数据结构(数组)
一.数组的概念
1. 数组定义
数组(Array)是一种线性结构。它用一组连续的内存空间,来存储一组具有相同数据类型的数据。
2. 数组的特点
①用来存储一组类型相同的数据。
②在内存中,分配连续的空间,数组创建时需要指定容量。因为数组为了保持内存的数据的连续性,所以会导致插入、删除这两个操作比较低效。
③数据类型[] 数组名 int[] arr = new int[10]; int[] arr2 = {1,2,3,4};
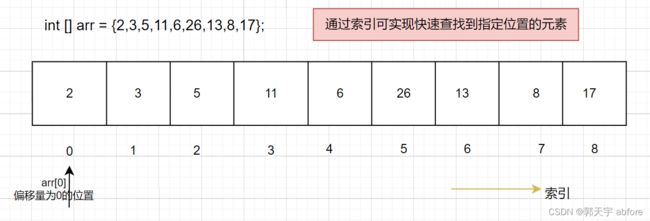
④访问数组中的数据时,通过索引访问,这也是数组的一大优点,可以实现随机访问(通过索引,时间复杂度为O(1)),所以随机访问时,效率比较高。 所以,数组是适合查找操作的,但查找的时间复杂度并不是O(1),即使是排好序的数组,使用二分查找法,时间复杂度也是(logn)。
⑤索引从0开始,最大到数组长度-1。索引从0开始,是因为索引(数组元素下标),确切的来说应该叫做偏移量,例如,arr[0]就表示偏移量为0的元素,也就是首地址。arr[k]就表示偏移量为k个type_size的位置。
⑥常见异常:NullPointException(空指针异常)、ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(数组索引越界异常)。
package com.gty.algo.lesson;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class ArrayDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1.创建数组
int[] arr = {11, 9, 1, 2, 26, 12};
// 2.访问指定位置的值
int num = arr[0]; //获取第一个位置的值
System.out.println("num = " + num);
// 3.修改指定位置的值
arr[3] = 15;
System.out.println("修改后的值为:" + arr[3]);
// 4.遍历数组
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
System.out.print(arr[i] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
// 5.数组中的异常(数组索引越界异常)
System.out.println(arr[arr.length]); //ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException
// 空指针异常
String[] s = new String[6];
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(s)); //[null, null, null, null, null, null]
System.out.println(s[0].length()); //NullPointerException
}
}注:
- 数组是一段连续的内存空间,用户来存放具有相同数据类型的元素。
- 在定义数组时,需要注意数组的类型和长度。类型决定了数组可以存储的元素的种类,长度定义了数组可以存储的元素的数量。
- 在修改与访问数组时,要注意数组的索引,避免出现数组索引越界异常。在修改数组中的元素的值时,要注意数组中元素的数据类型,避免出现类型不一致的错误。
3.数组的遍历
方法:for循环、for-each(增强for循环)、调用toString方法 。
package com.gty.algo.lesson;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class ArrayDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {11, 9, 1, 2, 26, 12};
/*
数组的遍历
*/
//1.for循环
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
System.out.print(arr[i] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
//2.for-each(增强for循环)
for (int x:arr) {
System.out.print(x + " ");
}
System.out.println();
//调用toString方法
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr));
}
}二.封装数组
基于java提供给我们的数组,进行二次封装,我们可以自己去写一个我们自己的数组(动态数组)去实现数组的各种基本功能。
1.封装数组
主要功能:
添加元素,获取元素,查看当前数组中元素的个数,获取容积,修改元素,数组扩容,判空,查询指定元素,删除指定位置的元素。
package com.gty.algo.lesson.array;
// 支持泛型
public class MyArray {
private T[] arr;
private int size;
private int capacity; //容积
// 构造方法
public MyArray(int capacity) {
// 入参判断
if (capacity <= 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("输入容积异常!");
}
this.capacity = capacity;
this.size = 0;
this.arr = (T[]) new Object[this.capacity];
}
// 获取元素个数
public int getSize() {
return this.size;
}
// 获取容积
public int getCapacity() {
return this.capacity;
}
// 添加元素
public void add(T item) {
this.arr[this.size] = item;
this.size++;
}
// 向指定位置添加元素
public void addValueByIndex(int index, T value) {
if (index < 0 || index > this.size) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("索引异常!");
}
if (this.size == this.capacity) {
resize(this.capacity * 2);
}
for (int i = this.size - 1; i >= index; i--) {
this.arr[i + 1] = this.arr[i];
}
this.arr[index] = value;
this.size++;
}
// 扩容
private void resize(int newCapacity) {
T[] newArr = (T[]) new Object[newCapacity];
for (int i = 0; i < this.size; i++) {
newArr[i] = this.arr[i];
}
// 改变容器与容积
this.arr = newArr;
this.capacity = newCapacity;
}
// 判空
public boolean isEmpty() {
return this.size == 0;
}
// 修改元素
public void modifyValueByIndex(int index, T value) {
// 入参判断
if (index < 0 || index > capacity) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("索引异常!");
}
this.arr[index] = value;
}
// 获取指定位置的值
public T getValueByIndex(int index) {
// 入参判断
if (index < 0 || index > capacity) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("索引异常!");
}
return this.arr[index];
}
// 查询指定的值在数组中是否存在,存在返回索引,不存在返回-1
public int containsValue(T value) {
for (int i = 0; i < this.size; i++) {
if (value.equals(this.arr[i])) {
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
// 删除指定位置的元素
public T deleteValueByIndex(int index) {
// 入参判断
if (index < 0 || index > capacity) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("索引异常");
}
// 1.找到删除的位置的元素
T deValue = this.arr[index];
// 2.将删除元素之后的元素前移
for (int j = index + 1; j < this.size; j++) {
this.arr[j - 1] = this.arr[j];
}
this.size--;
// 判断是否缩容
if (this.size <= this.capacity / 4 && this.capacity / 2 > 0) {
resize(this.capacity / 2);
}
return deValue;
}
// 重写toString方法,用于数组打印
@Override
public String toString() {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
sb.append("{");
for (int i = 0; i < this.size; i++) {
sb.append(this.arr[i]);
if (i < this.size - 1) {
sb.append(",");
}
}
sb.append("}");
return sb.toString();
}
} 2.例题介绍
两数之和(1. 两数之和 - 力扣(LeetCode))
- 题解:可以利用Map,将数组中的值和其对应的索引以键值对的方式存放在Map中。遍历数组,当发现target - nums[i](这是解决本题的重点思想,将两数之和转换为两数之差(值1 - 值2 = 目标值 即为,目标值 - 值1 = 值2))在Map中,说明找到了目标值,返回target - nums[i]的下标和i即可。基于以上思想,在向Map中存放键值对时,可以将数组中元素的值作为键,元素在数组中的索引作为值存放在Map中,方便我们获取索引。
- 代码实现
package com.gty.algo.subject;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.HashMap;
public class LeetCode_01 {
public int[] twoSum(int[] nums, int target) {
// 入参判断
if(nums == null || nums.length < 2){
return null;
}
// 利用Map,将数组中的值和其对应的索引以键值对的方式存放起来,可以将值作为Map中的键,索引作为值,
HashMap map = new HashMap<>();
// 遍历数组,求数组中两数之和等于目标值,即求目标值 - 值1 = 值2,
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
int temp = target - nums[i];
if(map.containsKey(temp)){ //判断值是否存在
return new int[]{map.get(temp),i}; //map.get(temp)---通过key获取key对应的value
}else{
map.put(nums[i],i); //向Map中添加元素
}
}
return null;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int [] nums = {2,7,11,15};
LeetCode_01 leetCode_01 = new LeetCode_01();
int [] res = leetCode_01.twoSum(nums,9);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(res)); //[0, 1]
}
}