力扣23题:合并升序链表:优先队列,分治,链表合并
23. 合并K个升序链表
给你一个链表数组,每个链表都已经按升序排列。
请你将所有链表合并到一个升序链表中,返回合并后的链表。
示例 1:
输入:lists = [[1,4,5],[1,3,4],[2,6]]
输出:[1,1,2,3,4,4,5,6]
解释:链表数组如下:
[
1->4->5,
1->3->4,
2->6
]
将它们合并到一个有序链表中得到。
1->1->2->3->4->4->5->6
示例 2:
输入:lists = []
输出:[]
示例 3:
输入:lists = [[]]
输出:[]
1.在原有链表上一直插入新的链表
class Solution23 {
public:
//先对链表数组的头指针排序,空指针在最前,后边按照升序排列
static bool compare_int(ListNode* elem1, ListNode* elem2){
if (elem1 != NULL &&elem2 != NULL)
return elem1->val < elem2->val;
else if (elem1 == NULL&&elem2 != NULL)
{
return true;
}
else if (elem1 != NULL &&elem2 == NULL)
{
return false;
}
else
{
return true;
}
}
ListNode* mergeKLists(vector<ListNode*>& lists)
{
//数组为空 返回nullptr
if(lists.empty())
{
return nullptr;
}
//排序
sort(lists.begin(),lists.end(),compare_int);
//返回值为数组第一个链表
ListNode* res = lists[0];
for(int i = 1;i<lists.size();i++)
{
res = merge(res,lists[i]);
}
return res;
}
//方法1 在原有链表上合并
ListNode* merge(ListNode* head1,ListNode* head2)
{
ListNode* p;
ListNode* q = new ListNode;
ListNode* s;
s = head2;
p = head1;
q = p;
if(!head1 || !head2)
{
return head1? head1:head2;
}
while(p!= NULL&&s!=NULL)
{
if(s->val >= p->val)
{
q = p;
p = p->next;
}
else if(s->val<p->val)
{
ListNode* r = new ListNode;
r->val = s->val;
r->next = q->next;
q->next = r;
s = s->next;
q = q->next;
}
}
if(p == NULL&&s != NULL)
{
q->next = s;
}
return head1;
}
};
2.新建一个链表,将每两个链表中,当前头结点较小的结点插入
//方法2 新建一个链表
ListNode* mergeKLists2(vector<ListNode*>& lists)
{
ListNode* res = nullptr;
for(int i = 0;i<lists.size();i++)
{
res = merge2(res,lists[i]);
}
return res;
}
ListNode* merge2(ListNode* head1,ListNode* head2)
{
ListNode Head ; //虚拟的头
ListNode *tail = &Head; //tail执行后面的插入操作
ListNode *aptr = head1;
ListNode *bptr = head2;
if(!head1 || !head2)
{
return head1?head1:head2;
}
while( aptr&&bptr)
{
if(aptr->val <bptr->val)
{
tail->next = aptr;
aptr = aptr->next;
}
else
{
tail->next = bptr;
bptr = bptr->next;
}
tail= tail->next;
}
tail->next = aptr?aptr:bptr;
return Head.next;
}
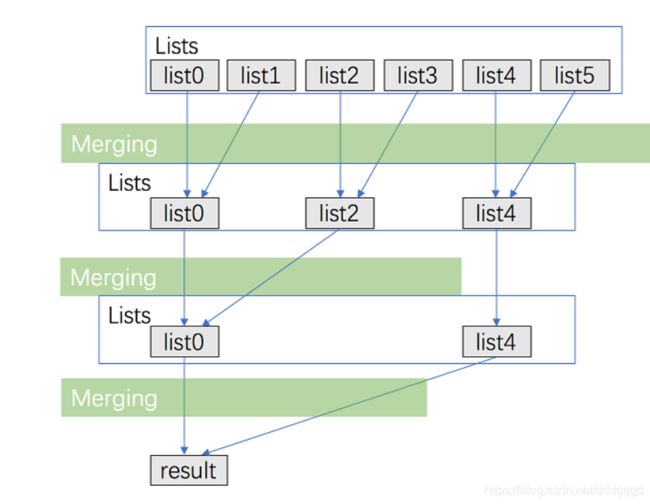
//方法3 分治,
ListNode* mergeKLists3(vector<ListNode*>& lists)
{
return mergefenzhi(lists,0,lists.size()-1);
}
ListNode* mergefenzhi(vector<ListNode*>& lists,int l,int r)
{
if(l ==r) return lists[l];
else if (l>r) return nullptr;
int mid = (l+r)/2;
return merge3( mergefenzhi(lists,l,mid),
mergefenzhi(lists,mid+1,r));
}
ListNode* merge3(ListNode* head1,ListNode* head2)
{
ListNode Head ; //虚拟的头
ListNode *tail = &Head; //tail执行后面的插入操作
ListNode *aptr = head1;
ListNode *bptr = head2;
if(!head1 || !head2)
{
return head1?head1:head2;
}
while( aptr&&bptr)
{
if(aptr->val <bptr->val)
{
tail->next = aptr;
aptr = aptr->next;
}
else
{
tail->next = bptr;
bptr = bptr->next;
}
tail= tail->next;
}
tail->next = aptr?aptr:bptr;
return Head.next;
}
4.优先队列合并
将所有头结点放入按val升序排列的优先队列中,每次将队列顶部元素取出插入到新链表中,同时将刚被插入到新链表的结点的下一结点放入到优先队列中
struct Status
{
int val;
ListNode *ptr;
friend bool operator < (const Status &rhs1,const Status &rhs2) {
return rhs1.val > rhs2.val;
}
};
priority_queue <Status> q;
ListNode* mergeKLists4(vector<ListNode*>& lists) {
for (auto node: lists) {
if (node) q.push({node->val, node});
}
ListNode head, *tail = &head;
while (!q.empty()) {
auto f = q.top(); q.pop();
tail->next = f.ptr;
tail = tail->next;
if (f.ptr->next) q.push({f.ptr->next->val, f.ptr->next});
}
return head.next;
}
void Solution23test()
{
ListNode* p1= new ListNode;
ListNode* p2= new ListNode;
ListNode* p3= new ListNode;
p1->val = 1;
p1->next = p2;
p2->val = 4;
p2->next = p3;
p3->val = 5;
p3->next = NULL;
ListNode* L1= new ListNode;
ListNode* L2= new ListNode;
ListNode* L3= new ListNode;
L1->val = 1;
L1->next = L2;
L2->val = 3;
L2->next = L3;
L3->val = 4;
L3->next = NULL;
ListNode* M1= new ListNode;
ListNode* M2= new ListNode;
M1->val = 2;
M1->next = M2;
M2->val = 6;
M2->next = NULL;
Solution23 sl23;
vector<ListNode*>input = {p1,L1,M1};
ListNode * p = sl23.mergeKLists3(input);
while(p != NULL)
{
cout<<p->val<<endl;
p = p->next;
}
}