静态分析C语言生成函数调用关系的利器——GCC
大纲
- 准备工作
- GCC生成单文件调用关系VCG
- 将VCG转为Dot
- 绘制图片
- 绘制全景图
- 代码
- 参考资料
在《静态分析C语言生成函数调用关系的利器——cally和egypt》中我们介绍了如何使用GCC生成RTL文件,然后再借助cally和egypt来分析出调用关系的方法。GCC自身有命令可以生成代码内部的调用关系,即-fcallgraph-info参数。
Makes the compiler output callgraph information for the program, on a per-object-file basis. The information is generated in the common VCG format.
gcc some.c -fcallgraph-info
它会生成后缀是ci的VCG格式文件。然后我们使用graph-easy将其转换为dot格式,最后使用graphviz将其绘制出来。
我们还是以libevent的为例。
准备工作
graph-easy 用于将vcg文件转换为dot格式
sudo apt install libgraph-easy-perl
因为脚本是Python写的,且会依赖第三方库,于是会使用《管理Python虚拟环境的脚本》介绍的工具构建一个虚拟环境并安装相应依赖。
source env.sh init
soure env.sh enter
source env.sh install pydot
GCC生成单文件调用关系VCG
gcc `find . -regextype posix-extended -regex '^./[^/]*\.c$' ! -name 'wepoll.c' ! -name 'win32select.c' ! -name 'evthread_win32.c' ! -name 'buffer_iocp.c' ! -name 'bufferevent_async.c' ! -name 'arc4random.c' ! -name 'event_iocp.c' ! -name 'bufferevent_mbedtls.c'` \
./test/test-time.c \
-I./build/include/ -I./include -I./ \
-L./build/lib/ -lcrypto -lssl \
-DLITTLE_ENDIAN -D__clang__ \
-UD_WIN32 -UDMBEDTLS_SSL_RENEGOTIATION \
-fcallgraph-info
将VCG转为Dot
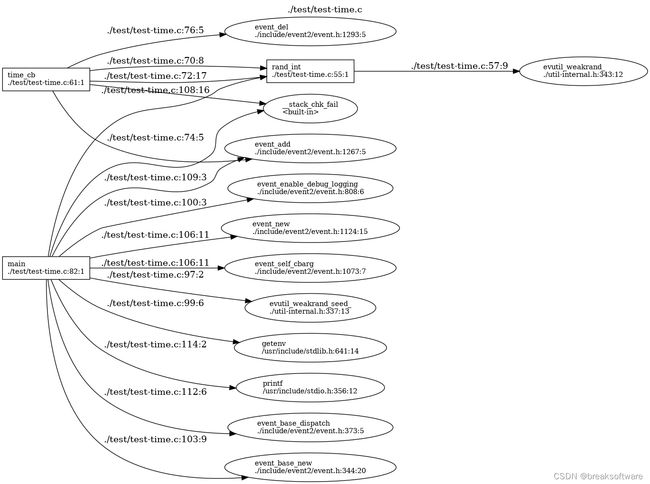
graph-easy a-test-time.ci --as_dot > a-test-time.dot
绘制图片
dot -Grankdir=LR -T png a-test-time.dot -o test_time.png
绘制全景图
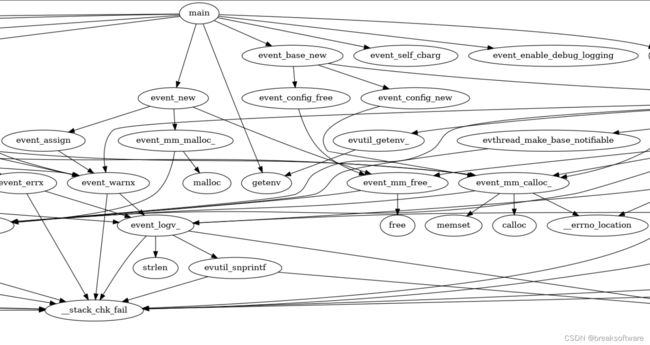
因为GCC生成VCG文件只是针对单个文件的,不能构成全景图。这个时候就需要我们自己手撸一点代码,让这些信息合并。
import pydot
class CallgraphInfoCombiner(object):
def __init__(self, dot_folder, function_name, output_file) -> None:
self._dot_folder = dot_folder
self._funciont_name = function_name
self._output_file = output_file
self._callee = dict()
self._graph = pydot.Dot("callgraph-info-combiner", graph_type="graph", bgcolor="white")
pass
def analyze(self, include_private=False):
for file in os.listdir(self._dot_folder):
self._read_dot(self._dot_folder + "/" + file)
nodes_in_graph = set()
if self._funciont_name in self._callee:
self._add_node_and_edge(self._funciont_name, nodes_in_graph, include_private)
self._graph.write_dot(self._output_file + ".dot")
self._graph.write_png(self._output_file + ".png")
def _add_node_and_edge(self, node_name, nodes_in_graph, include_private=False):
if include_private and node_name.startswith('"') and node_name.endswith('"'):
return
if node_name not in nodes_in_graph:
print("add node: " + node_name)
self._graph.add_node(pydot.Node(node_name))
nodes_in_graph.add(node_name)
if node_name in self._callee:
for callee in self._callee[node_name]:
if include_private == False and callee.startswith('"') and callee.endswith('"'):
continue
if callee not in nodes_in_graph:
self._add_node_and_edge(callee, nodes_in_graph, include_private)
self._graph.add_edge(pydot.Edge(node_name, callee))
print("add edge: " + node_name + " -> " + callee)
def _read_dot(self, dot_file):
graphs = pydot.graph_from_dot_file(dot_file)
for graph in graphs:
for edge in graph.get_edges():
if edge.get_source() in self._callee:
self._callee[edge.get_source()].add(edge.get_destination())
else:
self._callee[edge.get_source()] = {edge.get_destination()}
上面的代码会分析DOT文件,所以在使用前需要将VCG转换成DOT文件。
import os
import sys
import subprocess
class Vcg2Dot(object):
def __init__(self, vcg_file, dot_file):
self.vcg_file = vcg_file
self.dot_file = dot_file
def vcg_to_dot(self):
print("graph-easy --input=" + self.vcg_file + " -as=dot --output=" + self.dot_file)
subprocess.run("graph-easy --input=" + self.vcg_file + " -as=dot --output=" + self.dot_file, shell=True)
class VcgFiles2Dot(object):
def __init__(self, vcg_folder, dot_folder):
self.vcg_folder = vcg_folder
self.dot_folder = dot_folder
def vcg_to_dot(self):
if not os.path.exists(self.dot_folder):
os.makedirs(self.dot_folder)
for file in os.listdir(self.vcg_folder):
vcg_to_dot = Vcg2Dot(self.vcg_folder + file, self.dot_folder + file + ".dot")
vcg_to_dot.vcg_to_dot()
然后我们只要针对这个脚本传vcg文件目录、起始函数和输出的文件名,即可整合出调用关系。
python callgraph-info-combiner.py ./sample/ci/ main libevent
代码
https://github.com/f304646673/tools/tree/main/callgraph-info-combiner
参考资料
- https://gcc.gnu.org/onlinedocs/gcc/Developer-Options.html
- https://pypi.org/project/pydot/