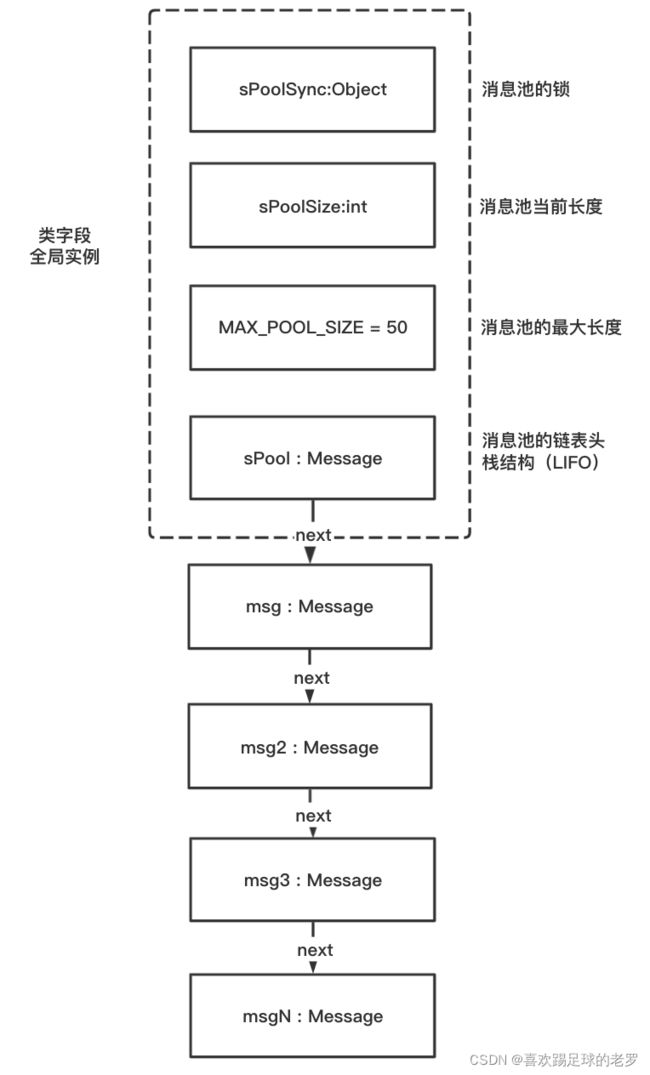
Message的消息池(sPool)
关键总结
1、消息池缓存有可重复使用的消息实例,避免过多的创建与回收消息实例
2、消息池是一个栈(LIFO/FILO=后进先出/先进后出)的数据结构,具体的数据存放是采用了链表方式
3、消息池一开始是空的,需要主动添加消息进入缓存池,然后供后续的取出与使用,消息池的长度是有限制的,这样可以避免缓存过多的对象,导致内存占用过多,尽可能的避免内存泄漏
3、消息入队列时会被设置为已经在使用的状态,消息从消息列表取出被消费后会放入消息池,大多数情况下我们是不需要调Message的回收方法,把消息存入消息池的
5、消息发出去后立刻调用消息的回收方法,可有能会触发"java.lang.IllegalStateException: This message cannot be recycled because it is still in use" 的异常
消息池的数据结构
消息添加到缓存池
Message提供对象方法recycle() 把对象自己放到缓存池中,对象放到消息池后就保存有对象的引用,所以JVM不会回收放到缓存池的对象
放到缓存池的主要操作步骤是
- 清空消息的内容(成员对象变量置空,基础类型变量置为零,状态恢复默认值等)
- 对缓存池加锁(线程安全操作)
- 缓存的消息对象入栈(next引用赋值为当前栈顶,当前栈顶赋值为当前缓存的消息对象),缓存元素大小加1
//回收利用,即入缓存池
public void recycle() {
//这里的状态我们后面再讲
if (isInUse()) {
if (gCheckRecycle) {
throw new IllegalStateException("This message cannot be recycled because it "
+ "is still in use.");
}
return;
}
recycleUnchecked();
}
//这个包访问限制,我们调不到该方法的,如方法的注释所说当消息从消息列表取出来消息后,looper会把消息回收(调用该方法,让消息入缓存池)
/**
* Recycles a Message that may be in-use.
* Used internally by the MessageQueue and Looper when disposing of queued Messages.
*/
void recycleUnchecked() {
// Mark the message as in use while it remains in the recycled object pool.
// Clear out all other details.
flags = FLAG_IN_USE;
what = 0;
arg1 = 0;
arg2 = 0;
obj = null;
replyTo = null;
sendingUid = UID_NONE;
workSourceUid = UID_NONE;
when = 0;
target = null;
callback = null;
data = null;
synchronized (sPoolSync) {
if (sPoolSize < MAX_POOL_SIZE) {
//指向当前的栈顶元素
next = sPool;
//栈顶元素替换为当前入缓存的消息对象
sPool = this;
//size + 1
sPoolSize++;
}
}
}
/**
* Run the message queue in this thread. Be sure to call
* {@link #quit()} to end the loop.
*/
public static void loop() {
final Looper me = myLooper();
if (me == null) {
throw new RuntimeException("No Looper; Looper.prepare() wasn't called on this thread.");
}
if (me.mInLoop) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Loop again would have the queued messages be executed"
+ " before this one completed.");
}
me.mInLoop = true;
final MessageQueue queue = me.mQueue;
// Make sure the identity of this thread is that of the local process,
// and keep track of what that identity token actually is.
Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
final long ident = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
// Allow overriding a threshold with a system prop. e.g.
// adb shell 'setprop log.looper.1000.main.slow 1 && stop && start'
final int thresholdOverride =
SystemProperties.getInt("log.looper."
+ Process.myUid() + "."
+ Thread.currentThread().getName()
+ ".slow", 0);
boolean slowDeliveryDetected = false;
for (;;) {
// 取出消息
Message msg = queue.next(); // might block
if (msg == null) {
// No message indicates that the message queue is quitting.
return;
}
try {
// 消费消息
msg.target.dispatchMessage(msg);
if (observer != null) {
observer.messageDispatched(token, msg);
}
dispatchEnd = needEndTime ? SystemClock.uptimeMillis() : 0;
} catch (Exception exception) {
if (observer != null) {
observer.dispatchingThrewException(token, msg, exception);
}
throw exception;
} finally {
ThreadLocalWorkSource.restore(origWorkSource);
if (traceTag != 0) {
Trace.traceEnd(traceTag);
}
}
if (logSlowDelivery) {
if (slowDeliveryDetected) {
if ((dispatchStart - msg.when) <= 10) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Drained");
slowDeliveryDetected = false;
}
} else {
if (showSlowLog(slowDeliveryThresholdMs, msg.when, dispatchStart, "delivery",
msg)) {
// Once we write a slow delivery log, suppress until the queue drains.
slowDeliveryDetected = true;
}
}
}
....删除了很多代码
// 回收消息
msg.recycleUnchecked();
}
}
即意味着我们在使用消息机制时,消息机制的框架里会帮我们缓存消息,我们只要在需要的地方调Message.obtain获取缓存的消息来使用就可以了!
如果要手动的回收消息,即调Message.recycle方法时,要考虑上下文操作中消息实例会不会存在跨线程的处理,即回收消息时,消息是不是还没有被消费的情况。
Android消息机制是这样做的,消息入队列时给消息设置为已经在使用的状态,于确保消息在被出队列前是不能调回收的。
如下是个错误的示例,消息被发送后,立刻调用消息的recycle方法,会触发到”This message cannot be recycled because it is still in use”的异常
2021-12-23 15:25:32.277 10716-10716/com.sdk.sdktestdemo E/AndroidRuntime: FATAL EXCEPTION: main
Process: com.sdk.sdktestdemo, PID: 10716
java.lang.IllegalStateException: This message cannot be recycled because it is still in use.
at android.os.Message.recycle(Message.java:311)
at com.sdk.sdktestdemo.MainActivity.sendMessageTest(MainActivity.java:66)
at com.sdk.sdktestdemo.MainActivity$1.onClick(MainActivity.java:27)
at android.view.View.performClick(View.java:7441)
at com.google.android.material.button.MaterialButton.performClick(MaterialButton.java:1119)
at android.view.View.performClickInternal(View.java:7418)
at android.view.View.access$3700(View.java:835)
at android.view.View$PerformClick.run(View.java:28676)
at android.os.Handler.handleCallback(Handler.java:938)
at android.os.Handler.dispatchMessage(Handler.java:99)
at android.os.Looper.loopOnce(Looper.java:201)
at android.os.Looper.loop(Looper.java:288)
at android.app.ActivityThread.main(ActivityThread.java:7842)
at java.lang.reflect.Method.invoke(Native Method)
at com.android.internal.os.RuntimeInit$MethodAndArgsCaller.run(RuntimeInit.java:548)
at com.android.internal.os.ZygoteInit.main(ZygoteInit.java:1003)
示例代码
package com.sdk.sdktestdemo;
import androidx.annotation.NonNull;
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.os.Handler;
import android.os.HandlerThread;
import android.os.Message;
import android.util.Log;
import android.view.View;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
// Used to load the 'native-lib' library on application startup.
// static {
// System.loadLibrary("native-lib");
// }
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
this.findViewById(R.id.bt_start).setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
sendMessageTest(HANDLER_THREAD_A.getHandler(), "发给A的第一个消息");
}
});
initHandlerThread();
}
/**
* A native method that is implemented by the 'native-lib' native library,
* which is packaged with this application.
*/
public native String stringFromJNI();
public static HandlerThreadEx HANDLER_THREAD_A;
public static void initHandlerThread() {
HANDLER_THREAD_A = new HandlerThreadEx("A");
HANDLER_THREAD_A.setMessageHandler(new HandlerThreadEx.MessageHandler() {
@Override
public void handler(Handler handler, Message msg) {
// 这里是handler处理其绑定的消息
Log.d("HandlerTest", String.format("%s", "这里是HANDLER_THREAD_A的handler在处理消息"));
handleMessageTest(msg);
sendMessageTest(handler, "测试");
}
});
HANDLER_THREAD_A.start();
}
public static int S_MSG_ID = 0;
public static void sendMessageTest(Handler handler, String msgInfo) {
int msgId = S_MSG_ID++;
Message message = Message.obtain();
message.what = msgId;
message.obj = msgInfo;
handler.sendMessageDelayed(message, 5 * 1000L);
//消息一发出去,就调消息的回收方法,会触发"java.lang.IllegalStateException: This message cannot be recycled because it is still in use" 的异常
message.recycle();
Log.d("HandlerTest", String.format("thread:%s >>> 发消息, msgId:%d, info:%s", Thread.currentThread().getName(), msgId, msgInfo));
}
public static void handleMessageTest(Message msg) {
Log.d("HandlerTest", String.format("thread:%s <<< 处理消息, hashcode: %d, msgId:%d, info:%s", Thread.currentThread().getName(), msg.hashCode(), msg.what, msg.obj));
}
}
class HandlerThreadEx extends HandlerThread {
private Handler mHandler;
private MessageHandler mMessageHandler;
public HandlerThreadEx(String name) {
super(name);
}
public HandlerThreadEx(String name, int priority) {
super(name, priority);
}
@Override
protected void onLooperPrepared() {
super.onLooperPrepared();
Log.d("HandlerTest", String.format("onLooperPrepared, thread:%s", Thread.currentThread().getName()));
mHandler = new Handler(getLooper()) {
@Override
public void handleMessage(@NonNull Message msg) {
if (mMessageHandler != null) {
mMessageHandler.handler(this, msg);
}
}
};
}
public Handler getHandler() {
return mHandler;
}
public void setMessageHandler(MessageHandler mMessageHandler) {
this.mMessageHandler = mMessageHandler;
}
public interface MessageHandler {
void handler(Handler handler, Message msg);
}
}
消息从缓存池取出
Message提供类方法(public static Message obtain),取出缓存池当中的栈顶元素供使用
主要操作步骤是
- 对缓存池锁对象加锁(保证线程安全)
- 获取的对象赋值为当前栈顶元素
- 当前栈元素赋值为当前栈顶元素的next,即新栈顶“指针”往下移一个单位
- 旧栈顶元素/获取的对象/出栈的元素的next置为空,即链表关系断开,出栈操作完成
- 消空出栈元素的使用状态(清空Flag值)
- 缓存池size减一
- 返回之前的栈顶元素
/**
* Return a new Message instance from the global pool. Allows us to
* avoid allocating new objects in many cases.
*/
public static Message obtain() {
synchronized (sPoolSync) {
if (sPool != null) {
//2.
Message m = sPool;
//3. 当前栈元素赋值为当前栈顶元素的next,即栈顶“指针”往下移一个单位
sPool = m.next;
//4. 旧栈顶元素/获取的对象/出栈的元素的next置为空,即链表关系断开,出栈操作完成
m.next = null;
//5.
m.flags = 0; // clear in-use flag
//6.
sPoolSize--;
//7.
return m;
}
}
return new Message();
}
消息的缓存状态
Message类中有一个int类型的旗标变量成员(flags)顾名思义,利用整型变量的二进制存储空间的某些位是否被置为1为表示某个状态已经为true,0表示某个状态为false;
目前代码中,flags第0位标示是否在使用状态,第1位标示是否为异步消息(异步消息跟同步消息后续找机会再整理与分享)
/** If set message is in use.
* This flag is set when the message is enqueued and remains set while it
* is delivered and afterwards when it is recycled. The flag is only cleared
* when a new message is created or obtained since that is the only time that
* applications are allowed to modify the contents of the message.
*
* It is an error to attempt to enqueue or recycle a message that is already in use.
*/
/*package*/ static final int FLAG_IN_USE = 1 << 0;
/** If set message is asynchronous */
/*package*/ static final int FLAG_ASYNCHRONOUS = 1 << 1;
/** Flags to clear in the copyFrom method */
/*package*/ static final int FLAGS_TO_CLEAR_ON_COPY_FROM = FLAG_IN_USE;
@UnsupportedAppUsage
/*package*/ int flags;
flags设置FLAG_IN_USE的地方有两个,一个是recycleUnchecked方法,还有markInUse方法,设置FLAG_IN_USE主要是明确消息已经在使用或已经入了缓存池,不能再次调Message的recycle,让消息入缓存池。如recycle方法的注释也是有说明的。
/**
* Return a Message instance to the global pool.
*
* You MUST NOT touch the Message after calling this function because it has
* effectively been freed. It is an error to recycle a message that is currently
* enqueued or that is in the process of being delivered to a Handler.
*
*/
public void recycle() {
if (isInUse()) {
if (gCheckRecycle) {
throw new IllegalStateException("This message cannot be recycled because it "
+ "is still in use.");
}
return;
}
recycleUnchecked();
}
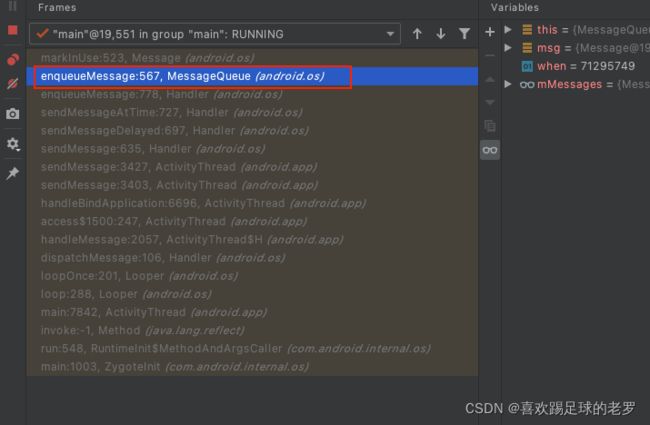
“the process of being delivered to a Handler” - 这里的意思是当我们通过handler发送一个消息,消息入消息队列的时候,消息队列会调消息的markUse方法,将消息标示为在使用当中,如下为调markUse方法时调用栈
参考文档
- Android Message解析
- 揭秘 Android 消息机制之同步屏障:target==null ?
- Android Studio: 查看android源代码
- 一个步骤教你调试Android系统源代码