
一键修复所有分区
msck repair table tableName
另外 drop partition
alter table test drop partition (dt='2021-12-21');
4.3 数据导入导出
4.3.1 将数据导入到hive的表
方式1:导入数据的一种方式:
手动用hdfs命令,将文件放入表目录;
方式2:在hive的交互式shell中用hive命令来导入本地数据到表目录
hive>load data local inpath '/root/order.data.2' into table t_order;
方式3:用hive命令导入hdfs中的数据文件到表目录
hive>load data inpath '/access.log.2017-08-06.log' into table t_access partition(dt='20170806');
4.3.2 将hive表中的数据导出到指定路径的文件
1、将hive表中的数据导入HDFS的文件
insert overwrite directory '/root/access-data'
row format delimited fields terminated by ','
select * from t_access;
2、将hive表中的数据导入本地磁盘文件
insert overwrite local directory '/root/access-data'
row format delimited fields terminated by ','
select * from t_access limit 100000;
4.4 修改字段名
ALTER TABLE table_nameCHANGE name new_name type;
出现问题
当表存储结构为parquet时,修改字段名后被修改的字段全部为空
solution:
ALTER TABLE tes SET TBLPROPERTIES ('parquet.column.index.access'='true');
5. 数据类型
5.1 数字
create table t_test(a string ,b int,c bigint,d float,e double,f tinyint,g smallint)
注意先写变量名,再写数据类型
5.2 日期
TIMESTAMP (Note: Only available starting with Hive 0.8.0)
DATE (Note: Only available starting with Hive 0.12.0)
create table t_customer(id int,name string,birthday date)
row format delimited fields terminated by ',';
5.3 字符串类型
STRING
VARCHAR (Note: Only available starting with Hive 0.12.0)
CHAR (Note: Only available starting with Hive 0.13.0)
5.4 混杂类型
BOOLEAN
BINARY (Note: Only available starting with Hive 0.8.0)
5.5 复合类型
5.5.1 array数组类型
假如有如下数据需要用hive的表去映射:
战狼2,吴京:吴刚:龙母,2017-08-16
三生三世十里桃花,刘亦菲:痒痒,2017-08-20
设想:如果主演信息用一个数组来映射比较方便
建表:
create table t_movie(moive_name string,actors array<string>,first_show date)
row format delimited fields terminated by ','
collection items terminated by ':';
导入数据:
load data local inpath '/root/movie.dat' into table t_movie;
查询:
select * from t_movie;
#取演员列表的第一个演员
select moive_name,actors[0] from t_movie;
# 查出包含吴刚的电影名字还有演员
select moive_name,actors from t_movie where array_contains(actors,'吴刚');
#有多少个演员
select moive_name,size(actors) from t_movie;
5.5.2 map类型
maps: MAP
假如有以下数据:
1,zhangsan,father:xiaoming#mother:xiaohuang#brother:xiaoxu,28
2,lisi,father:mayun#mother:huangyi#brother:guanyu,22
3,wangwu,father:wangjianlin#mother:ruhua#sister:jingtian,29
4,mayun,father:mayongzhen#mother:angelababy,26
可以用一个map类型来对上述数据中的家庭成员进行描述
2)建表语句:
create table t_person(id int,name string,family_members map<string,string>,age int)
row format delimited fields terminated by ','
collection items terminated by '#'
map keys terminated by ':';
3)查询
select * from t_person;
取map字段的指定key的值
select id,name,family_members['father'] as father from t_person;
取map字段的所有key
select id,name,map_keys(family_members) as relation from t_person;
取map字段的所有value
select id,name,map_values(family_members) from t_person;
select id,name,map_values(family_members)[0] from t_person;
综合:查询有brother的用户信息
select id,name,father
from
(select id,name,family_members['brother'] as brotherfrom t_person) tmp
where brotheris not null;
5.5.3 struct类型
structs: STRUCT
1)假如有如下数据:
1,zhangsan,18:male:beijing
2,lisi,28:female:shanghai
其中的用户信息包含:年龄:整数,性别:字符串,地址:字符串
设想用一个字段来描述整个用户信息,可以采用struct
2)建表:
create table t_person_struct(id int,name string,info struct<age:int,sex:string,addr:string>)
row format delimited fields terminated by ','
collection items terminated by ':';
3)查询
select * from t_person_struct;
select id,name,info.age from t_person_struct;
6. 某些函数的使用
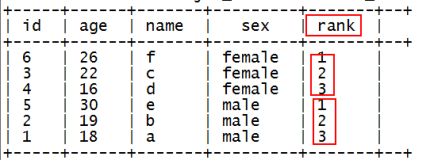
6.1 row_number() over() —— 分组TOPN
有如下数据:
1,18,a,male
2,19,b,male
3,22,c,female
4,16,d,female
5,30,e,male
6,26,f,female
需要查询出每种性别中年龄最大的2条数据
使用row_number函数,对表中的数据按照性别分组,按照年龄倒序排序并进行标记
select id,age,name,sex,
row_number() over(partition by sex order by age desc) as rank
from t_rownumber
select id,age,name,sex
from
(select id,age,name,sex,
row_number() over(partition by sex order by age desc) as rank
from t_rownumber) tmp
where rank<=2;
6.2 sum() over()
有如下数据:
A,2015-01,5
A,2015-01,15
B,2015-01,5
A,2015-01,8
B,2015-01,25
A,2015-01,5
C,2015-01,10
C,2015-01,20
A,2015-02,4
A,2015-02,6
C,2015-02,30
C,2015-02,10
B,2015-02,10
B,2015-02,5
A,2015-03,14
A,2015-03,6
B,2015-03,20
B,2015-03,25
C,2015-03,10
C,2015-03,20
需要要开发hql脚本,来统计出如下累计报表:
| 用户 | 月份 | 月总额 | 累计到当月的总额 |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | 2015-01 | 33 | 33 |
| A | 2015-02 | 10 | 43 |
| A | 2015-03 | 30 | 73 |
| B | 2015-01 | 30 | 30 |
| B | 2015-02 | 15 | 45 |
建表映射并导入数据:
create table t_access_times(username string,month string,counts int)
row format delimited fields terminated by ',';
load data local inpath '/root/accumulate.dat' into table t_access_times;
传统做法
1、第一步,先求每个用户的月总金额
select username,month,sum(salary) as salary from t_access_times group by username,month
±----------±---------±--------±-+
| username | month | salary |
±----------±---------±--------±-+
| A | 2015-01 | 33 |
| A | 2015-02 | 10 |
| B | 2015-01 | 30 |
| B | 2015-02 | 15 |
±----------±---------±--------±-+
2、第二步,将月总金额表自己连接 自己连接
select A.*,B.* FROM
(select username,month,sum(salary) as salary from t_access_times group by username,month) A
inner join
(select username,month,sum(salary) as salary from t_access_times group by username,month) B
on
A.username=B.username
where B.month <= A.month
±------------±---------±----------±------------±---------±----------±-+
| a.username | a.month | a.salary | b.username | b.month | b.salary |
±------------±---------±----------±------------±---------±----------±-+
| A | 2015-01 | 33 | A | 2015-01 | 33 |
| A | 2015-02 | 10 | A | 2015-01 | 33 |
| A | 2015-02 | 10 | A | 2015-02 | 10 |
| B | 2015-01 | 30 | B | 2015-01 | 30 |
| B | 2015-02 | 15 | B | 2015-01 | 30 |
| B | 2015-02 | 15 | B | 2015-02 | 15 |
±------------±---------±----------±------------±---------±----------±-+
第3步:
select A.username,A.month,max(A.salary),sum(B.salary)
from t_tmp2
group by A.username,A.month;
得到最终结果
当然,也可以把整个逻辑过程写成一个SQL语句:
select A.username,A.month,max(A.salary) as salary,sum(B.salary) as accumulate
from
(select username,month,sum(salary) as salary from t_access_times group by username,month) A
inner join
(select username,month,sum(salary) as salary from t_access_times group by username,month) B
on
A.username=B.username
where B.month <= A.month
group by A.username,A.month
order by A.username,A.month;
sum() over()
首先要有每个用户的月总金额的表
±----------±---------±--------±-+
| username | month | salary |
±----------±---------±--------±-+
| A | 2015-01 | 33 |
| A | 2015-02 | 10 |
| B | 2015-01 | 30 |
| B | 2015-02 | 15 |
±----------±---------±--------±-+
然后利用sum() over() 窗口函数
select id,month
,sum(amount) over(partition by id order by month rows between unbounded preceding and current row)
from
(select id,month,
sum(fee) as amount
from t_test
group by id,month) tmp;
#这句话的意思是对id进行分组然后对month升序排序
#然后对于每一组(每一个窗口),按行执行时,执行该行到该行往上(无边界)的所有行的sum算法
sum(partition by id order by month rows between unbounded preceding and current row)
#例如第一组(第一个窗口)有两行A
#对于第一行执行sum()时只有自己,所以是33
#第二行因为上面有1行,所以是33+10=43
#同理对于第二组(第二个窗口)也有两行B,所以第一行是30,第二行是45
7. springboot 结合 hive
pom.xml
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parentartifactId>
<version>2.6.0version>
<relativePath/>
parent>
<groupId>com.examplegroupId>
<artifactId>hivePrestoTestartifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOTversion>
<name>hivePrestoTestname>
<description>hivePrestoTestdescription>
<properties>
<java.version>1.8java.version>
properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-webartifactId>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombokgroupId>
<artifactId>lombokartifactId>
<optional>trueoptional>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-testartifactId>
<scope>testscope>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.tomcatgroupId>
<artifactId>tomcat-jdbcartifactId>
<version>9.0.21version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-jdbcartifactId>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.datagroupId>
<artifactId>spring-data-hadoopartifactId>
<version>2.5.0.RELEASEversion>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.hivegroupId>
<artifactId>hive-jdbcartifactId>
<version>1.2.1version>
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<groupId>org.eclipse.jetty.aggregategroupId>
<artifactId>*artifactId>
exclusion>
exclusions>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.facebook.prestogroupId>
<artifactId>presto-jdbcartifactId>
<version>0.183version>
dependency>
dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-pluginartifactId>
<configuration>
<excludes>
<exclude>
<groupId>org.projectlombokgroupId>
<artifactId>lombokartifactId>
exclude>
excludes>
configuration>
plugin>
plugins>
build>
project>
application.yml
# 配置tomcat端口号
server:
port: 8080
# 配置数据源
hive:
url: jdbc:hive2://192.168.1.100:10000/default
driver-class-name: org.apache.hive.jdbc.HiveDriver
type: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
user: root
# password: Pure@123
# 下面为连接池的补充设置,应用到上面所有数据源中
# 初始化大小,最小,最大
initialSize: 1
minIdle: 3
maxActive: 20
# 配置获取连接等待超时的时间
maxWait: 60000
# 配置间隔多久才进行一次检测,检测需要关闭的空闲连接,单位是毫秒
timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis: 60000
# 配置一个连接在池中最小生存的时间,单位是毫秒
minEvictableIdleTimeMillis: 30000
validationQuery: select 1
testWhileIdle: true
testOnBorrow: false
testOnReturn: false
# 打开PSCache,并且指定每个连接上PSCache的大小
poolPreparedStatements: true
maxPoolPreparedStatementPerConnectionSize: 20
presto:
name: presto
type: org.apache.tomcat.jdbc.pool.DataSource
driver-class-name: com.facebook.presto.jdbc.PrestoDriver
url: jdbc:presto://192.168.1.100:8181
user: root
# 配置mybatis
#mybatis:
# # 配置类型别名包扫描
# type-aliases-package: com.xxx.xxx.pojo
# # 配置sql语句映射文件路径
# mapper-locations:
# - classpath:mappers/*.xml
# # 驼峰映射
# configuration:
# map-underscore-to-camel-case: true
# 配置日志
logging:
level:
com.test.hive.hivePrestoApplication: info
config
package com.test.hive.config;
import org.apache.tomcat.jdbc.pool.PoolConfiguration;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.core.env.Environment;
import org.apache.tomcat.jdbc.pool.DataSource;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
@Configuration
public class hiveConfig {
private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(hiveConfig.class);
@Autowired
private Environment env;
@Bean(name = "hiveJdbcDataSource")
@Qualifier("hiveJdbcDataSource")
public DataSource dataSource() {
DataSource dataSource = new DataSource();
dataSource.setUrl(env.getProperty("hive.url"));
dataSource.setDriverClassName(env.getProperty("hive.driver-class-name"));
dataSource.setUsername(env.getProperty("hive.user"));
// dataSource.setPassword(env.getProperty("hive.password"));
logger.debug("Hive DataSource Inject Successfully...");
return dataSource;
}
@Bean(name = "hiveJdbcTemplate")
public JdbcTemplate hiveJdbcTemplate(@Qualifier("hiveJdbcDataSource") DataSource dataSource) {
return new JdbcTemplate(dataSource);
}
}
controller
package com.test.hive.controller;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier;
import org.springframework.dao.DataAccessException;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
@RestController
public class hivePrestoController {
private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(hivePrestoController.class);
@GetMapping("/test")
public String test(){
return "test success!";
}
@Autowired
@Qualifier("hiveJdbcTemplate")
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
@Autowired
@Qualifier("prestoTemplate")
private JdbcTemplate prestoTemplate;
@GetMapping("/list")
public String list() {
String sql = "select * from ods_app_log limit 10";
List<Map<String, Object>> list = jdbcTemplate.queryForList(sql);
System.out.println(list);
return "success!!";
}
@GetMapping("/insert")
public String insertIntoTable() {
//String sql = "INSERT INTO TABLE test(device_id,device_version,time) VALUES('1','v1','2021-11-19 10:23:24') PARTITION(datetime='2021-11-19')";
// parquet
String sql = "INSERT INTO TABLE test PARTITION(dt='2021-11-19') VALUES(?,?,?) ";
List<Object[]> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(new Object[]{'1',"v1","2021-11-19 01:01:01"});
list.add(new Object[]{'2',"v2","2021-11-19 02:01:01"});
list.add(new Object[]{'3',"v3","2021-11-19 03:01:01"});
// txt
//String sql = "INSERT INTO TABLE dcu_metadata_2 PARTITION(datetime='2021-11-19') VALUES('1','v1','2021-11-19 10:23:24') ";
String result = "Insert into table successfully...";
try {
// jdbcTemplate.execute(sql);
jdbcTemplate.batchUpdate(sql,list);
} catch (DataAccessException dae) {
result = "Insert into table encounter an error: " + dae.getMessage();
logger.error(result);
}
return result;
}
/**
* 示例:创建新表
*/
@GetMapping("/table/create")
public String createTable() {
StringBuffer sql = new StringBuffer("CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS ");
sql.append("user_sample");
sql.append("(user_num BIGINT, user_name STRING, user_gender STRING, user_age INT)");
sql.append("ROW FORMAT DELIMITED FIELDS TERMINATED BY ',' LINES TERMINATED BY '\n' "); // 定义分隔符
sql.append("STORED AS TEXTFILE"); // 作为文本存储
logger.info("Running: " + sql);
String result = "Create table successfully...";
try {
// hiveJdbcTemplate.execute(sql.toString());
jdbcTemplate.execute(sql.toString());
} catch (DataAccessException dae) {
result = "Create table encounter an error: " + dae.getMessage();
logger.error(result);
}
return result;
}
/**
* 示例:将Hive服务器本地文档中的数据加载到Hive表中
*/
@GetMapping("/table/load")
public String loadIntoTable() {
String filepath = "/home/hadoop/user_sample.txt";
String sql = "load data local inpath '" + filepath + "' into table user_sample";
String result = "Load data into table successfully...";
try {
// hiveJdbcTemplate.execute(sql);
jdbcTemplate.execute(sql);
} catch (DataAccessException dae) {
result = "Load data into table encounter an error: " + dae.getMessage();
logger.error(result);
}
return result;
}
/**
* 示例:删除表
*/
@GetMapping("/table/delete")
public String delete(String tableName) {
String sql = "DROP TABLE IF EXISTS "+tableName;
String result = "Drop table successfully...";
logger.info("Running: " + sql);
try {
// hiveJdbcTemplate.execute(sql);
jdbcTemplate.execute(sql);
} catch (DataAccessException dae) {
result = "Drop table encounter an error: " + dae.getMessage();
logger.error(result);
}
return result;
}
@GetMapping("/presto/query")
public String query(){
List<Map<String, Object>> maps = prestoTemplate.queryForList("select * from test");
System.out.println(maps);
return "!!!";
}
}
使用druid操作请参考:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_22165667/article/details/116738993