【C项目】顺序表
简介:本系列博客为C项目系列内容,通过代码来具体实现某个经典简单项目
适宜人群:已大体了解C语法同学
作者留言:本博客相关内容如需转载请注明出处,本人学疏才浅,难免存在些许错误,望留言指正
作者博客链接:睡觉待开机
引言:
一般来说,顺序表作为基本的数据结构类型是不需要我们进行实现的,因为一些高级语言比如C++或者java直接具备的这样的内置数据结构,但是为了深入了解顺序表的底层,这里也是建议自己动手用C写一下,一是便于复习C学到的知识,二是更加深入了解顺序表的实现底层逻辑。
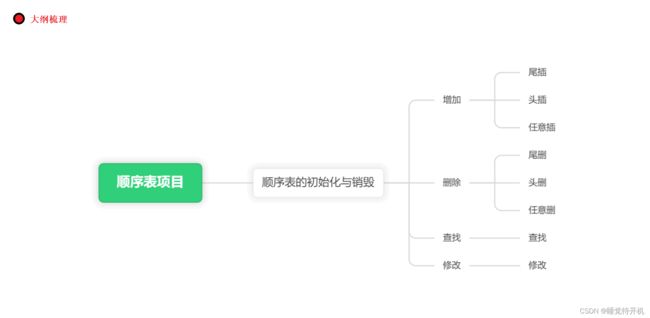
1.顺序表思路
为了明晰顺序表的实现思路,我们首先来铺垫一下我到底要在怎么写一个顺序表。
首先啥是顺序表?
一种线性表,底层是数组,只不过这个顺序表所谓的数组不单单可以放各种类型的数据,还可以有各种接口,包括增删查改操作的接口等等。
注:线性表的概念:逻辑结构上是连续的,物理结构不一定连续的数据结构称为线性表。
顺序表的概念:逻辑结构上是连续的,物理结构上也是连续的,底层是以数组为实现,有着增删查改各种接口的基本数据组织结构。
那么我就可以大致明白了我要写一个顺序表,这个顺序表实现了一些功能。
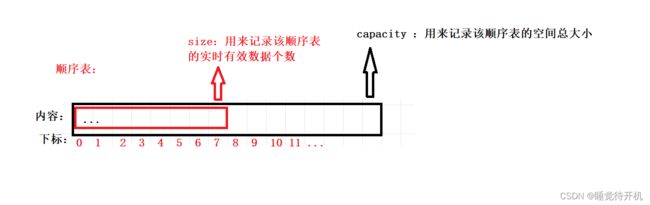
首先我要写一个顺序表的话,要有一个顺序表的大体类型吧,所以我就写了一个动态顺序表的类型
typedef int SLDateType;
typedef struct SeqList
{
SLDateType* arr;
int size;
int capacity;
}SL;
然后我想要在这个顺序表中实现各种功能(接口),那这个顺序表首先得初始化吧,有初始化顺序表了那肯定对应着销毁这个接口,自然也需要顺序表销毁,然后还要有头插尾插任意插入这个”增“的功能,还有有头删尾删任意删的这个”删“的共能,然后还要有查找功能,还要修改功能,那么我针对该顺序表的每个接口专门搞一个函数
为了便于代码书写,我将各种接口以及顺序表类型本身定义在SeqList.h头文件中进行声明与定义:
#pragma once
#include2.具体实现各种接口
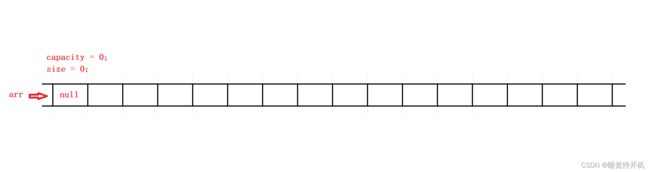
顺序表初始化接口:
void SLInit(SL* ps)
{
assert(ps);
ps->arr = NULL;
ps->capacity = ps->size = 0;
}
顺序表销毁接口:
void SLDestroy(SL* ps)
{
assert(ps);
if (ps->arr)
{
free(ps->arr);
}
ps->arr = NULL;
ps->capacity = ps->size = 0;
}
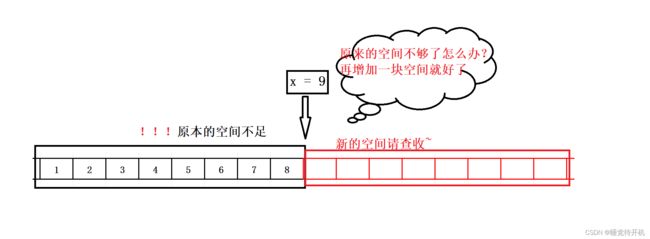
顺序表扩容接口:
void SLCheckCapacity(SL* ps)
{
assert(ps);
if (ps->capacity == ps->size)
{
//小问题:刚开始的时候,sl->capacity是0值
int newcapacity = ps->capacity == 0 ? 4 : 2 * ps->capacity;
SLDateType* temp = realloc(ps->arr,sizeof(SLDateType)*newcapacity);
if (!temp)
{
perror("realloc fail!");
return;
}
ps->arr = temp;
ps->capacity = newcapacity;
}
}
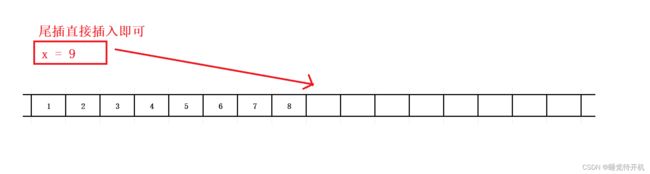
顺序表插入接口
void SLPushBack(SL* ps,SLDateType x)
{
assert(ps);
//1.空间不足需要扩大容量
//2.空间足够直接放入数据
SLCheckCapacity(ps);
ps->arr[ps->size] = x;
ps->size++;
}
void SLPushFront(SL* ps, SLDateType x)
{
assert(ps);
SLCheckCapacity(ps);
//挪动数据
int i = 0;
for (i = ps->size - 1; i >= 0; i--)
{
ps->arr[i+1] = ps->arr[i];
}
//放入数据
*(ps->arr) = x;
ps->size++;
}
void SLInsert(SL* ps, int pos, SLDateType x)
{
assert(ps);
assert(pos >= 0 && pos <= ps->size);
SLCheckCapacity(ps);
int i = 0;
for (i = ps->size - 1; i >= pos; i--)
{
ps->arr[i+1] = ps->arr[i];
}
ps->arr[pos] = x;
ps->size++;
}
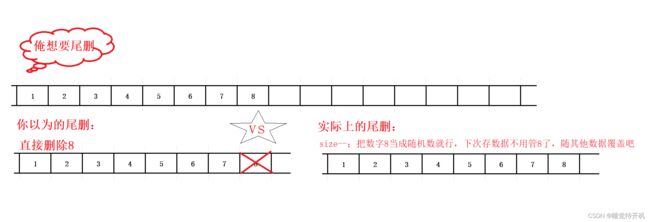
顺序表删除接口:
void SLPopBack(SL* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(ps->size);
ps->size--;
}
void SLPopFront(SL* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(ps->size);
int i = 0;
for (i = 1; i < ps->size; i++)
{
ps->arr[i-1] = ps->arr[i];
}
ps->size--;
}
void SLErase(SL* ps, int pos)
{
assert(ps);
assert(pos >= 0 && pos < ps->size);
int i = 0;
for (i = pos + 1; i < ps->size; i++)
{
ps->arr[i-1] = ps->arr[i];
}
ps->size--;
}
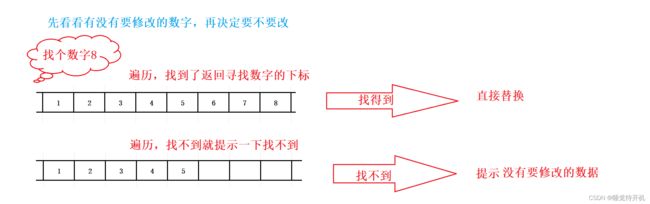
顺序表查找接口:
int SLFind(SL* ps, SLDateType x)
{
assert(ps);
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i < ps->size; i++)
{
if (x == ps->arr[i])
{
printf("%d找到了:",x);
return i;
}
}
printf("没有找到\n");
return -1;
}
void SLModify(SL* ps, int pos, SLDateType x)
{
assert(ps);
assert(pos >= 0 && pos <= ps->size - 1);
ps->arr[pos] = x;
printf("修改成功\n");
}
3.全部接口代码实现:
#include"SeqList.h"
void SLCheckCapacity(SL* ps)
{
assert(ps);
if (ps->capacity == ps->size)
{
//小问题:刚开始的时候,sl->capacity是0值
int newcapacity = ps->capacity == 0 ? 4 : 2 * ps->capacity;
SLDateType* temp = realloc(ps->arr,sizeof(SLDateType)*newcapacity);
if (!temp)
{
perror("realloc fail!");
return;
}
ps->arr = temp;
ps->capacity = newcapacity;
}
}
void SLInit(SL* ps)
{
assert(ps);
ps->arr = NULL;
ps->capacity = ps->size = 0;
}
void SLDestroy(SL* ps)
{
assert(ps);
if (ps->arr)
{
free(ps->arr);
}
ps->arr = NULL;
ps->capacity = ps->size = 0;
}
void SLPrint(SL* ps)
{
assert(ps);
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i < ps->size; i++)
{
printf("%d ", *(ps->arr + i));//ps->arr[i];
}
printf("\n");
}
void SLPushBack(SL* ps,SLDateType x)
{
assert(ps);
//1.空间不足需要扩大容量
//2.空间足够直接放入数据
SLCheckCapacity(ps);
ps->arr[ps->size] = x;
ps->size++;
}
void SLPushFront(SL* ps, SLDateType x)
{
assert(ps);
SLCheckCapacity(ps);
//挪动数据
int i = 0;
for (i = ps->size - 1; i >= 0; i--)
{
ps->arr[i+1] = ps->arr[i];
}
//放入数据
*(ps->arr) = x;
ps->size++;
}
void SLPopBack(SL* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(ps->size);
ps->size--;
}
void SLPopFront(SL* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(ps->size);
int i = 0;
for (i = 1; i < ps->size; i++)
{
ps->arr[i-1] = ps->arr[i];
}
ps->size--;
}
void SLInsert(SL* ps, int pos, SLDateType x)
{
assert(ps);
assert(pos >= 0 && pos <= ps->size);
SLCheckCapacity(ps);
int i = 0;
for (i = ps->size - 1; i >= pos; i--)
{
ps->arr[i+1] = ps->arr[i];
}
ps->arr[pos] = x;
ps->size++;
}
void SLErase(SL* ps, int pos)
{
assert(ps);
assert(pos >= 0 && pos < ps->size);
int i = 0;
for (i = pos + 1; i < ps->size; i++)
{
ps->arr[i-1] = ps->arr[i];
}
ps->size--;
}
int SLFind(SL* ps, SLDateType x)
{
assert(ps);
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i < ps->size; i++)
{
if (x == ps->arr[i])
{
printf("%d找到了:",x);
return i;
}
}
printf("没有找到\n");
return -1;
}
void SLModify(SL* ps, int pos, SLDateType x)
{
assert(ps);
assert(pos >= 0 && pos <= ps->size - 1);
ps->arr[pos] = x;
printf("修改成功\n");
}
完。