代码随想录刷题笔记-Day16
1. 二叉树的所有路径
257. 二叉树的所有路径![]() https://leetcode.cn/problems/binary-tree-paths/description/
https://leetcode.cn/problems/binary-tree-paths/description/
给你一个二叉树的根节点 root ,按 任意顺序 ,返回所有从根节点到叶子节点的路径。
叶子节点 是指没有子节点的节点。
示例 1:
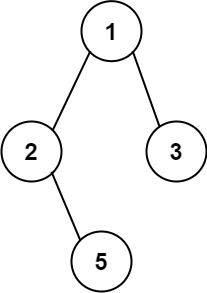
输入:root = [1,2,3,null,5]
输出:["1->2->5","1->3"]示例 2:
输入:root = [1]
输出:["1"]解题思路
无非是在深度优先遍历的时候要记录路径,所以参数列表内需要一个当前路径。
当遇到叶子节点的时候就终止递归,回到上一层(上一层开始的这一次递归调用。)
代码
class Solution {
private List result = new ArrayList<>();
public List binaryTreePaths(TreeNode root) {
order(root, "");
return result;
}
private void order(TreeNode root, String path) {
if (root.left == null && root.right == null) {
result.add(new StringBuilder(path).append(root.val).toString());
return;
}
String temp = new StringBuilder(path).append(root.val + "->").toString();
if (root.left != null) {
order(root.left, temp);
}
if (root.right != null) {
order(root.right, temp);
}
}
} 2. 左叶子之和
404. 左叶子之和![]() https://leetcode.cn/problems/sum-of-left-leaves/description/给定二叉树的根节点 root ,返回所有左叶子之和。
https://leetcode.cn/problems/sum-of-left-leaves/description/给定二叉树的根节点 root ,返回所有左叶子之和。
示例 1:
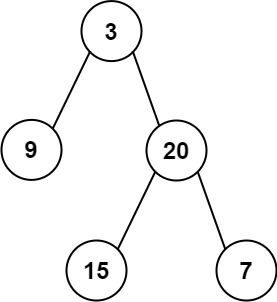
输入: root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
输出: 24
解释: 在这个二叉树中,有两个左叶子,分别是 9 和 15,所以返回 24示例 2:
输入: root = [1]
输出: 0解题思路
要计算左叶子累加和,重点就在于如何区分左叶子。要区分左叶子只能是父节点才能区分,所以计算值的时候得比往常先一步。
当左子树存在且它没有左右子树的时候,val就是需要累加的值,返回val和右子树的返回值和。
同时,需要进入左右子树去继续递归。返回左右子树的返回值和
代码
class Solution {
public int sumOfLeftLeaves(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null)
return 0;
if (root.left != null && root.left.left == null && root.left.right == null)
return root.left.val + sumOfLeftLeaves(root.right);
return sumOfLeftLeaves(root.left) + sumOfLeftLeaves(root.right);
}
}3. 找树左下角的值
513. 找树左下角的值![]() https://leetcode.cn/problems/find-bottom-left-tree-value/description/
https://leetcode.cn/problems/find-bottom-left-tree-value/description/
给定一个二叉树的 根节点 root,请找出该二叉树的 最底层 最左边 节点的值。
假设二叉树中至少有一个节点。
示例 1:
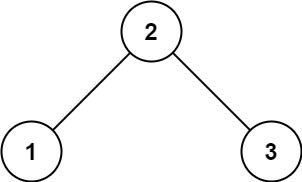
输入: root = [2,1,3]
输出: 1示例 2:
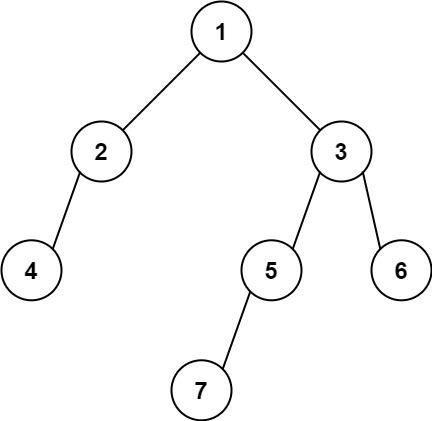
输入: [1,2,3,4,null,5,6,null,null,7]
输出: 7解题思路
通过层次遍历来实现。
代码
class Solution {
public int findBottomLeftValue(TreeNode root) {
Deque queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(root);
int result = 0;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int len = queue.size();
result = queue.peek().val;
while (len > 0) {
TreeNode node = queue.poll();
if (node.left != null)
queue.offer(node.left);
if (node.right != null)
queue.offer(node.right);
len--;
}
}
return result;
}
}