《实战 Linux Socket 编程》Warren W.Gay 图解Key-point学习笔记-1
第一章 套接口简介
————————本文为作者原创,转载请注明出处————————
此系列为本人的学习笔记,欢迎大家在留言区对概念进行拓展延伸、纠错讨论!
注:所有的例子程序均来自于原书,笔者亲自录入,如果有读者有全书源码链接,也欢迎在评论区分享给其他读者!!!
1.1简要的历史回顾
1.定义套接口:代表通信线路中的端点(端点之间通信线路网络);
2.与管道的根本区别:套接口允许进程双向通信
1.4创建套接口
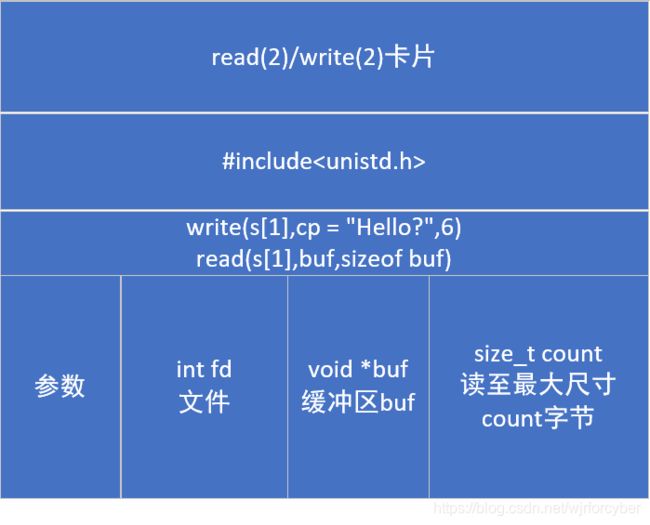
1.本节主要讲解socketpair(2)的使用方法,并给出了例子程序(清单1.1),运行即可出结果;
2.关于socketpair(2)参数:AF_UNIX = AF_LOCAL;

示例及运行结果:
/*Testfile 1.1
socketpair(2)func ex*/
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
int main(int argc,char **argv){
int z;
int s[2];
z = socketpair(AF_LOCAL,SOCK_STREAM,0,s);
if(z == -1){
fprintf(stderr,"%s:socketpair(AF_LOCAL,SOCK_STREAM,0,s)\n",strerror(errno));
return 1; /*failed*/
}
printf("s[0] = %d;\n",s[0]);
printf("s[1] = %d;\n",s[1]);
system("netstat --unix -p");
return 0;
}
1.5用套接口实现I/O
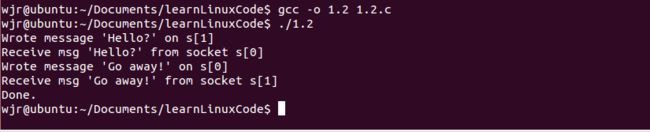
1.例子程序(清单1.2)套接口可以实现双向通信,且关闭方式与文件相同;
示例及运行结果:
/*Testfile 1.1
socketpair(2)func ex*/
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
int main(int argc,char **argv){
int z;
int s[2]; /*套接口对*/
char *cp; /*工作指针*/
char buf[80]; /*buffer*/
/*生成本地套接口*/
z = socketpair(AF_LOCAL,SOCK_STREAM,0,s);
if(z == -1){
fprintf(stderr,"%s:socketpair(AF_LOCAL,SOCK_STREAM,0,s)\n",strerror(errno));
return 1; /*failed*/
}
/*s[1]写入信息*/
z = write(s[1],cp = "Hello?",6);
if(z<0){
fprintf(stderr,"%s:write(%d,\"%s\",%d)\n",strerror(errno),s[1],cp,strlen(cp));
return 2;
} /*写操作失败*/
printf("Wrote message '%s' on s[1]\n",cp);
/*从s[0]读消息*/
z = read(s[0],buf,sizeof buf);
if(z<0){
fprintf(stderr,"%s:read(%d,buf,%d)\n",strerror(errno),s[0],sizeof buf);
return 3;
} /*读操作失败*/
/*报告接收的消息*/
buf[z] = 0; /*NULL 终止符*/
printf("Receive msg '%s' from socket s[0]\n",buf);
/*s[0]向s[1]发送应答消息*/
z = write(s[0],cp="Go away!",8);
if(z<0){
fprintf(stderr,"%s:write(%d,\"%s\",%d)\n",strerror(errno),s[0],cp,strlen(cp));
return 4;
} /*写操作失败*/
printf("Wrote message '%s' on s[0]\n",cp);
/*从s[1]读消息*/
z = read(s[1],buf,sizeof buf);
if(z<0){
fprintf(stderr,"%s:read(%d,buf,%d)\n",strerror(errno),s[1],sizeof buf);
return 3;
} /*读操作失败*/
/*报告s[0]接收的消息*/
buf[z] = 0;
printf("Receive msg '%s' from socket s[1]\n",buf);
/*关闭套接字*/
close(s[0]);
close(s[1]);
puts("Done.");
return 0;
}
1.6关闭套接口
1.close终止的是两个方向,而需要shutdown对套接口进行半关闭;
2.shutdown(2);
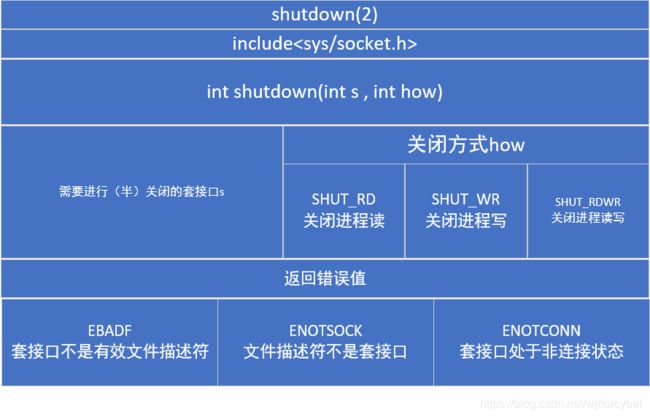
3.关闭向套接口的写入后,向远程接口发送文件结束标识符但仍然可以接受远程套接口发送的确认消息,同时访问计数清零;
4.处理复制套接口:dup(2)或dup2(2)复制套接口文件描述符后,必须再次使用close(2)函数关闭,有一个还在运行就不能关闭套接口,但如果使用shutdown就完全避免了这个问题;
5.关闭套接口的读入将忽视任何等待读入的数据,目的是为满足某些协议的要求和调试程序;
6.只能在已连接的套接口上调用shutdown(2);
1.7客户/服务器应用编程
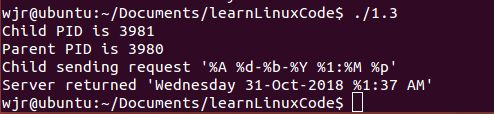
(清单1.3)示例及运行结果:
/*Listing 1.3 使用socketpair(2);fork(2)客户、服务器示例*/
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#ifndef SHUT_WR
#define SHUT_RD 0
#define SHUT_WR 1
#define SHUT_RDWR 2
#endif
/*主程序*/
int main(int argc,char **argv){
int z;
int s[2];
char *msgp; /*消息指针*/
int mlen; /*消息长度*/
char buf[80]; /*工作缓冲区*/
pid_t chpid; /*子进程PID*/
/*生成本地套接口对*/
z = socketpair(AF_LOCAL,SOCK_STREAM,0,s);
if(z==-1){
fprintf(stderr,"%s:socketpair(2)\n",strerror(errno));
exit(1);
}
/*fork()调用后生成两个进程*/
if((chpid = fork()) == (pid_t)-1){
/*fork failed*/
fprintf(stderr,"%s:fork(2)\n",strerror(errno));
exit(1);
}
else if(chpid == 0){
/*子进程*/
char rxbuf[80]; /*接收缓冲区*/
printf("Parent PID is %ld\n",(long)getppid());
close(s[0]);
s[0]=-1;
/*形成消息并记录长度*/
msgp = "%A %d-%b-%Y %1:%M %p";
mlen = strlen(msgp);
printf("Child sending request '%s'\n",msgp);
fflush(stdout);
/*向服务器写入请求*/
z = write(s[1],msgp,mlen);
if(z<0){
fprintf(stderr,"%s:write(2)\n",strerror(errno));
exit(1);
}
/*关闭套接口的写端*/
if(shutdown(s[1],SHUT_WR)==-1){
fprintf(stderr,"%s:shutdown(2)\n",strerror(errno));
exit(1);
}
/*接受来自服务器的内容*/
z = read(s[1],rxbuf,sizeof rxbuf);
if(z<0){
fprintf(stderr,"%s:read(2)\n",strerror(errno));
exit(1);
}
/*将来自服务器的消息末尾加入一个空字节*/
rxbuf[z] = 0;
/*报告结果*/
printf("Server returned '%s'\n",rxbuf);
fflush(stdout);
close(s[1]);
}
else{
/*父进程服务器*/
int status;
char txbuf[80];
time_t td;
printf("Child PID is %ld\n",(long)chpid);
fflush(stdout);
close(s[1]);
s[1] = -1;
/*等待来自客户的需求*/
z = read(s[0],buf,sizeof buf);
if(z<0){
fprintf(stderr,"%s:read(2)\n",strerror(errno));
exit(1);
}
/*将来自客户的消息末尾加入一个空字节*/
buf[z]=0;
/*根据接收的请求实现服务器功能*/
time(&td);/*获取时间*/
strftime(txbuf,sizeof txbuf,buf,localtime(&td));
/*结果发送给客户*/
z = write(s[0],txbuf,strlen(txbuf));
if(z<0){
fprintf(stderr,"%s:write(2)\n",strerror(errno));
exit(1);
}
/*关闭套接口*/
close(s[0]);
/*等待子进程退出*/
waitpid(chpid,&status,0);
}
return 0;
}