【mysql】InnoDB引擎的索引
目录
1、B+树索引
1.1 二叉树
1.1.1 二分查找(对半查找)
1.1.2 树(Tree)
1.1.2.1 树的定义
1.1.2.2 树的特点
1.1.2.3 二叉树
1.1.2.4 二叉查找(搜索)树
1.2 B+树
1.2.1 聚簇索引(clustered index)
主键索引(primary key)
1.2.2 辅助索引(secondary key)
唯一索引(unique index)
普通索引(normal index)
组合索引(composite index)
前缀索引(prefix index)
1.2.3 索引覆盖及回表
索引覆盖
回表
1.2.4 最左前缀匹配原则
2、哈希索引
2.1 hash索引的优缺点
优点:
缺点:
2.2 innoDB的自适应hash
3、倒排索引(Inverted index)
全文索引(Full text)
4、索引的优缺点
优点:
缺点:
InnoDB存储引擎支持以下几种常见的索引:B+树索引、全文索引、哈希索引,其中比较关键的是B+树索引
1、B+树索引
InnoDB中的索引自然也是按照B+树来组织的,前面我们说过B+树的叶子节点用来放数据的,但是放什么数据呢?索引自然是要放的,因为B+树的作用本来就是就是为了快速检索数据而提出的一种数据结构,不放索引放什么呢?但是数据库中的表,数据才是我们真正需要的数据,索引只是辅助数据,甚至于一个表可以没有自定义索引。InnoDB中的数据到底是如何组织的?
1.1 二叉树
1.1.1 二分查找(对半查找)
二分查找法(binary search) 也称为折半查找法,用来查找一组有序的记录数组中的某一记录。
例:在以下数组中找到数字48对应的下标
通过3次二分查找 就找到了我们所要的数字,而顺序查找需8次。
对于上面10个数来说,顺序查找平均查找次数为(1+2+3+4+5+6+7+8+9+10)/10=5.5次。而二分查找法为(4+3+2+4+3+1+4+3+2+3)/10=2.9次。在最坏的情况下,顺序查找的次数为10,而二分查找的次数为4。
所以为了索引查找的高效性,我们引入了二叉查找树。
1.1.2 树(Tree)
1.1.2.1 树的定义
N个结点构成的有限集合。
-
树中有一个称为”根(Root)”的特殊结点
-
其余结点可分为M个互不相交的树,称为原来结点的”子树”
1.1.2.2 树的特点
非树结构:
- 子树是不相交的
- 除了根结点外,每个节点有且只有一个父节点
- 一个N个结点的树只有N-1条边
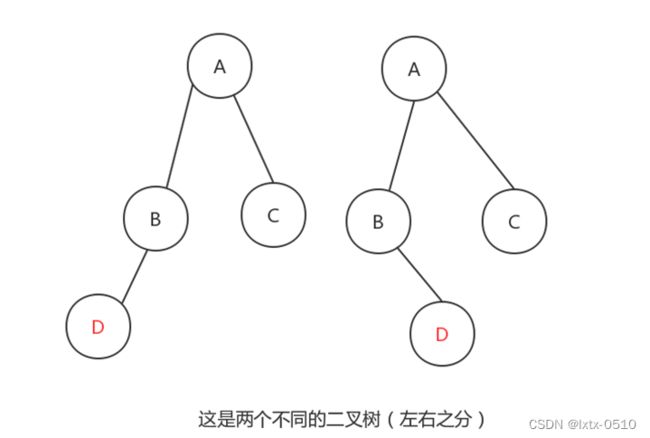
1.1.2.3 二叉树
度为2的树(也可称之为阶):(树的度:树中所有结点中最大的度。结点的度:结点的子树个数)
子树有左右顺序之分:
1.1.2.4 二叉查找(搜索)树
二叉查找树首先肯定是个二叉树,除此之外还符合以下几点:
-
左子树的所有的值小于根节点的值
-
右子树的所有的值大于或等于根节点的值
-
左、右子树满足以上两点
1.2 B+树
B+树是从最早的平衡二叉树演化而来,但是B+树不是一个二叉树。
1.2.1 聚簇索引(clustered index)
聚簇索引就是一种B+树结构,其叶子节点中存放着每一行完整的数据
非聚簇索引中,叶子节点存放的是主键值
主键索引(primary key)
就是一聚簇索引,主键索引的定义方式
- 主键存在:以主键作为聚簇索引
- 主键不存在,存在非空唯一索引:以非空的唯一索引作为聚簇索引
- 两者都不存在:选择 隐式字段
DB_ROW_ID定义为主键作为聚簇索引
添加主键索引:
alter table 表名 add primary key(列名);
alter table user add primary key(`id`);1.2.2 辅助索引(secondary key)
非聚簇索引都是辅助索引又称二级索引,非聚簇索引其叶子节点的 data 中存的不是完整的数据,而是主键值,如果没有 索引覆盖 则通过 回表 查询聚簇索引找到数据。
唯一索引(unique index)
索引列的值必须是唯一的,允许空值。唯一索引不允许表中任何两行的值具有相同的索引值。
添加唯一索引:
alter table 表名 add unique index 索引名(列名);
alter table user add unique index index_id_card(`id_card`);
普通索引(normal index)
基本索引类型,没有什么限制,允许在定义索引的列中插入重复值和空值。
添加普通索引:
alter table 表名 add index 索引名(列名);
alter table user add index index_name(`name`);
组合索引(composite index)
组合索引又称为复合索引,使用时需要遵循 最左前缀匹配原则 。如果条件允许的情况下使用组合索引替代多个单列索引使用,所以创建多列索引时,要根据业务场景,将where子句中使用最频繁的一列放在最左边。
添加组合索引:
alter table 表名 add index 索引名(列名1,列名2.......);
alter table user add index index_age_name(`age`,`name`);
前缀索引(prefix index)
在文本类型如 char、varchar、text 类列上创建索引时,可以指定索引列的长度,但是数值类型不能指定。
添加前缀索引:
alter table 表名 add index 索引名(列名(长度));
alter table user add index index_address(address(2));
1.2.3 索引覆盖及回表
索引覆盖
创建的索引,包含了查询中的所有字段,只需要通过索引就可以查找和返回查询所需要的数据。索引覆盖的优势是能够一次性完成查询工作,减少IO,提高了查询效率
回表
回表的原因是,我们在查询中,通过辅助索引获取到数据的主键Id,然后在通过主键ID去查询聚簇索引找到一行的完整数据。要求是查询所需数据有非索引列
1.2.4 最左前缀匹配原则
针对组合索引,索引以最左边的创建的顺序,进行索引匹配。在创建多列索引时,要根据业务需求,where子句中使用最频繁的一列放在最左边,这样能够提高查询效率
2、哈希索引
哈希表(Hash table,也叫散列表),是根据关键码值(Key value)而直接进行访问的数据结构。也就是说,它通过把关键码值映射到表中一个位置来访问记录,以加快查找的速度。
哈希表 是 数组 + 链表 的形式,通过哈希函数计算每个节点数据中键所对应的哈希桶位置,如果出现哈希冲突,就使用拉链法来解决。
2.1 hash索引的优缺点
优点:
Hash 索引结构的特殊性,其检索效率非常高,索引的检索可以一次定位,不像B-Tree 索引需要从根节点到枝节点,最后才能访问到页节点这样多次的IO访问,所以 Hash 索引的查询效率要远高于 B-Tree 索引。
使用的场景: 一些读操作密集的表建议使用hash索引,因为hash索引的查找速度是很快的。但是也有一些局限。
缺点:
1、hash索引只包含哈希码和行指针,不能使用索引的值避免读取行,也就是要回表,不能像覆盖索引那样避免回表。
2、hash索引不能进行排序以及范围查找,只支持 = 、in 、<=>的比较,因为它们不会按照顺序保存行数据。
3、有可能产生hash碰撞,那么就必须要访问链表的每一个行指针,然后逐行进行比较得出正确数据。
4、因为hash算法是基于等值计算的,不支持部分键匹配,例如有个组合索引a_b,那么此时即使我们的where子句中使用到了a,也不会使用索引,like 等范围查找同理。
2.2 innoDB的自适应hash
当Innodb注意到一些索引值被频繁的访问时,内部会在b-tree索引的顶端为其创建索引保存在内存之中,使其具有快速哈希查找的特性,这个过程是它自动完成的。
可以通过参数 innodb_adaptive_hash_index 来决定是否开启。默认是打开的。
mysql> show variables like "innodb_adaptive_hash_index";
+----------------------------+-------+
| Variable_name | Value |
+----------------------------+-------+
| innodb_adaptive_hash_index | ON |
+----------------------------+-------+
1 row in set (0.16 sec)
自适应哈希索引是对innodb的缓冲池的B+树页进行创建,不是对整张表创建,因此速度很快。
可以通过查看innodb的 status 命令来查看自适应哈希索引的使用情况。
mysql> show engine innodb status;
+--------+------+---------+
| Type | Name | Status
+--------+------+---------+
| InnoDB | |
=====================================
2022-12-13 15:06:03 0x62f0 INNODB MONITOR OUTPUT
=====================================
Per second averages calculated from the last 6 seconds
-----------------
BACKGROUND THREAD
-----------------
srv_master_thread loops: 191 srv_active, 0 srv_shutdown, 708026 srv_idle
srv_master_thread log flush and writes: 708217
----------
SEMAPHORES
----------
OS WAIT ARRAY INFO: reservation count 4025
OS WAIT ARRAY INFO: signal count 4057
RW-shared spins 0, rounds 40132, OS waits 3309
RW-excl spins 0, rounds 4589, OS waits 141
RW-sx spins 54, rounds 1573, OS waits 50
Spin rounds per wait: 40132.00 RW-shared, 4589.00 RW-excl, 29.13 RW-sx
------------
TRANSACTIONS
------------
Trx id counter 3233592
Purge done for trx's n:o < 3233410 undo n:o < 0 state: running but idle
History list length 90
LIST OF TRANSACTIONS FOR EACH SESSION:
---TRANSACTION 283413858068272, not started
0 lock struct(s), heap size 1136, 0 row lock(s)
--------
FILE I/O
--------
I/O thread 0 state: wait Windows aio (insert buffer thread)
I/O thread 1 state: wait Windows aio (log thread)
I/O thread 2 state: wait Windows aio (read thread)
I/O thread 3 state: wait Windows aio (read thread)
I/O thread 4 state: wait Windows aio (read thread)
I/O thread 5 state: wait Windows aio (read thread)
I/O thread 6 state: wait Windows aio (write thread)
I/O thread 7 state: wait Windows aio (write thread)
I/O thread 8 state: wait Windows aio (write thread)
I/O thread 9 state: wait Windows aio (write thread)
Pending normal aio reads: [0, 0, 0, 0] , aio writes: [0, 0, 0, 0] ,
ibuf aio reads:, log i/o's:, sync i/o's:
Pending flushes (fsync) log: 0; buffer pool: 0
198289 OS file reads, 27374 OS file writes, 1469 OS fsyncs
0.00 reads/s, 0 avg bytes/read, 0.00 writes/s, 0.00 fsyncs/s
-------------------------------------
INSERT BUFFER AND ADAPTIVE HASH INDEX
-------------------------------------
Ibuf: size 1, free list len 552, seg size 554, 552 merges
merged operations:
insert 13450, delete mark 1, delete 0
discarded operations:
insert 0, delete mark 0, delete 0
Hash table size 17393, node heap has 1 buffer(s)
Hash table size 17393, node heap has 18 buffer(s)
Hash table size 17393, node heap has 1 buffer(s)
Hash table size 17393, node heap has 189 buffer(s)
Hash table size 17393, node heap has 2 buffer(s)
Hash table size 17393, node heap has 1 buffer(s)
Hash table size 17393, node heap has 0 buffer(s)
Hash table size 17393, node heap has 1 buffer(s)
0.00 hash searches/s, 0.00 non-hash searches/s
---
LOG
---
Log sequence number 30110810223
Log flushed up to 30110810223
Pages flushed up to 30110810223
Last checkpoint at 30110810214
0 pending log flushes, 0 pending chkp writes
509 log i/o's done, 0.00 log i/o's/second
----------------------
BUFFER POOL AND MEMORY
----------------------
Total large memory allocated 68648960
Dictionary memory allocated 685290
Buffer pool size 4096
Free buffers 1024
Database pages 2859
Old database pages 1035
Modified db pages 0
Pending reads 0
Pending writes: LRU 0, flush list 0, single page 0
Pages made young 53454, not young 2806497
0.00 youngs/s, 0.00 non-youngs/s
Pages read 197570, created 18349, written 25879
0.00 reads/s, 0.00 creates/s, 0.00 writes/s
No buffer pool page gets since the last printout
Pages read ahead 0.00/s, evicted without access 0.00/s, Random read ahead 0.00/s
LRU len: 2859, unzip_LRU len: 0
I/O sum[0]:cur[0], unzip sum[0]:cur[0]
--------------
ROW OPERATIONS
--------------
0 queries inside InnoDB, 0 queries in queue
0 read views open inside InnoDB
Process ID=1864, Main thread ID=1912, state: sleeping
Number of rows inserted 505838, updated 2, deleted 0, read 6824874
0.00 inserts/s, 0.00 updates/s, 0.00 deletes/s, 0.00 reads/s
----------------------------
END OF INNODB MONITOR OUTPUT
============================
|
+--------+------+---------+
1 row in set (0.17 sec)
mysql>
3、倒排索引(Inverted index)
全文索引(Full text)
全文索引 通常使用 倒排索引 来实现。倒排索引(Inverted index),也常被称为反向索引、置入档案或反向档案,是一种索引方法,被用来存储在全文搜索下某个单词在一个文档或者一组文档中的存储位置的映射。它是文档检索系统中最常用的数据结构,同B+树索引一样,也是一种索引结构。通过倒排索引,可以根据单词快速获取包含这个单词的文档列表。
添加全文索引:
alter table 表名 add fulltext index 索引名(列名);
alter table user add fulltext index index_profile(`profile`);
4、索引的优缺点
优点:
- 创建索引可以大幅提高系统性能,帮助用户提高查询的速度;
- 可以加速表与表之间的链接;
- 降低查询中分组和排序的时间。
缺点:
- 索引的存储需要占用磁盘空间;
- 当数据的量非常巨大时,索引的创建和维护所耗费的时间也是相当大的;
- 当每次执行create、update、delete操作时,索引也需要动态维护,降低了数据的维护速度。