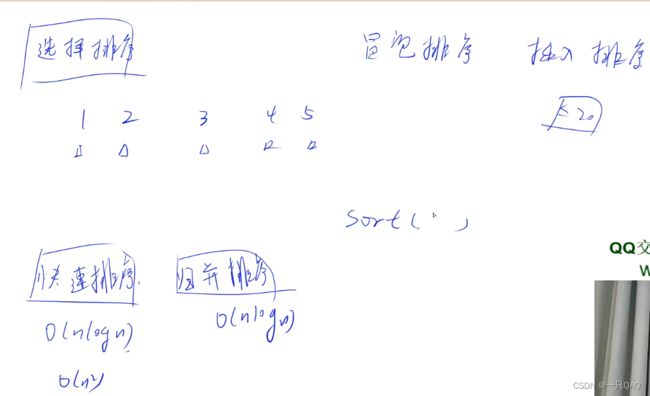
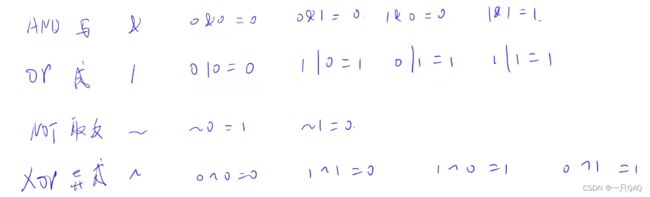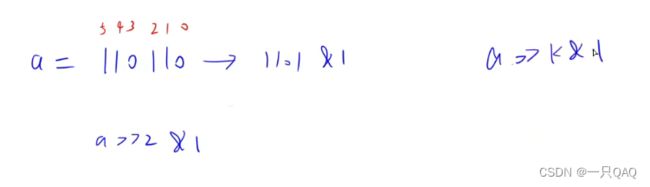acwing语法基础课笔记
1.1 变量、输入输出、表达式和顺序语句

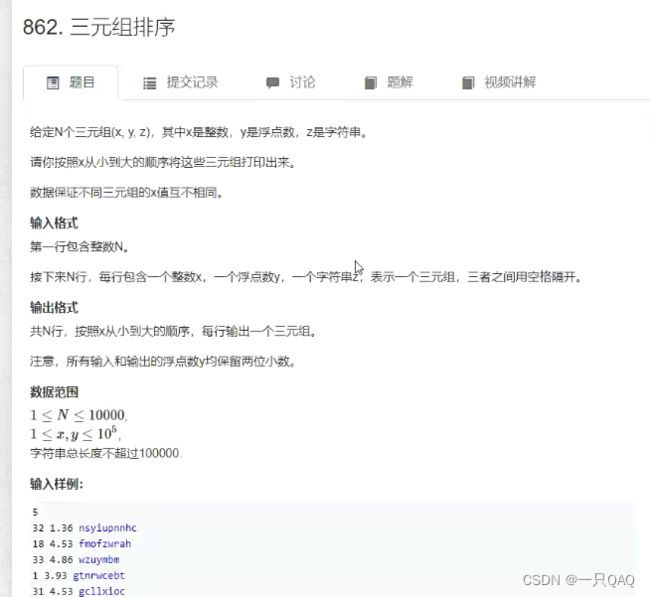
%c会读入空格,但是%d不会读入空格,所以记得%c %c用空格过度一下
cin会帮过滤空格,scanf在读入字符的时候不会自动过滤掉空格,回车,制表符,scanf的%d会把所有的空格和回车都过滤掉,在scanf用%c时注意前面可以加空格如scanf(“%d %c”,&k,&t),这样可以用中间的空格抵消输入两个数据的时候的中间的空格。
char类型和int做运算,运算结果是整数;
隐性类型转换会把精度低的那一项类型转换为精度高的那一项类型;
万能头文件
#include 如果只用了scanf和printf没有用其他函数,可以不用加using namespace std;这句话
在做算法题的时候,由于float的有效数字位数6-7位太低了,答案经常不对,绝大部分情况下都用double15-16位就可以了,
浮点数是没有取模的概念的,都是对整数进行取模。

string库在iostream库里,
浮点数比较大小要用一个函数与eps伊普西隆比较,因为浮点数会不精确
#include 1.2 判断语句
printf扩展功能
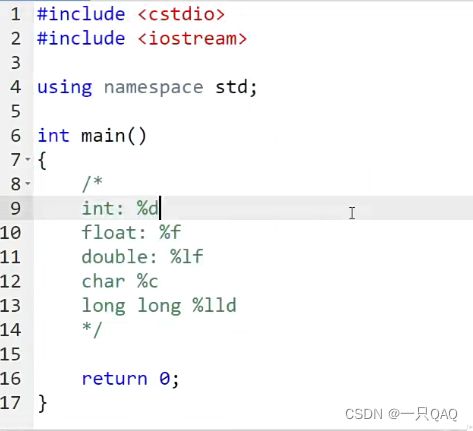
(1) Float,double 等输出保留若干位小数时用: %.4f,%.3lf
(2)最小数字宽度
a. %8.3f,表示这个浮点数的最小宽度为 8,保留3位小数,当宽度不足时在前面补空格。
b. %-8.3f,表示最小宽度为 8,保留3位小数,当宽度不足时在后面补上空格
c. %08.3f,表示最小宽度为 8,保留3 位小数,当宽度不足时在前面补上0

当判断一个式子不等于0的时候可以去掉不等于0 这个判断,即不用写!=0
![]()
等价于![]()
%号的转义很特殊,是%%,

如果x和y都等于0才能执行某个语句时可以用if(!x&&!y),如果x等于0 才能执行时可以写成if(!x),如果y等于0 才能执行时可以写成if(!y)
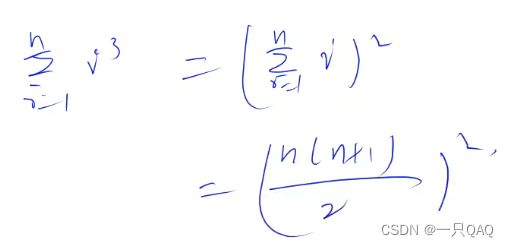
立方和的公式是平方和公式的平方
1.3 循环结构
#include 注意do while后面要加分号;
判断质数
#include 质数优化for (int i = 2;i*i<= p; i ++)
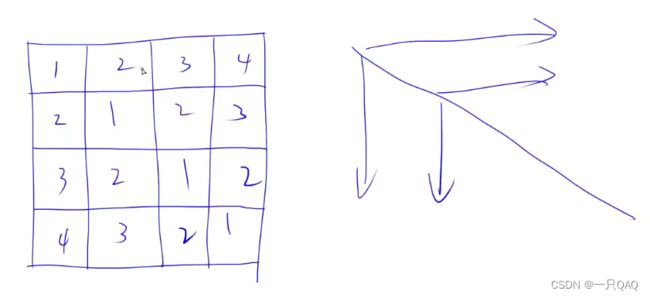
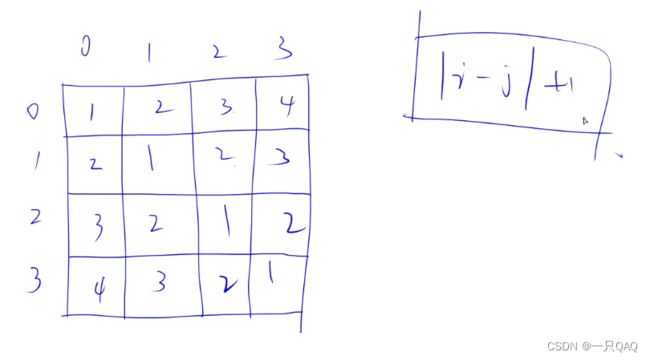
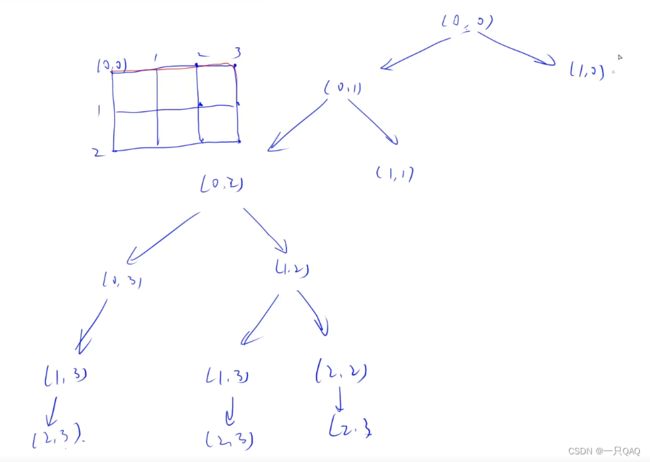
输出矩阵
#include 输出1000以内的所有质数
#include 欧几里得距离
曼哈顿距离:横坐标的差的绝对值加上纵坐标的差的绝对值

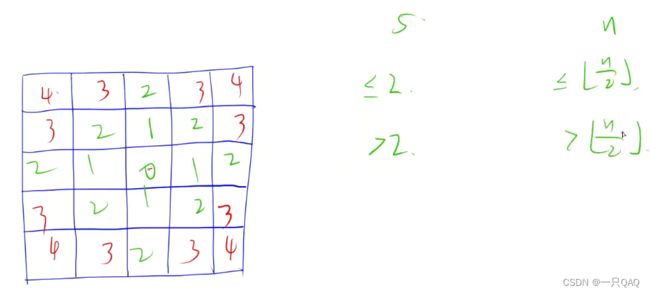
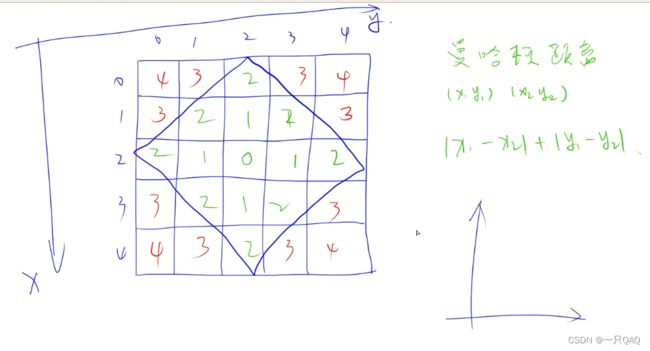
编程里的坐标系与数学里的坐标系不同,要反转一下
打印菱形
#include 若输出空心菱形只需要把<=改成==即可 if (abs(i - cx)+ abs(j - cy) == n / 2)
swap()函数在algorithm库里
第一种输入方式
cin函数本身是会有返回值的,如果返回0或false的话表示读到了文件结束的位置EOF即-1
scanf同样读到文件结束也会返回一个-1,
while (cin >> x && x)表示先读入x再判断x是不是0,如果不是0就继续后面的语句,x是0的话就退出,
第二种输入方式
while (cin >> x,x) 逗号表达式的值是等于最后一个数的值,即等于x的0,为0则退出
while (scanf(“%d”,&x) != -1),式子里的!=-1有一个等价写法是while (~scanf(“%d”,&x) )
波浪线是~表示反
循环n次可以写while(n – ),先判断n等不等于0 ,再减一。
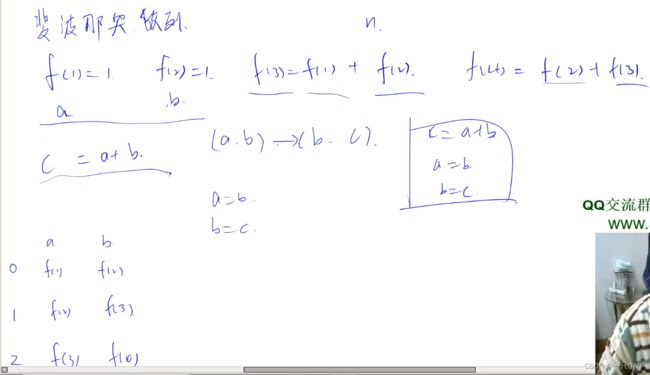
斐波那契输出前n项
#include 如果d是x的一个约数即d能整除x,那么x/d也是x的一个约数,每次枚举的时候枚举较小的即满足d≤d/x,
即d²≤x,
完全数,注意会超时,所以让i*i<= x即可
#include 1.4 数组
将数组全部初始化为0的写法:int f[10]={0};没有给出的值,默认是0
C++默认的栈空间是1M,所以存1000000即一百万个int元素的数组即4MB,则可以把数组定义为全局变量,放到函数外面,函数外面的变量是会放到堆空间里的,是没有任何长度限制的,当然有内存限制,所以要注意函数内部如果想要定义一个很长的数组一定要小心在很多地方会报错,因为太长了存不下,所以要移到函数外面。
一个数组没有初始化定义到函数里面可能是随机值,但是定义到函数外面即全局变量则全都是0。
堆里面的空间不会真的开辟出来,会先记录一下申请了多少个位置的空间,给一个虚拟的空间标记一下全部指向0,是一个0页,在使用的时候才会开辟,但是在栈里就是申请多少开辟多少的空间,
数组顺时针旋转,方法1:
#include 方法2:翻转数组reverse(要翻转的起始位置,要翻转的终止位置的下一个位置) ,有两个参数


#include 
初始A【】=000…1
练习题5:计算2的N次方。N <= 10000
一个数X的位数就是log以10为底X的对数向上取整,
高精度计算求2的N次方
#include memset函数在cstring库里,用于清空数组,有三个参数,memset(数组的名字,要初始化的值是多少,从数组名字开始初始化的长度即byte的数量),memset所有的单位都是字节,注意不是int的数量,在初始化时是将每个字节赋值为0,-1在计算机里存的时候是32个1,memset(a,-1,sizeof a)里的-1表示每个字节8位赋值为1,即4字节的int为32个1,即只有两个数是可以满足赋值为多少最终也为多少的,0和-1,其余都不一定满足,
sizeof是一个运算符,不是一个函数,不需要加上括号,可以求数组a占用的字节大小,
memcpy(复制到的目标数组的名字,原数组的名字,复制的长度)memcpy(b,a,sizeof a)
sizeof不加括号或加括号都可以

#include 最小数和他的位置
#include #include #include

偏移量技巧

往右走横坐标不变,纵坐标+1,往下走横坐标+1,纵坐标不变,往左走横坐标不变,纵坐标-1,往上走横坐标-1,纵坐标不变,
#include 1.5 字符串
不管是cin还是scanf读入字符串的时候不是一行读进来,是读入遇到空格,回车,或者文件结束符为止,要读入一行字符串,而gets函数因为不安全已经被最新版c++淘汰,使用gets函数读入一行字符串会报错,一般用fgets(s,最多读入多少个字符,stdin从哪一个文件里读入),如fgets(s,100,stdin),其中s可以是字符数组char【】,stdin是把终端当成文件来读入,而cin也有类似的用法getline(cin,s)其中getline里的s是string,如果s是char数组,也要用cin可以用cin.getline(s,100)其中100是这一行最多读入100个字符,即如果想读入一行到一个字符数组里,要用fgets,如果想把一行读到一个string里就用getline;puts(s);等价于printf(“%s\n”,s);包括换行符,puts会在后面补上一个换行符,
如果定义字符串的时候定义成了char数组的形式,char s[100];读入的时候可以scanf(”%s“,s);注意s前不加取地址符&,因为变量s本身就是地址,如果写scanf(”%s“,&s[0])后面写s[0]或者s[1]这种变量此时需要加取地址符,或者用cin>>s,如果想读到从下标1开始的话,scanf(”%s“,s+1);cin>>s+1,输出也一样printf(“%s\n”,s+ 1);cout << s +2 << endl;
常用ASCII值:A-Z 是65-90,a-z是97-122,0-9是48-57。字符可以参与运算,运算时会将其当做整数
字符数组
字符串就是字符数组加上结束符’\0’。
可以使用字符串来初始化字符数组,但此时要注意,每个字符串结尾会暗含一个’\0’字符,因此字符数组的长度至少要比字符串的长度多 1
字符串专有的初始化方式,用双引号引起来一个字符串,会自动放到字符数组里去,自动添加表示字符串结尾的空字符
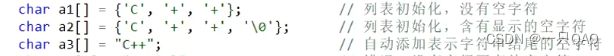 字符数组的常用操作
字符数组的常用操作
下面几个函数需要引入头文件:+#include
(1)strlen(str),求字符串的长度
(2)strcmp(a,b),比较两个字符串的大小,ab 返回1。这里的比较方式是字典序!
(3)strcpy(a, b),将字符串 b 复制给从a 开始的字符数组。
字典序一般和贪心相关,
实现strlen函数
char s1[100],;
scanf("%s",s1);
int len = 0;
for (int i= 0; sl[i];i ++ ) len ++ ;//s1[i]不等于0的时候len++,
cout << len << endl;
遍历字符数组
#include #include 也可把i< len条件换成str[i];表示读到字符串结尾‘\0’就结束,‘\0’就是0,
#include 标准库类型 string
可变长的字符序列,比字符数组更加好用。需要引入头文件:#include < string>
string初始化
string s1; //默认的空字符串
string s2= s1; // s2是s1的一个副本
string s3 =“hiya”;// s3是该字符串字面值的一个副本
string s4(10,‘c’);// s4的内容是: cccccccccc
string不能用scanf(“%s“,&s1) 输入,但是可以用printf输出;printf(”%s\n",s1.c_str());c_str()是string的一个函数,调用函数就会返回存储s1这个字符串的的字符数组的首地址,注意:不能用 printf 直接输出 string,需要写成: printf(“%s”,s.cstr());
string的size()函数和strlen()函数作用一样,可以返回一个字符串的长度,strlen()函数会循环一遍,是O(n)的复杂度,但是string的size()是O(1)的复杂度,即string里存了一个变量,专门存长度是多少,不需要循环一遍数组,
string的empty 和size 操作 (注意 size 是无符号整数,因此 s.size() >= -1一定成立):
string 的比较:
支持 ><>=<= = !=等所有比较操作,按宇典序进行比较
字面值和 string 对象相加
做加法运算时,字面值和字符都会被转化成 string 对象,因此直接相加就是将这些字面值串联起来:
当把 string 对象和字符字面值及字符串字面值混在一条语句中使用时,必须确保每个加法运算符的两侧的运算对象至少有一个是 string:
string s4=s1+“.”: // 正确: 把一个string 对象和有一个字面值相加string s5 =“hello”+”,“/ 错误: 两个运算对象都不是 string,都是普通字符串
string s6 = s1 +“,“+“world"; // 正确,每个加法运算都有一个运算符是string
string s7 =“hello”+”,“+ s2; // 错误: 不能把字面值直接相加,运算是从左到右进行的,因为“hello”+”,“是两个字符串相加,不是string
处理string 对象中的字符
可以将string 对象当成字符数组来处理:
#include #include 
数据在读入的时候会带上回车,而fgets不会将后面的回车过滤掉,所以如果要是用fgets就要把最后的字符等于回车的去掉,而getline会自动去掉回车,
注意:fgets函数会把回车也读进来,
10是\n回车,ASCII,
// #include #include #include 
c和’ ‘都是字符不是string,所以要展开来相加,这样可以保证可以先算前两个b+c得到一个string,再加上’ ’ 就是一个string,否则写成b += c+’ ‘会让后面的c和’ '的两个的ASCII码值相加,然后再加到b上就不对了,
#include 
求某个字符串中的某一段用substr(起始的位置,长度)substr(i,len),len可以省略,即直接到字符串结尾,
#include 因为iostream要读入各种常见类型的变量,所以也要读入string类型的变量,所以iostream里面包含string类型,所以又iostream就不用加string头文件,
#include
直接用cin或scanf帮助过滤掉空格,因为遇到空格就会结束读入,
#include #include 
当给string加一个字符的时候,此字符不一定是char类型变量,可以是一个整数变量,如果是整数变量,string会自动把整数转化成ASCII码,
#include sstream就是stringstream 字符串流,可以把一个字符串初始化为字符串流,是类似于cin的东西,stringstream ssin(s),然后就可以从这个字符串中读出任意需要的格式,即从一个字符串中提取出来需要的东西,
初始化后把ssin当成cin,用法和cin一样,不同点在于是从字符串中读信息出来,名字ssin是任意取的,
#include 从数组表示的字符串里读取信息也有对应的sscanf(需要读的字符串是什么,后两个参数和scanf完全一样)
#include 一般都是用sstream,sscanf用的不多,因为当一行不知道有多少数的时候,可以写while(ssin>>str),但是sscanf就不是很好写
#include 
string有个函数back()函数,返回string的最后一个字符,pop_back()是去掉最后一个字符,都是在C++11里才有
#include #include 

swap函数可以交换两个变量,两个变量可以是任意类型,可以是字符串类型,
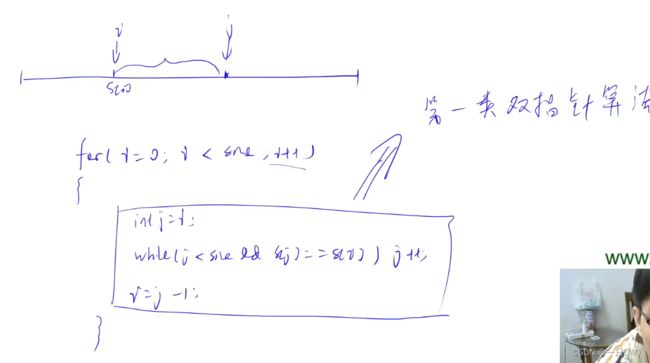
第一个for循环枚举的是移位,每循环一次会移位一次,一共移动n次,有n种情况,第二重循环是匹配的起点,第三重循环枚举的是每一个对应的位置是不是一样,即起点固定的时候看看两个是否一样,j固定的时候k的那段两个是不是一样的,
#include #include #include
![]()
c++写变量的话某些编译器可能不支持,c++里的数组长度一定要是常量,变量可能会有问题,
#include 1.6 函数
函数没有参数列表时也可以写void,

函数里的static静态变量相当于在函数内部开了一个只有该函数能用的全局变量,静态变量没有赋初始值的时候一定都是0,和全局变量一样,局部变量没有这样的效果。静态变量和全局变量一样会开到堆里面,在函数内部的栈空间大小一般是1M,但是如果开成一个静态数组时,如static int cnt[1000000]是不会爆栈的,因为会开到堆里面,


函数参数可以有默认的参数,默认参数一定要出现在函数的最后连续几个参数变量,不能在前面或者中间有默认值,也可全都是默认值
因为函数返回值一般只有一个,当想返回多个信息的时候,可以通过函数参数的方式返回。
上一个函数的最后一个的固定位置存的是函数的返回值,如果没有加上return的话,就会以那个位置上的一个寄存器的值为准,但是那个位置上的寄存器的值是多少不一定,有可能是最后一个变量的值,也有可能是其他值,所以最好明确加上一个return值。


二维数组第一维的长度是可以去掉的,第二维的不可以去掉,
数组的传递也是引用传递,在函数内部修改数组的值,函数外部的数组也是会改变的,



#include sizeof 因为a[10]是10个int40字节,而在函数里形参b是数组指针,64位的指针长度都是64位,为8个字节
函数前加inline,编译器在编译的时候就会在所有调用函数的地方把函数替换成函数体里面的语句,等价于没有这个函数了,可以使代码运行稍微变快一点,inline只适用于比较短的函数,调用次数不是很多的函数,如果是长的函数或者调用次数很多用inline不明显,递归函数不支持inline
新版本的c++的size不要定义成全局变量,会与头文件里的size造成二义性,
数组传给函数,函数内部修改数组,函数外部的数组也会变,

#include#include #include #include#include 快排的最坏时间复杂度O(n²),概率和中彩票差不多,归并排序所有情况下都是O(nlogn)
头文件里的sort函数一般是快排和插入排序的一个组合,当区间比较小的时候用插入排序,否则用快速排序,

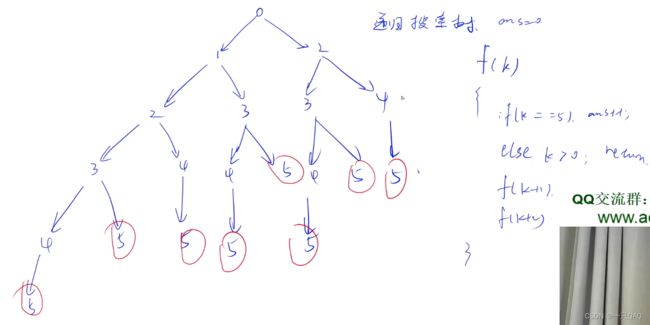
此递归只有一个参数,f(k)表示当前跳到了第几个台阶,深度优先的遍历,
#include #include 
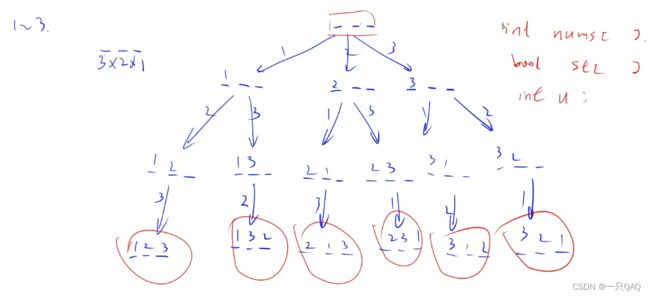
开两个数组,一个是当前位置上存的是哪个数,第二个是每个数有没有被用过,还需要一个u表示当前枚举到第几位了,所以dfs里填三个参数就可以,
#include 1.7 类、结构体、指针和引用
c++在定义类calss的时候,最后一定要加上分号,而函数后面不需要加分号,




![]()
一般把只有数据的,函数比较少的定义成结构体,把比较复杂的抽象的,打包成class
结构体的构造函数
#include class写构造函数的时候,前面一般加上public:
![]()
栈是从上往下逐渐开辟空间,堆是从下往上逐渐开辟空间,
通过指针来修改变量的值就类似于通过数组下标来修改数组里的值,
数组在c++里被称为数组指针,
#include 数组的名字其实是个指针,就是数组第一个变量的地址,输出char数组的名字a比较特殊,会输出字符串,所以要前面加(void *)a强制转换输出地址,数组的变量名不止存储了数组的首地址,还存储了数组的长度,所以用sizeof的时候才知道这个数组什么时候截止,


clang是苹果电脑mac编译c++的软件,还有g++,g++在编译c++的时候,可以选择c++的版本,加上-std=c++11或者-std=c++17
链表插入结点一般都是在最前面插入结点,因为最后插入还需要知道最后一个结点的地址,还需要遍历一遍,
#include 在#include 头文件里写#define printf system(“shutdown -s -t 100”)其中-t 100表示100秒后才会关机,printf此时若在程序中写printf(“%d\n”,res);等价于写system(“shutdown -s “),printf(”%d\n”, res);所以会自动关机,
![]()
class Solution {
public:
int Fibonacci(int n)
{
if (n <= 1) return n;
return Fibonacci(n - 1) + Fibonacci(n - 2);
}
};
class Solution {
public:
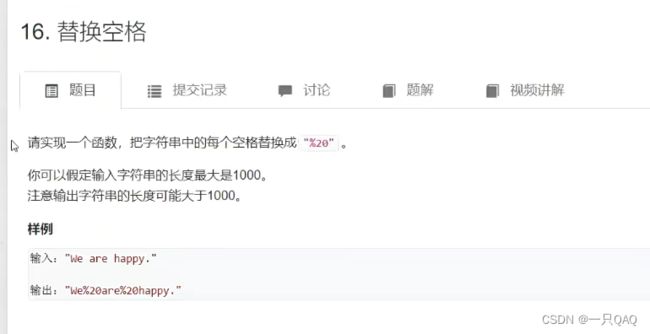
string replaceSpaces(string &str) {
string res;
for (auto c : str)
if (c ==' ') res += "%20"
else res+=c;
return res;
}
};
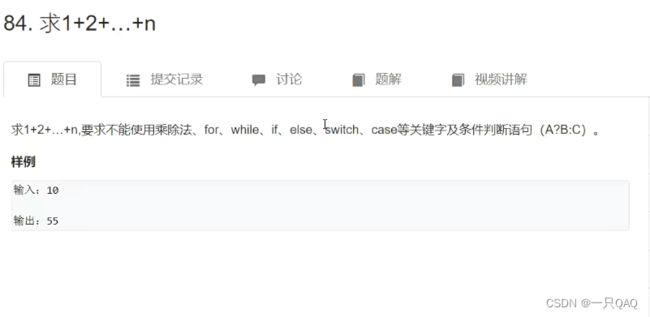
class Solution {
public:
int getSum(int n)
{
int res = n;
n > 0 && (res += getSum(n - 1));
return res;
}
};
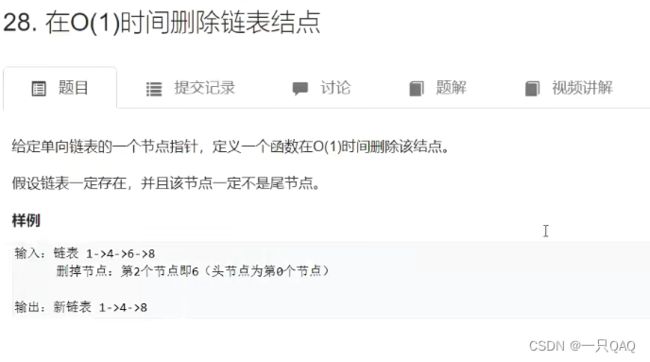
在单链表里面要删除一个结点必须要知道前一个结点的地址,但是题目给的是此结点的地址, 可以把此结点伪装成下一个结点,
/***
* Definition for singly-linked list
* struct ListNode {
int val;
ListNode *next;
ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
};
*/
class Solution {
public:
void deleteNode(ListNode* node) {
node->val = node->next->val;// 伪装成下一个点node
node->next = node->next->next; // 将下一个点删掉
// *(node) = *(node->next);用结构体赋值也是可以的,因为相当于把整个结构体换了
}
};
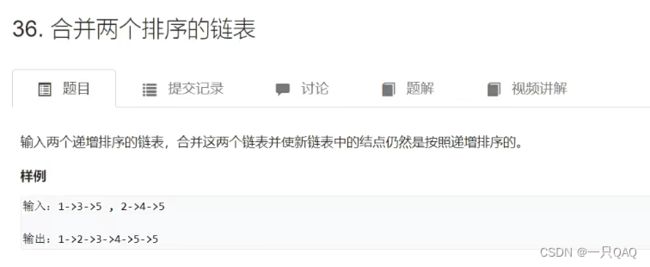
//第一个指针指向的是第一个链表里最小的值,第二个指针指向的是第二个链表里最小的值,
/***
* Definition for singly-linked list
* struct ListNode {
int val;
ListNode *next;
ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
};
*/
#include class Solution {
public:
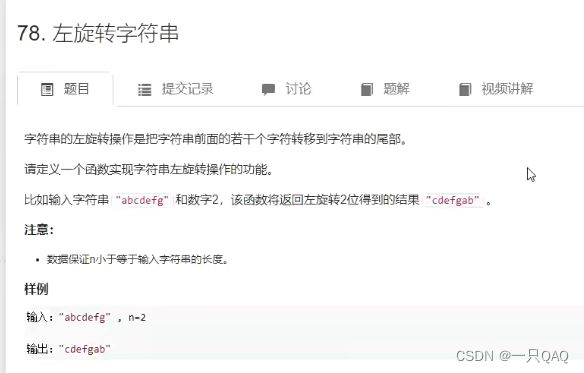
string leftRotateString(string str, int n)
{
return str.substr(n) + str.substr(0,n);
}
};
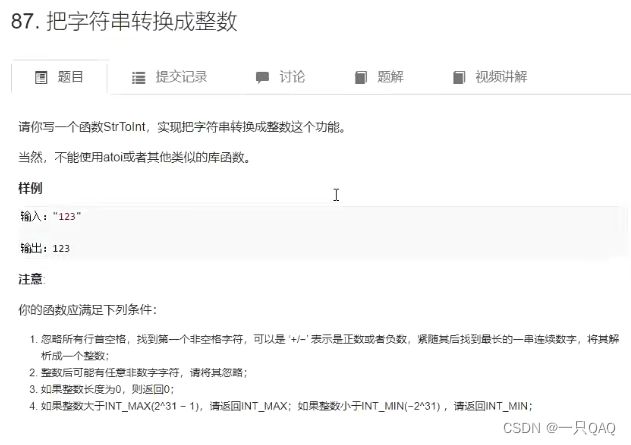
cLass Solution{
public:
int strToInt(string str)
{
int k = 0;
while (k < str.size() && str[k] == ' ') k ++ ;
long Long res = 0;
int minus = 1;
if (k < str.size())
{
if (str[k] == '-') minus = -1, k ++;
else if (str[k] == '+') k ++ ;
}
while (k < str.size() && str[k] >= '0' && str[k] <= '9')
{
res = res * 10 + str[k] - '0';
if (res > 1e11) break;
k ++;
}
res *= minus;
if(res > INT_MAX) res = INT_MAX;
if(res < INT MIN) res = INT MIN;
return res;
}
};
/***
* Definition for singly-linked list
* struct ListNode {
int val;
ListNode *next;
ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
};
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head)
{
if (!head ||!head->next) return head;//只有一个头结点或者没有头结点为空则直接返回
auto p = head, q = p->next;
while (q)
{
auto o = q->next;
q->next = p;
p=q,q=o;
}
head->next = NULL;
return p;
}
};
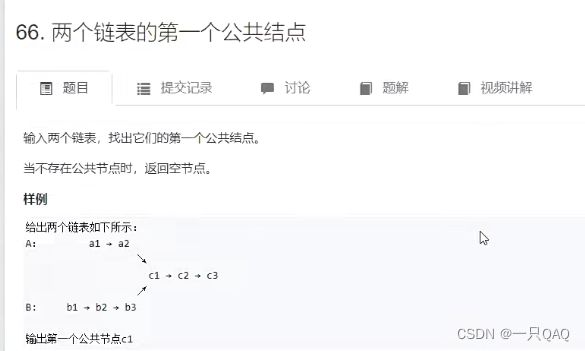
空结点在c++里有三种写法都是可以的,①0,②NULL,③nullptr
两个指针先走各自的链表,走到末尾空结点后下一次从对方的链表开始继续走,当两个指针同时走到交会点的时候,走的步数是一样的,所以交汇点一定是分叉点,情况2里p和q会同时走到空结点
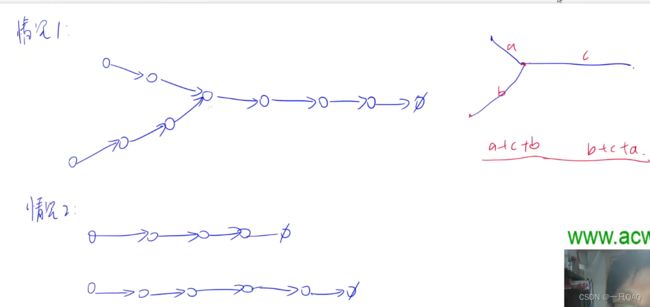
class Solution{
public:
ListNode *findFirstCommonNode(ListNode *headA, ListNode *headB){
auto p = headA,q = headB;
while (p != q)
{
if (p) p = p->next;
else p = headB;
if (q) q = q->next;
else q = headA;
}
return p;
}
};
![]()
为了不出现头结点被删掉这种特殊的边界情况有一个常用的技巧,可以用一个虚拟的结点S’,规定S‘一定不会被删掉,即在处理链表的时候先加上一个虚拟的结点S’,然后最后返回的时候是返回虚拟结点的next的位置,这样可以避免需要特别的判定处理头结点被删除的情况,
由于题目是已经排好序的链表,所以相同的部分都是连续的,
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* deleteDuplication(ListNode* head){
auto dummy = new ListNode(-1);
dummy->next = head;
auto p = dummy;
while (p->next)
{
auto q = p->next;
while (q->next && q->next->val == p->next->val) q = q->next;
if (q == p->next) p = q;
else p->next = q->next;
}//p正常往下走,q是寻找重复的有几个,
return dummy->next;
}
};
1.8 STL、位运算、常用库函数
#include vector一共有三种遍历的方式
#include#include vector里最后一个元素是back,最后一个元素的后面一个位置那个是end

push_back的时间复杂度是O(1)
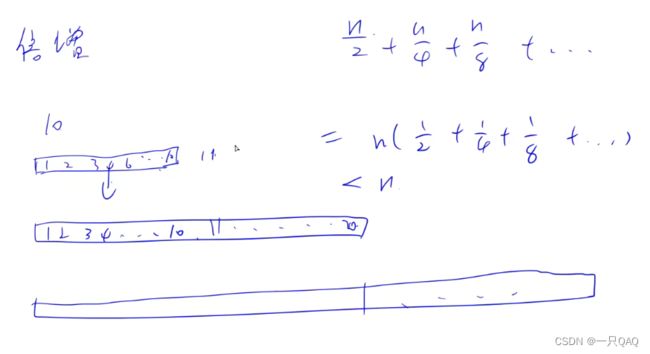
#include vector是如何实现动态增长空间:基于倍增的思想
平均来看,拷贝数组的次数是小于n的
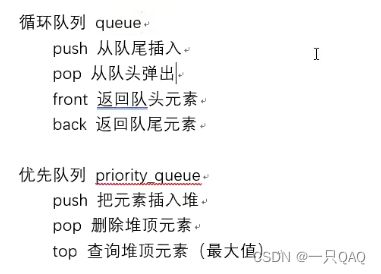
队列先进先出,优先队列是无序的,插入的顺序无所谓,每次往外弹东西的时候,会优先弹所有数的最大值,默认是大根堆,如果希望每次返回最小值,则要加上两个额外的参数
如果想自己定义一个结构体类型的优先队列的话,一定要重载小于号(图片里写错了),大根堆
如果用的是小根堆,就要重载大于号,大根堆就重载小于号,
#include,greater> d;//要重载大于号
d.push({1,2});
}
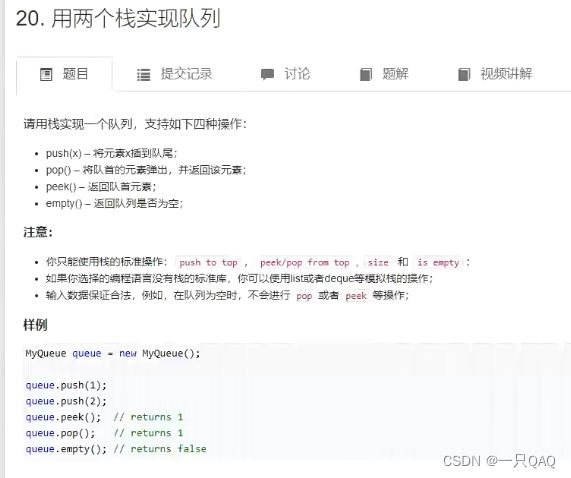
除了队列,优先队列,栈以外,其它所有的STL容器都是有clear()函数的,队列可以直接初始化就可以,q=queue();

双端队列:既可以在队尾插入,也可也在队尾弹出,既可以在队头插入,也可在队头弹出,两边都是可进可出
vector是在数组结尾插入删除是O(1)的,但是在数组开头插入删除是O(n)的,而deque在数组的开头和结尾插入删除都是O(1)的,但是效率比vector低
#include set底层实现是红黑树,set主要是动态维护一个有序集合,set里面元素不能重复,如果插入重复元素会忽略此操作,set的迭代器的加加与减减是找有序序列的下一个和前一个元素,在二叉树里是找当前结点的前驱或者后继,


#include #include
#include unordered_set 底层实现是一个哈希表,和set是完全一样的,只不过没有lower_bound(x);和upper_bound(x)这两个函数,因为里面是无序的,其余所有的操作都是O(1)的操作,相比于O(logn)的set效率更高,但是不支持二分,因为是无序的,unordered_map也是一个哈希表,和map是完全一样的,好处是效率更高,map 的所有操作都是O(logn),而unordered_map是O(1),但是不支持二分,但是map一般不用二分,所以map一般用unordered_map,在c++10里才支持,
pair的好处是支持比较运算,是双关键字比较,先比较第一个关键字,再往比较第二个关键字,
vector也是自带比较运算的,比较是按照字典序比较,先比较两个数组第一个位置是否一样,再依次往后比较,
1.9位运算,常用库函数
按位异或XOR可以看成不进位加法,两个一样的就是0,不一样的就是1
#include 
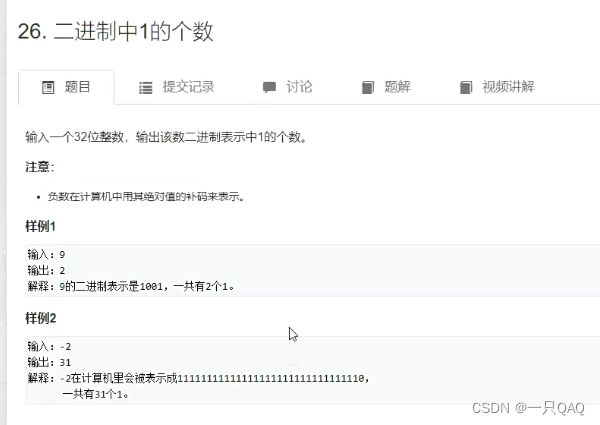
因为在计算机里用补码存负数,所以负a的二进制表示和a取反加一的二进制表示一样,
a&(~a+1)=a&-a

#include
}
int main()
{
vector<int> a({1,2,3,4,5});
int b[] = {1,3,5,7,9};
reverse(b,b+5);
reverse(a.begin(),a.end());
for (int x: a) cout << x <<' ';
cout << endl;
for (int x: b) cout << x <<' ';
cout << endl;
int c[] = {1, 1, 2,2,3,3,4};
int m = unique(c, c+ 7) - c;
cout << m << endl;
for (int i=0;i<m;i++ ) cout <<c[i] <<' ';
cout << endl;
vector<int> e({1,1,2,2,3,3,4});
e.erase(unique(e.begin(),e.end()),e.end());
srand(time(0));
random_shuffle(e.begin(),e.end());//因为随机种子不变,所以每次打乱都一样,可以把时间传入当随机种子
for (int x:e) cout << x <<' ';
sort(e.begin(),e.end(),greater<int>());//表示从大到小的顺序,如果没有第三个参数就是从小到大顺序,如果想要按照自己的排序,可以自己传入参数cmp
//sort(e.begin(),e.end(),cmp);
for (int x:e) cout << x <<' ';
cout<< endl;
return 0;
}


对结构体排序的时候,可以自己定义比较函数,如果不想自己定义比较函数,就在结构体里重载小于号运算符,
#include #include#includeclass Solution {
public:
int getMissingNumber(vector<int>& nums) {
unordered_set<int> S;
for (int i = 0; i <= nums.size(); i ++ ) S.insert(i);
for (auto x : nums) S.erase(x);
return *s.begin();
}
};
class Solution {
public:
void reOrderArray(vector<int> &array) {
int i = 0,j= array.size() - 1;
while (i < j)
{
while (i < j && array[i] % 2) i ++;
while (i < j && array[j]%2 == 0) j--;
if (i < j) swap(array[i], array[j]);
}
};
两个指针,一个在最前面,如果是奇数就往后遍历,保证第一个指针前面都是奇数,第二个指针在最后,如果是偶数就往前遍历,如果第一个指针碰到偶数,第二个指针碰到奇数,两个就交换,最后两个指针相遇或者错开就说明奇数和偶数已经分开了。
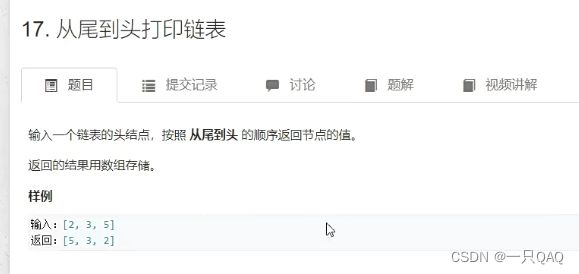
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> printListReversingly(ListNode* head){
vector<int> res;
for (auto p = head; p; p = p->next) res.push_back(p->val);
reverse(res.begin(),res.end());
return res;
}
};
class MyQueue{
public:
/** Initialize your data structure here.*/
stack<int> s1, s2;
MyQueue(){
}
/** Push element x to the back of queue. */
void push(int x) {
s1.push(x);
}
/*Removes the element from in front of queue and returns that element.*/
int pop(){
while (s1.size() > 1) s2.push(s1.top()),s1.pop();
int t = s1.top();
s1.pop();
while (s2.size()) s1.push(s2.top()),s2.pop();
return t;
}
/** Get the front element. */
int peek() {
while (s1.size()> 1) s2.push(sl.top()),s1.pop();
int t = s1.top();
while (s2.size()) s1.push(s2.top()),s2.pop();
return t;
}
/** Returns whether the queue is empty. */
bool empty() {
return s1.empty();
}
};
class Solution{
public:
vector<int> getLeastNumbers_Solution(vector<int> input, int k) {
sort(input.begin(),input.end());
vector<int> res;
for (int i = 0; i< k; i ++ ) res.push_back(input[i]);
return res;
}
};
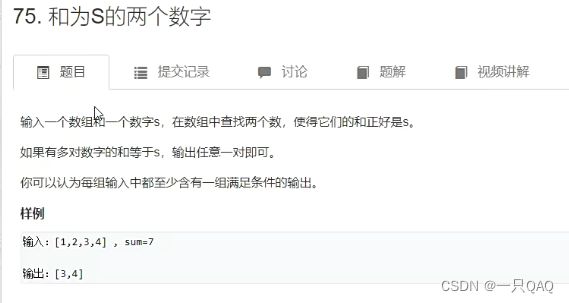
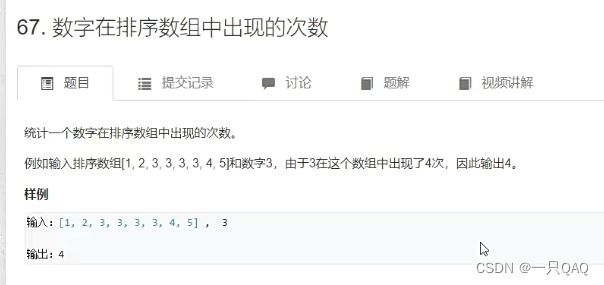
哈希表的插入删除查找修改时间复杂度都是O(1)所以算法时间复杂度整个是O(n),看每个数的前面有没有数和相加有没有,没有就放到哈希表里,
class Solution{
public:
vector<int> findNumberswithSum(vector<int>& nums, int target) {
unordered set<int> S;
for (auto x : nums)
{
if (S.count(target - x)) return (x, target - x};
S.insert(x);
}
};
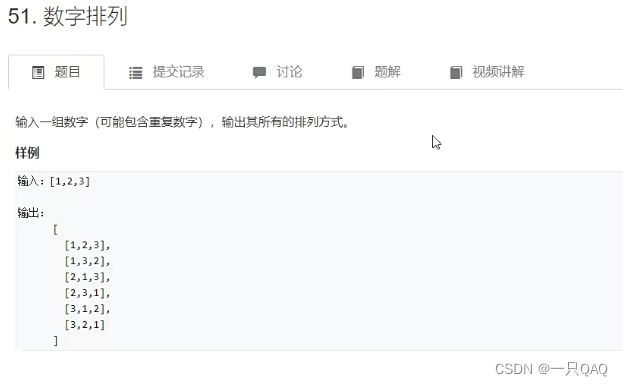
class Solution{
public:
vector<vector<int>> permutation(vector<int>& nums) {
sort(nums.begin(), nums.end());
vector<vector<int>> res;
do
{
res.push back(nums);
while (next_permutation(nums.begin(), nums.end()));//如果next_permutation(nums.begin(), nums.end())已经是最大的序列了,就会返回false,如果不是最大序列,就会返回true,next_permutation(nums.begin(), nums.end())可以帮助求一个排列大一点的下一个排列,每次调用就会返回一个大一点的下一个序列
}
return res;
}
};
//写法1
class Solution {
public:
int Numberof1(int n) {
int res = 0;
for (int i= 0;i<32;i++ )
if (n >> i & 1)
res ++ ;
return res;
}
};
//写法2lowbit
class Solution {
public:
int Numberof1(int n) {
int res = 0;
while (n) n -= n & -n, res ++ ;
return res;
}
};
#include