二叉搜索树的模拟实现
文章目录
- 二叉搜索树概念
- 二叉搜索树的实现
-
- 二叉搜索树的结点
- 二叉搜索树的查找
- 二叉搜索树的插入
- 二叉搜索树的删除
- 二叉搜索树其他成员函数
- 二叉搜索树的性能分析
二叉搜索树概念
二叉搜索树又称二叉排序树,具有以下性质的二叉树:
- 若它的左子树不为空,则左子树上所有节点的值都小于根节点的值
- 若它的右子树不为空,则右子树上所有节点的值都大于根节点的值
- 它的左右子树也分别为二叉搜索树
如图就是一棵二叉搜索树
二叉搜索树的实现
二叉搜索树的结点
二叉搜索树的结点和二叉树的结点类似,有两个指针分别指向左右子树,还有一个存储数据的成员变量。
template <class K>
struct BSTreeNode
{
BSTreeNode<K>* _left;
BSTreeNode<K>* _right;
K _key;
BSTreeNode(const K& key)
:_left(nullptr)
, _right(nullptr)
, _key(key)
{}
};
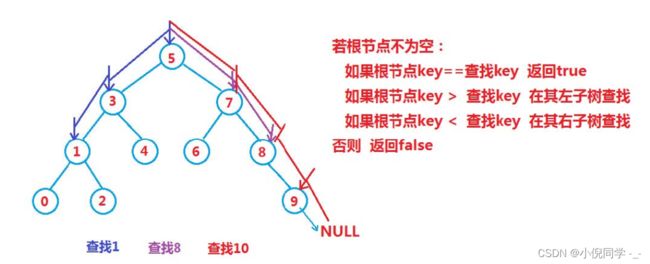
二叉搜索树的查找
Node* Find(const K& key)
{
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
// 根结点<查找key,在右子树查找
if (cur->_key < key)
{
cur = cur->_right;
}
// 根结点>查找key,在左子树查找
else if (cur->_key>key)
{
cur = cur->_left;
}
// 找到返回key
else
{
return cur;
}
}
return nullptr;
}
递归版本
Node* FindR(const K& key)
{
return _FindR(_root, key);
}
Node* _FindR(Node* root, const K& key)
{
if (root == nullptr)
return nullptr;
if (root->_key > key)
{
return _FindR(root->_left, key);
}
else if (root->_key < key)
{
return _FindR(root->_right, key);
}
else
{
return root;
}
}
二叉搜索树的插入
插入过程:
- 如果树为空,则直接插入。
- 树不空,按二叉搜索树性质查找插入位置,插入新节点。
实现代码
bool Insert(const K& key)
{
// 树为空的情况
if (_root == nullptr)
{
_root = new Node(key);
return true;
}
// 先找到指定位置再插入
Node* parent = nullptr;// 记录结点的父结点
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_key < key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_right;
}
else if (cur->_key>key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_left;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
// 将结点插入二叉搜索树中
cur = new Node(key);
if (parent->_key < cur->_key)
{
parent->_right = cur;
}
else
{
parent->_left = cur;
}
return true;
}
递归版本
bool InsertR(const K& key)
{
return _InsertR(_root, key);
}
bool _InsertR(Node*& root, const K& key)
{
if (root == nullptr)
{
root = new Node(key);
return true;
}
else
{
if (root->_key < key)
{
_InsertR(root->_right, key);
}
else if (root->_key>key)
{
_InsertR(root->_left, key);
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
}
二叉搜索树的删除
二叉搜索树的删除是二叉搜索树中最为复杂的部分,需要分多种情况考虑。
先找到要删除的结点,如果没有就直接返回,找到后需要分以下四种情况讨论
- 要删除的结点无孩子结点
- 要删除的结点只有左孩子结点
- 要删除的结点只有右孩子结点
- 要删除的结点有左、右孩子结点
其中第一种情况可以和第二种或第三种合并
情况二:删除该结点且使被删除节点的双亲结点指向被删除节点的左孩子结点
情况三:删除该结点且使被删除节点的双亲结点指向被删除结点的右孩子结点
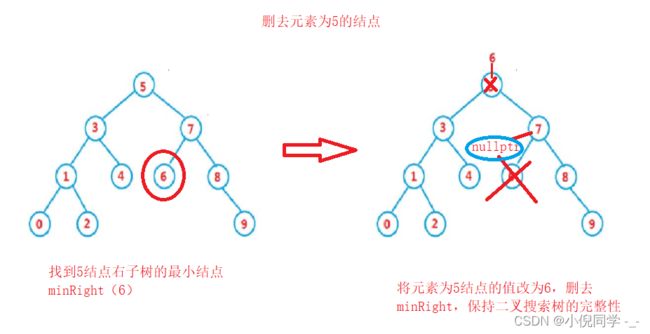
情况四:在它的右子树中寻找中序下的第一个结点(关键码最小),用它的值填补到被删除节点中,再来处理该结点的删除问题。
bool Erase(const K& key)
{
Node* parent = nullptr;
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_key < key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_right;
}
else if (cur->_key>key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_left;
}
else
{
// 右子树为空的情况
if (cur->_right == nullptr)
{
if (_root == cur)// 结点为根结点
{
_root = _root->_left;
}
else
{
// 让该结点的父结点指向该结点的左子树
if (parent->_left == cur)
{
parent->_left = cur->_left;
}
else
{
parent->_right = cur->_left;
}
}
delete cur;
return true;
}
// 左子树为空的情况
else if (cur->_left == nullptr)
{
if (_root == cur)
{
_root = _root->_right;
}
else
{
// 让该结点的父结点指向该结点的右子树
if (parent->_left == cur)
{
parent->_left = cur->_right;
}
else
{
parent->_right = cur->_right;
}
}
delete cur;
return true;
}
// 左右子树都不为为空的情况
else
{
// 找到右树最小节点去替代删除
Node* minRightParent = cur;
// 找到右树最小节点
Node* minRight = cur->_right;
while (minRight ->_left)
{
minRightParent = minRight;
minRight = minRight->_left;
}
// 删去结点,保持二叉搜索树的完整性
cur->_key = minRight->_key;
if (minRightParent->_left == minRight)
{
minRightParent->_left = minRight->_right;
}
else
{
minRightParent->_right = minRight->_right;
}
delete minRight;
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
递归版本
bool EraseR(const K& key)
{
return _EraseR(_root, key);
}
bool _EraseR(Node*& root, const K& key)
{
if (root == nullptr)
return false;
if (root->_key < key)
{
return _EraseR(root->_right, key);
}
else if (root->_key>key)
{
return _EraseR(root->_left, key);
}
else
{
Node* del = root;
if (root->_left == nullptr)
{
root = root->_right;
}
else if (root->_right == nullptr)
{
root = root->_left;
}
else
{
Node* minRight = root->_right;
while (minRight->_left)
{
minRight = minRight->_left;
}
root->_key = minRight->_key;
// 转换成递归在右子树种删除最小节点
return _EraseR(root->_right, minRight->_key);
}
delete del;
return true;
}
}
二叉搜索树其他成员函数
拷贝构造
BSTree(const BSTree& t)
{
_root = _Copy(t._root);
}
Node* _Copy(Node* root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
{
return nullptr;
}
Node* newRoot = new Node(root->_key);
newRoot->_left = _Copy(root->_left);
newRoot->_right = _Copy(root->_right);
return newRoot;
}
赋值重载
BSTree<k>& operator=(BSTree<K>& t)
{
std::swap(_root, t._root);
return *this;
}
打印
void InOrder()
{
_InOrder(_root);
cout << endl;
}
void _InOrder(Node* root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
{
return;
}
_InOrder(root->_left);
cout << root->_key << " ";
_InOrder(root->_right);
}
析构函数
~BSTree()
{
_Destroy(_root);
}
void _Destroy(Node* root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
return;
_Destroy(root->_left);
_Destroy(root->_right);
delete root;
}
二叉搜索树的性能分析
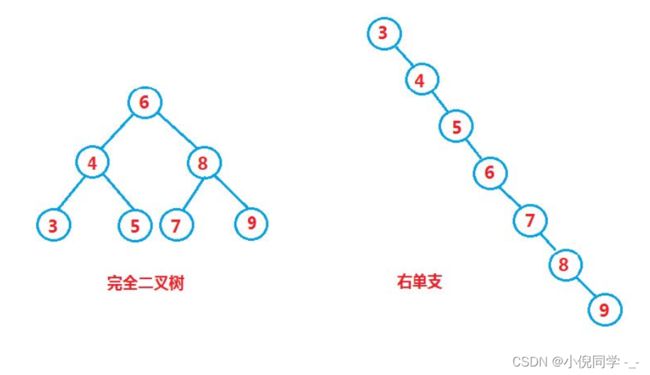
插入和删除操作都必须先查找,查找效率代表了二叉搜索树中各个操作的性能。
对有n个结点的二叉搜索树,若每个元素查找的概率相等,则二叉搜索树平均查找长度是结点在二叉搜索树的深度的函数,即结点越深,则比较次数越多。
但对于同一个关键码集合,如果各关键码插入的次序不同,可能得到不同结构的二叉搜索树,如图所示