【算法实验】算法分析与设计第三次实验Lab3
文章目录
- 第1关:加1乘2平方
- 第2关:电子老鼠闯迷宫
- 第3关:跳马
- 第4关:独轮车
- 第5关:六数码问题
- 第6关:木乃伊迷宫
- 第7关:推箱子
- 第8关:polygon
- 第9关:八数码
- 第10关:僵尸来了
- 第11关:僵尸又来了
- 第12关:分酒问题
第1关:加1乘2平方
描述
最简单的队列的使用
#include
#include
using namespace std;
queue q1;
int main()
{
int temp, x;
q1.push(5);//入队
q1.push(8);//入队
temp = q1.front();//访问队首元素
q1.pop();//出队
q1.empty();//判队列是否为空
q1.back();//返回队尾元素
q1.size();//返回队列长度
}
给定两个正整数m、n,问只能做加1、乘2和平方这三种变化,从m变化到n最少需要几次
输入
输入两个10000以内的正整数m和n,且m小于n
输出
输出从m变化到n的最少次数
输入样例
1 16
输出样例
3
#include 第2关:电子老鼠闯迷宫
描述
有一只电子老鼠被困在如下图所示的迷宫中。这是一个12*12单元的正方形迷宫,黑色部分表示建筑物,白色部分是路。电子老鼠可以在路上向上、下、左、右行走,每一步走一个格子。现给定一个起点S和一个终点T,求出电子老鼠最少要几步从起点走到终点。
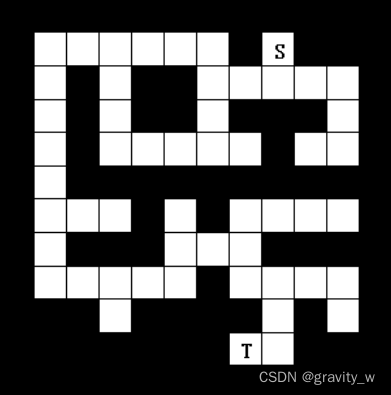
输入
本题包含一个测例。在测例的第一行有四个由空格分隔的整数,分别表示起点的坐标S(x.y)和终点的坐标T(x,y)。从第二行开始的12行中,每行有12个字符,描述迷宫的情况,其中’X’表示建筑物,'.'表示路.
输出
输出一个整数,即电子老鼠走出迷宫至少需要的步数。
输入样例
2 9 11 8
XXXXXXXXXXXX
X…X.XXX
X.X.XX…X
X.X.XX.XXX.X
X.X…X…X
X.XXXXXXXXXX
X…X.X…X
X.XXX…XXXX
X…X…X
XXX.XXXX.X.X
XXXXXXX…XXX
XXXXXXXXXXXX
输出样例
28
#include 第3关:跳马
描述
在国际象棋中,马的走法与中车象棋类似,即俗话说的“马走日”,下图所示即国际象棋中马(K)在一步能到达的格子(其中黑色的格子是能到达的位置)。
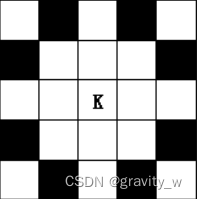
现有一200*200大小的国际象棋棋盘,棋盘中仅有一个马,给定马的当前位置(S)和目标位置(T),求出马最少需要多少跳才能从当前位置到达目标位置。
输入
本题包含多个测例。输入数据的第一行有一个整数N(1<=N<=1000),表示测例的个数,接下来的每一行有四个以空格分隔的整数,分别表示马当前位置及目标位置的横、纵坐标C(x,y)和G(x,y)。坐标由1开始。
输出
对于每个测例,在单独的一行内输出一个整数,即马从当前位置跳到目标位置最少的跳数。
输入样例
2
1 1 2 1
1 5 5 1
输出样例
3
4
#include 第4关:独轮车
描述
独轮车的轮子上有红、黄、蓝、白、绿(依顺时针序)5种颜色,在一个如下图所示的20*20的迷宫内每走一个格子,轮子上的颜色变化一次。独轮车只能向前推或在原地转向。每走一格或原地转向90度均消耗一个单位时间。现给定一个起点(S)和一个终点(T),求独轮车以轮子上的指定颜色到达终点所需的最短时间。

输入
本题包含一个测例。测例中分别用一个大写字母表示方向和轮子的颜色,其对应关系为:E-东、S-南、W-西、N-北;R-红、Y-黄、B-蓝、W-白、G-绿。在测试数据的第一行有以空格分隔的两个整数和两个大写字母,分别表示起点的坐标S(x,y)、轮子的颜色和开始的方向,第二行有以空格分隔的两个整数和一个大写字母,表示终点的坐标T(x,y)和到达终点时轮子的颜色,从第三行开始的20行每行内包含20个字符,表示迷宫的状态。其中’X’表示建筑物,'.'表示路.
输出
在单独的一行内输出一个整数,即满足题目要求的最短时间。
输入样例
3 4 R N
15 17 Y
XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX
X.X…XXXXXX…XX
X.X.X…X…XXXX…X
X.XXXXXXX.XXXXXXXX.X
X.X.XX…X…X
X…XXXXX.X.XX.X.XXX
X.X.XX…X.X…X.X.X
X.X.X…XX…XXXX.XXX
X.X.XX.XX.X…X.X.X
X.X…XX.X.XX.X.X.X
X.X.X.XXXXX.XX.X.XXX
X.X.X.XXXXX…X…X
X.X…X.XX…X.X
X.XXX.XXX.X.XXXXXXXX
X…XX…X…X
XXXXX…X.XXXXXXX.X
X…XXXXXXX.XXX.XXX.X
X.XX…X…X
X…X.XXXX.XXXX…XXX
XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX
输出样例
56
提示
56
#include 第5关:六数码问题
描述
现有一两行三列的表格如下:
A B C
D E F
把1、2、3、4、5、6六个数字分别填入A、B、C、D、E、F格子中,每个格子一个数字且各不相同。每种不同的填法称为一种布局。如下:
1 3 5
2 4 6
布局1
2 5 6
4 3 1
布局2
定义α变换如下:把A格中的数字放入B格,把B格中的数字放入E格,把E格中的数字放入D格,把D格中的数字放入A格。
定义β变换如下:把B格中的数字放入C格,把C格中的数字放入F格,把F格中的数字放入E格,把E格中的数字放入B格。
问:对于给定的布局,可否通过有限次的α变换和β变换变成下面的目标布局:
1 2 3
4 5 6
目标布局
输入
本题有多个测例,每行一个,以EOF为输入结束标志。每个测例的输入是1到6这六个数字的一个排列,空格隔开,表示初始布局ABCDEF格中依次填入的数字。
输出
每个输出占一行。可以转换的,打印Yes;不可以转换的,打印No。
输入样例
1 3 5 2 4 6
2 5 6 4 3 1
输出样例
No
Yes
提示
第二个示例即布局2的一种转换方法:αααβαα
#include第6关:木乃伊迷宫
描述
木乃伊地下宫殿是一个6行6列的迷宫。作为敢到木乃伊地下宫殿里去探险的你,有没有跟木乃伊抓迷藏的心理准备呵!游戏在木乃伊所在的迷宫里展开,任务就是尽快赶到出口。你一次只能走一步,而木乃伊可以走两步,但木乃伊是很笨的,他总是先尽量跟你达到同一列,如果已经是同一列了,他才会像你走来,有墙的地方人和木乃伊都不能过,你可以利用障碍物牵制住木乃伊。
输入
先输入墙的数量n,然后在后续的n行里每行有3个数表示一堵墙,3个数分别为格子的行、列和墙的位置(0表示这个格子的下方是墙,1表示这个格子的右方是墙),再下来的3行每行2个数,分别表示木乃伊、人还有出口的位置。
输出
如果能安全逃生则输出Yes,否则输出No,答案占一行。
输入样例
5
0 0 0
1 1 1
1 4 1
3 4 1
4 3 0
3 3
3 1
5 5
输出样例
No
#include 第7关:推箱子
描述
绝大多数人都玩过推箱子的游戏,控制一个人将箱子推动到目标位置即获得胜利。现请你编写一个程序,判断将箱子推到目标位置至少需要多少步。
输入
推箱子的平面区域为固定大小(10*10),使用10行10列输入推箱子的初始局面。其中,0代表空格,1代表墙,2代表箱子,3代表目标位置,4代表人。
注:游戏中只有一个箱子,一个目标位置,一个人。
输出
输出将箱子推到目标位置的最小步数;若箱子不可能被推到目标位置,输出-1。
输入样例
0000000000
0000000300
0100000000
0100000000
0101111100
0000010000
0000010000
0020010040
0000010000
0000010000
输出样例
34
#include 第8关:polygon
描述
在一个周长为10000的圆上等距分布着n个点,即这n个点是一个正n边形的顶点。现在要另加m个点到圆上,新加的m个点可以任意选择位置(可以与原有的点重合)。然后将这n+m个点中的一些点延圆周移动,最终使n+m个点均匀分布,即在一个正n+m边形的顶点上。输出最小总移动距离。

输入
输入两个整数 n, m。 (2≤n≤1000, 1≤m≤1000).
输出
输出最小总移动距离,保留4位小数。
输入样例
sample input #1 2 1 sample input #2 2 3 sample input #3 3 1 sample input #4 10 10
输出样例
sample output #1 1666.6667 sample output #2 1000.0 sample output #3 1666.6667 sample output #4 0.0 图对应前3个样例
#include 第9关:八数码
描述
在九宫格里放在1到8共8个数字还有一个是空格,与空格相邻的数字可以移动到空格的位置,问给定的状态最少需要几步能到达目标状态(用0表示空格):
1 2 3
4 5 6
7 8 0
输入
输入一个给定的状态。
输出
输出到达目标状态的最小步数。不能到达时输出-1。
输入样例
1 2 3
4 0 6
7 5 8
输出样例
2
#include 第10关:僵尸来了
描述
僵尸要来佳佳家做客了,佳佳把花园布置了一下,你拿到了花园的地图(以二维矩阵的形式表示)以及起点和佳佳家的位置。花园里某些位置有地刺,僵尸过的时候每次需要消耗一个单位的生命值,僵尸有一定数量的生命值,看看最聪明的僵尸能否在天亮前到达你的家里?能的话,最少花费多少时间。
输入
输入的第一行包含三个整数:m,n,t。代表m行n列的地图和僵尸的生命值t。m,n都是小于200的正整数,t是小于10的正整数,第2行开始的m行是m行n列的花园地图,其中!代表起点,+表示佳佳家。*代表通路,w代表地刺。
输出
输出僵尸到达佳佳家最少需要花费的时间。如果无法到达,则输出-1。
输入样例
4 4 2
w!ww
**ww
www+
输出样例
6
//结构体才是最终归宿,不要挣扎了啊!!!
#include 第11关:僵尸又来了
描述
由于聪明的佳佳很善于布置花园,所以僵尸没能在天亮之前冲到佳佳家里,这次僵尸又要来佳佳家做客了,佳佳很高兴,因为姑妈送给佳佳的大嘴花派上了用场。你拿到了花园的地图(以二维矩阵的形式表示)以及起点和佳佳家的位置。花园里一个位置有大嘴花,僵尸到达时会被吃掉,同时从起点又会出来一个新的僵尸,如果僵尸到达大嘴花的位置时,前一个僵尸还没有吃完,大嘴花将被吃掉,看看僵尸能否在天亮前到达佳佳家里?能的话,最少花费多少时间。
输入
输入的第一行包含4个整数:m,n,t, p。代表m行n列的地图、大嘴花吃掉僵尸花费的时间t和距离天亮的时间p。m,n都是小于200的正整数,t是小于10的正整数,第2行开始的m行是m行n列的花园地图,其中!代表起点,+表示佳佳家。*代表通路,@代表大嘴花,#表示墙。
输出
输出僵尸到达佳佳家最少需要花费的时间。如果在天亮之前无法到达,则输出-1。
输入样例
4 4 5 50
#!##
**##
**#+
***@
输出样例
-1
#include第12关:分酒问题
描述
有一酒瓶装有8斤酒,没有量器,只有分别装5斤和3斤的空酒瓶。设计一程序将8斤酒分成两个4斤,并以最少的步骤给出答案。
输入
输入三个正整数,m、n、k,其中n+k=m,且m为偶数,表示有一个酒瓶装有m斤就,只有两个分别装n斤和k斤的空酒瓶。问最少几次能够将酒分成两个m/2斤。
输出
输出最少的次数。
输入样例
8 5 3
输出样例
7
提示
初始状态:8 0 0
1次后:3 5 0
2次后:3 2 3
3次后:6 2 0
4次后:6 0 2
5次后:1 5 2
6次后:1 4 3
7次后:4 4 0
#include