STM32入门教程---USART串口协议
文章目录
- 通信接口
- 串口通信
-
- 简介
- 硬件电路
- 电平标准
- 串口参数及时序
- 串口时序
- USART外设
-
- 简介
- USART框图
- 引脚定义表
- USART基本结构
- 数据帧
-
- 字长设置
- 配置停止位
- 起始位侦测
- 数据采样
- 波特率发生器
- 数据模式
- 代码
-
- 串口发送
-
- 接线图
- 代码思路
- 库函数
- 代码
- 串口发送+接收
- 接线图
- 代码
- 总结
通信接口
- 通信的目的:将一个设备的数据传送到另一个设备,扩展硬件系统;
- 通信协议:制定通信的规则,通信双方按照协议规则进行数据收发;

- TX是数据发送脚,RX是数据接收脚;
- SCL是时钟,SDA是数据;
- SCLK是时钟,MOSI是主机输出数据脚,MISO是主机输入数据脚,CS是片选,用于指定通信的对象;
- CAN_H和CAN_L是差分数据脚,用两个引脚表示一个差分数据;
- DP和DM也是一对差分数据脚;
- 全双工:指的是通信双方可以同时进行双向通信,一般全双工的通信都有两根通信线,发送线路和接收线路互不影响;
- 半双工:一般只有一根通信线,通信双方不能同时双向通信;
- 单工:数据只能从一个设备到另一个设备,不能反着来;
- 单端电平:就是它们的引脚的高低电平都是对GND的电压差,所以单端信号通信的双方必须要共地,把GND连在一起;
- 差分电平:靠两个差分引脚的电压差来传输信号,在通信时可以不需要GND,可以极大提高抗干扰特性;
- 多设备:相当于老师在教室里对所有同学讲话,需要有一个寻址的过程,以确定通信的对象;
- 点对点:相当于老师在办公室找你谈话,直接传输数据就可以;
串口通信
简介
- 串口是一种应用十分广泛的通信接口,串口成本低,容易使用,通信线路简单,可实现两个设备的互相通信;
- 单片机的串口可以使单片机与单片机、单片机与电脑、单片机与各式各样的模块互相通信,极大地扩展了单片机的应用范围,增强了单片机系统的硬件实力;
硬件电路
电平标准
电平标准是数据1和数据0的表达方式,是传输线缆中人为规定的电压与数据的对应关系,串口常用的电平标准有如下三种:
- TTL电平:+3.3V或+5V表示1,0V表示0;
- RS232电平:-3~-15V表示1,+3 ~+15V表示0;
- RS485电平:两线压差+2 ~ +6V表示1,-2 ~ -6V表示0(差分信号,抗干扰能力强)
【如果在做设备时需要其他电平,加电平转换芯片就可以了,在软件层面程序没有多大变化】
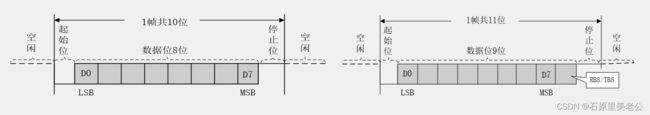
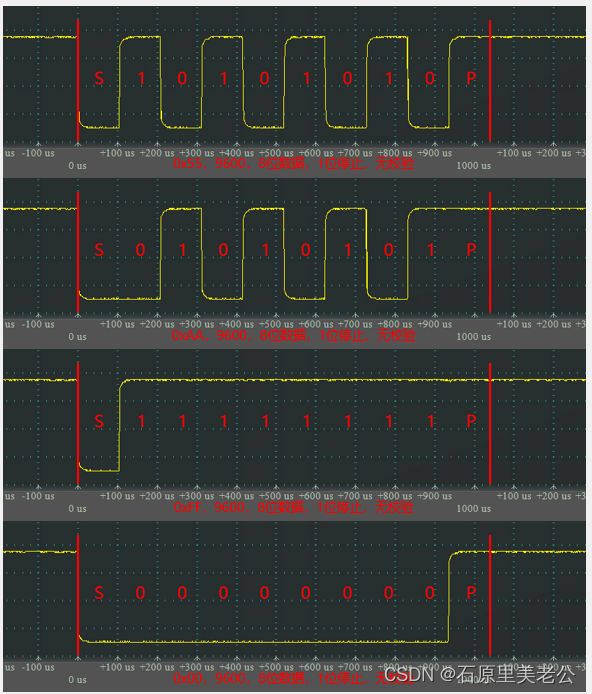
串口参数及时序
- 波特率:串口通信的速率,每秒传输码元的个数,规定了每隔多久发送一位;
- 比特率:每秒传输的比特数;
在二进制调制下,一个码元=一个比特,此时波特率=比特率;如果是多进制调制,波特率≠比特率;
- 起始位:标志一个数据帧的开始,固定为低电平;
- 数据位:数据帧的有效载荷,1为高电平,0为低电平,低位先行;
- 校验位:用于数据验证,根据数据位计算得来;
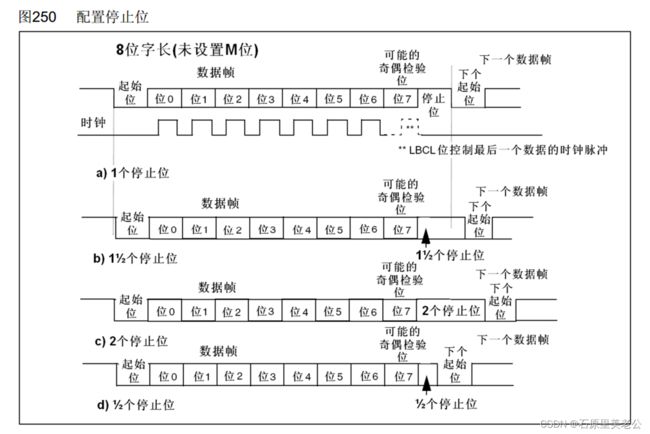
(奇校验和偶校验检出率只有一定程度,如果想要更高检出率,可以选择CRC校验) - 停止位:用于数据帧间隔,固定为高电平;
串口时序
USART外设
简介
- USART通用同步/异步收发器;
- USART是STM32内部集成的硬件外设,可根据数据寄存器的一个字节数据自动生成数据帧时序,从TX引脚发送出去,也可自动接收RX引脚的数据帧时序,拼接为一个字节数据,存放在数据寄存器里;
- 自波特率发生器,其实就是个分频器,最高达4.5Mbits/s
- 可配置数据位长度(8/9)、停止位长度(0.5/1/1.5/2)
- 可选校验位(无校验/奇校验/偶校验)
- 支持同步模式、硬件流控制、DMA、智能卡、IrDA(红外通信)、LIN(局域网的通信协议)
- STM32F103C8T6 USART资源:USART1、USART2、USART3;
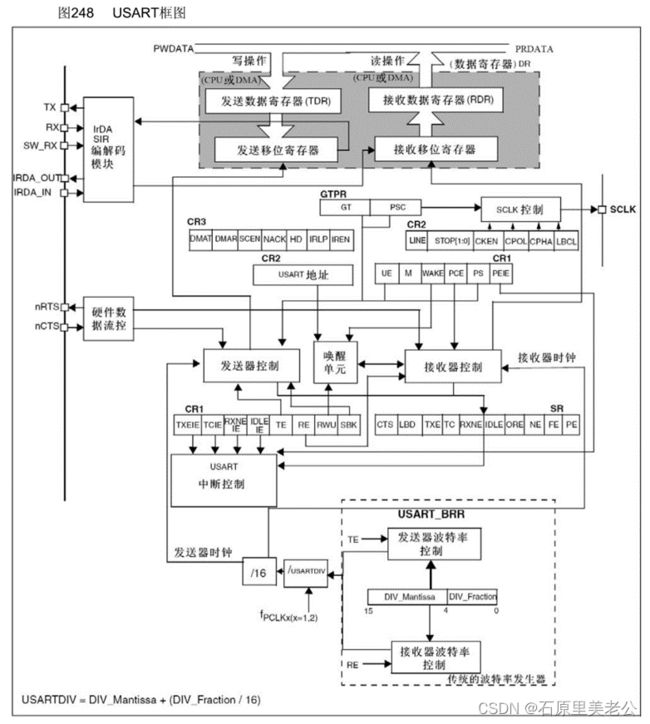
USART框图
- TDR和RDR占用同一个地址,在程序上只表现为一个寄存器DR,TDR是只写的,RDR是只读的,进行写操作时,数据写入TDR,进行读操作时,数据从RDR读出;
- 发送移位寄存器:把一个字节的数据一位一位的移出去,当数据从TDR移动到发送移位寄存器时,会置一个标志位TXE(当TXE标志位置1时,说明数据从TDR移动到发送移位寄存器了,我们可以写入新的数据)
- 接收移位寄存器同理,在转移过程中,会置一个标志位RXNE,接收数据寄存器非空,当RXNE置1时,就可以把数据读取;
- 硬件数据流控:如果发送设备太快,接收设备来不及处理,就会出现丢弃或覆盖数据的现象;nRTS是请求发送,为输出脚,用于输出能不能接收的反馈信号;nCTS是清除发送,为输入脚,用于接收别人nRTS的信号;(n的意思是低电平有效,nRTS和nCTS也是交叉连接)
- SCLK:用于兼容别的协议和做自适应波特率;
- 唤醒单元:实现串口挂载多设备;
- TXE发送寄存器空,RXNE接收寄存器非空,是判断发送状态和接收状态的必要标志位;
- USARTDIV是一个数值,分有整数部分和小数部分,再除以16得到发送器时钟和接收器时钟,通向控制部分;若TE为1,即发送器使能,发送部分的波特率有效;若RE为1,即接收器使能,接收部分的波特率有效;
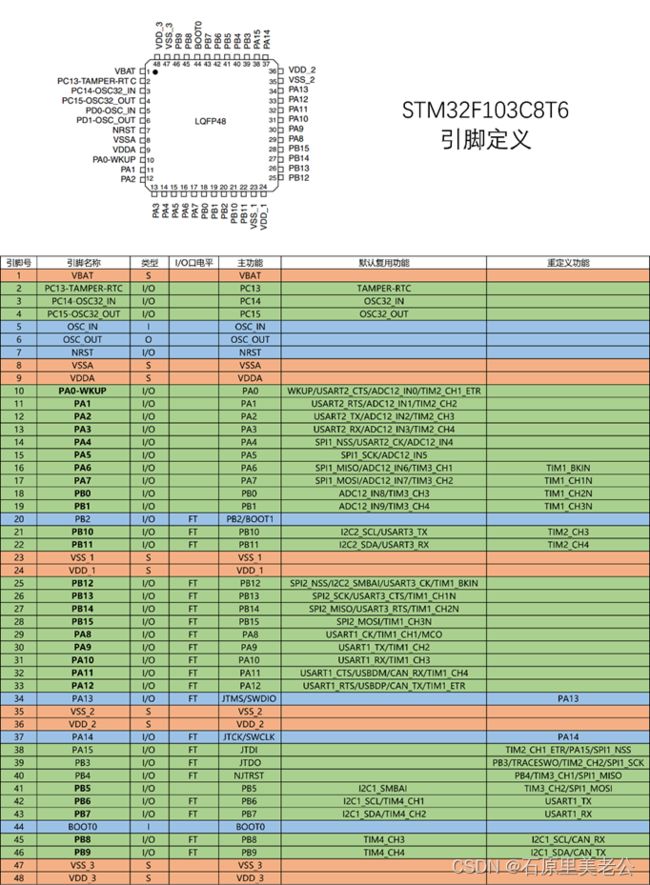
引脚定义表
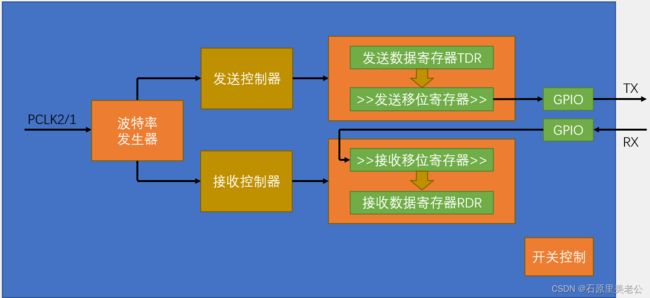
USART基本结构
- 波特率发生器用于产生约定的通信速率,时钟来源PCLK2/1,经过波特率发生器分频后,产生的时钟通向发送控制器和接收控制器;
- 发送控制器和接收控制器用来控制发送移位和接收移位;
- 右移符号代表移位寄存器是往右移的,低位先行;
- 数据从数据寄存器转移到移位寄存器时,会置一个TXE标志位,通过判断该标志位就可以知道是不是可以写下一个数据;
- 接收寄存器类似;
数据帧
字长设置
配置停止位
起始位侦测
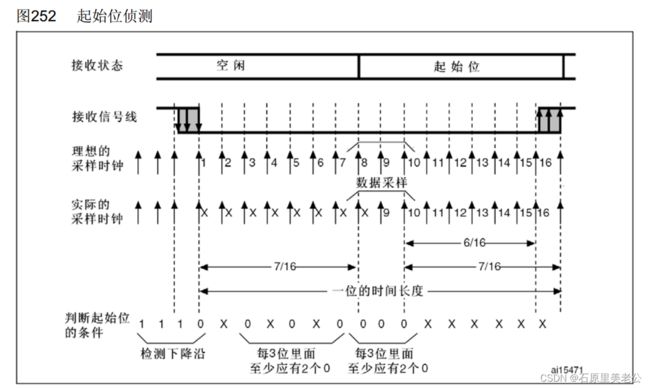
当输入电路侦测到一个数据帧的起始位之后,就会以一个波特率的频率,连续采样一帧数据,同时从起始位开始,采样位置就要对齐到位的正中间;
在起始位进行16次采样,其中第3、4、5、6、7次采样中每3位里面至少有2个0,8、9、10位里面每3位至少有2个0成立的话,就算检测到了标志位,然后后续数据的采样都是在第8,、9、10位进行采样,也就是数据的中间位置进行采样;
数据采样
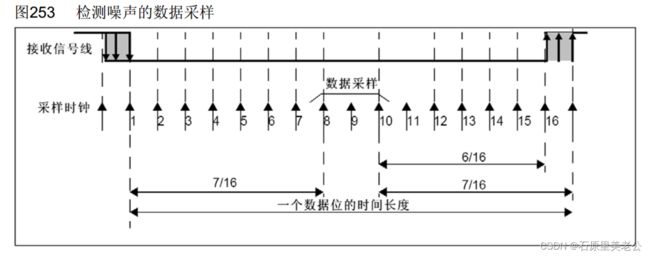
如果8,9,10位的3位里面有1位是0/1,2位是1/0,就会在噪声标志位置1,表示有噪声;
波特率发生器
- 发送器和接收器的波特率由波特率寄存器BRR里的DIV确定;
- 计算公式:波特率=fPCLK2/1/(16×DIV);
数据模式
- HEX模式/十六进制模式/二进制模式:以原始数据的形式显示;
- 文本模式/字符模式:以原始数据编码后的形式显示
代码
串口发送
接线图
代码思路
- 开启RCC时钟,把需要用的USART和GPIO的时钟打开;
- GPIO初始化,把TX配置成复用输出,RX配置成输入;
- 配置USART;
- 开关控制,开启USART;
- 如果还需要中断,配置NVIC;
库函数
- USART_DMACmd可以开启USART到DMA的触发通道;
- USART_SendData发送数据,写DR寄存器;
- USART_ReceiveData接收数据,读DR寄存器;
- 最后是四个与标志位相关的函数;
代码
#include "stm32f10x.h" // Device header
#include 使用printf函数的移植方法:在工程选项中勾选Use MicroLIB,然后对printf进行重定向,即在头文件中加上 #include ,然后重写fputc函数,fputc函数是printf的底层;
打印中文,需要在工程选项的C/C++的杂项控制栏中写上--no-multibyte-chars,串口助手中译码方式选择UTF-8,就可以输出中文;
串口发送+接收
接线图
代码
#include "stm32f10x.h" // Device header
#include #include "stm32f10x.h" // Device header
#include "Delay.h"
#include "OLED.h"
#include "Serial.h"
uint8_t RxData;
int main(void)
{
OLED_Init();
OLED_ShowString(1, 1, "RxData:");
Serial_Init();
while (1)
{
if (Serial_GetRxFlag() == 1)
{
RxData = Serial_GetRxData();
Serial_SendByte(RxData);
OLED_ShowHexNum(1, 8, RxData, 2);
}
}
}
总结
本节内容对应手册里的第25章USART