蓝桥 python笔记6——heapq、functool、itertools
目录
heapq
functool
itertools
heapq
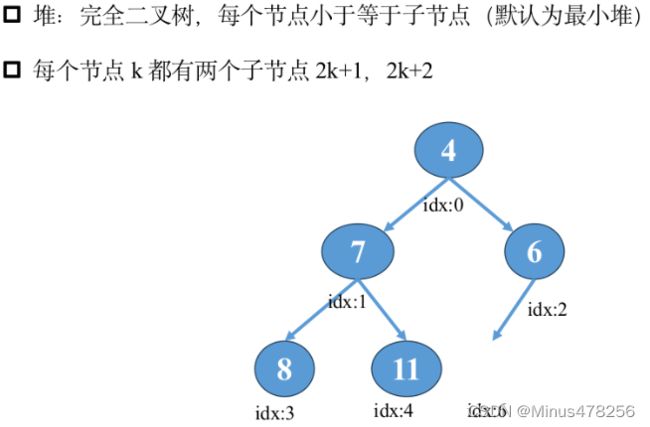
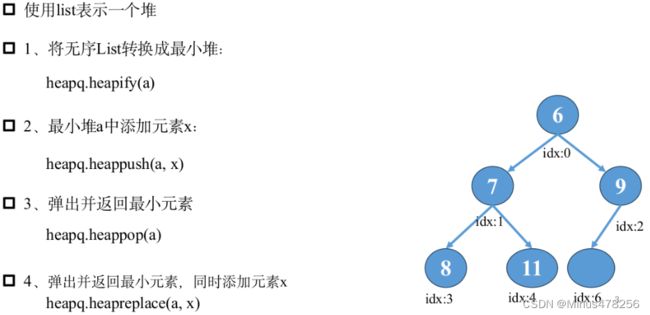
这里涉及到一点数据结构的知识,后续会讲解。
(此处,只要将其理解为按某种规则包装数据的结构体即可。
可以动态地求最值(此处为最小值,因为是最小堆
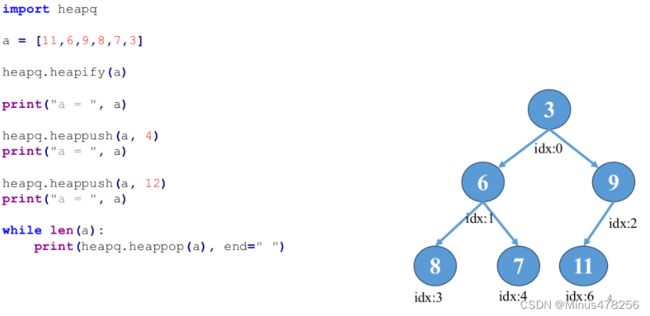
import heapq
a = [11,6,9,8,7,3]
print(a)
heapq.heapify(a)
print(a)
heapq.heappush(a,4)
print(a)
heapq.heappush(a,12)
print(a)
while len(a):
print(heapq.heappop(a),end=" ")
# [3, 6, 9, 8, 7, 11]
# [3, 6, 4, 8, 7, 11, 9]
# [3, 6, 4, 8, 7, 11, 9, 12]
# 3 4 6 7 8 9 11 12 functool
from functools import partial
def Add(a,b,c):
print(a)
print(b)
print(c)
print(a+b+c)
add_fix_c=partial(Add,c=10) #把Add函数的c固定住了,这样定义为方法add_fix_c
add_fix_c(1,2) #方法add_fix_c只需传入a、b的值即可
# 1
# 2
# 10
# 13itertools
无限迭代器:
from itertools import count,cycle,repeat
for x in count(start=0,step=1):
print(x)
if x>3:
break
# 0
# 1
# 2
# 3
# 4
for x in cycle('hello'):
print(x)
if x =='o':
break
# h
# e
# l
# l
# o
for x in repeat('hello',3):
print(x)
# hello
# hello
# hello有限迭代器:
from itertools import accumulate
a=[1,2,3,4,5]
b=list(accumulate(a)) #计算前缀和
print(b)
a=[3,4,2,1,5]
b=list(accumulate(a,max)) #计算前缀最大值
print(b)
b=list(accumulate(a,min)) #计算前缀最小值
print(b)
# [1, 3, 6, 10, 15]
# [3, 4, 4, 4, 5]
# [3, 3, 2, 1, 1]排列组合迭代器:
这些方法可以自己写,但是用迭代器会更方便快速。
from itertools import product,permutations,combinations
# 笛卡尔积:
ans=list(product([1,2,3],[4,5,6]))
print(ans)
ans=list(product([1,2,3],repeat=2))
print(ans)
# [(1, 4), (1, 5), (1, 6), (2, 4), (2, 5), (2, 6), (3, 4), (3, 5), (3, 6)]
# [(1, 1), (1, 2), (1, 3), (2, 1), (2, 2), (2, 3), (3, 1), (3, 2), (3, 3)]
# 排列:
a=list(permutations([1,2,3]))
print(a)
a=list(permutations([1,2,3],2)) #选两个进行排列
print(a)
# [(1, 2, 3), (1, 3, 2), (2, 1, 3), (2, 3, 1), (3, 1, 2), (3, 2, 1)]
# [(1, 2), (1, 3), (2, 1), (2, 3), (3, 1), (3, 2)]
# 组合:
b=list(combinations([1,2,3],2))
print(b)
# [(1, 2), (1, 3), (2, 3)]