v-if及v-for、computed计算属性的使用
v-if 概念及使用
v-if是Vue.js中的一个指令,用于根据表达式的真假值条件性地渲染一块内容。如果表达式的值返回真,则Vue会渲染这块内容;如果返回假,则不渲染。
基本用法:
<p v-if="isVisible">看到我了吗?p>
在这个例子中,只有当isVisible的值为true时,
标签才会被渲染。
v-for 概念及使用
v-for是Vue.js中的一个指令,用于基于源数据多次渲染元素或模板块。v-for指令需要使用item in items形式的特殊语法,其中items是源数据数组,item是为数组元素提供的别名。
基本用法:
<ul>
<li v-for="item in items">{{ item.text }}li>
ul>
这里,对于items数组中的每个元素,都会渲染一个
text属性的值。
结合使用原理及例子
当v-if与v-for一起使用时,v-for具有比v-if更高的优先级。这意味着v-if将分别作用于每个v-for循环迭代中的元素。然而,Vue官方推荐尽量避免同时使用v-if和v-for。如果需要这样做,考虑通过计算属性先过滤列表。
结合使用的例子:
假设你有一个任务列表,但只想显示未完成的任务:
<ul>
<li v-for="task in tasks" v-if="!task.isCompleted">{{ task.description }}li>
ul>
在上面的代码中,每个任务都会被v-for遍历,但只有当task.isCompleted为false时(即任务未完成时),对应的任务描述才会被渲染。
更好的做法是使用计算属性:
computed: {
unfinishedTasks() {
return this.tasks.filter(task => !task.isCompleted);
}
}
然后在模板中使用这个计算属性:
<ul>
<li v-for="task in unfinishedTasks">{{ task.description }}li>
ul>
这种方法更清晰,并且性能更好,因为它避免了在每次渲染中对列表的重复评估和过滤,而是只在任务列表发生变化时才重新计算过滤后的列表。
下面我们通过例子进行详解:
DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>v-iftitle>
<script src="../vue 初识/vue.js">script>
<style>
table,tr,th,td{
border: 1px solid red;
border-collapse: collapse;
}
th ,td{
width: 200px;
text-align: center;
height: 30px;
line-height: 30px;
}
style>
head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<div v-if="this.age > 18">
<div>成人div>
<ul>
<li>江西li>
<li>湖南li>
<li>四川li>
ul>
div>
<div v-else>
<div>儿童div>
<ul>
<li>动漫li>
<li>故事会li>
<li>武侠li>
ul>
div>
<table >
<tr>
<th>序号th>
<th>书名th>
<th>价格th>
<th>出版社th>
tr>
<tr v-for="(book,index) in books">
<td>{{index+1}}td>
<td>{{book.name}}td>
<td>{{book.price}}td>
<td>{{book.publish}}td>
tr>
table>
div>
<script>
const app={
data(){
return{
use:"liqiang" ,
age:18,
books:[
{name:"水浒传",price:3999,publish:"人民出版社"},
{name:"红楼梦",price:299,publish:"机械出版社"},
{name:"西游记",price:399,publish:"西瓜出版社"},
{name:"西厢记",price:499,publish:"香蕉出版社"}
]
}
}
}
vm=Vue.createApp(app).mount('#app')
script>
body>
html>
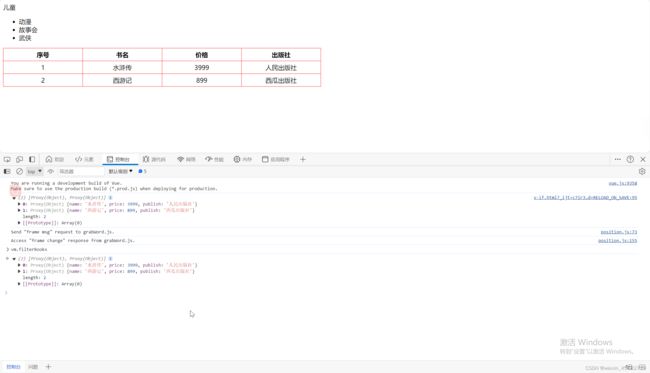
页面展示效果如下图:

如果此刻想对价格进行过滤该如何操作?比如只显示价格大于500的书籍?
解决方法一:
<template v-for="(book,index) in books">
<tr v-if="book.price > 500" >
<td>{{index+1}}td>
<td>{{book.name}}td>
<td>{{book.price}}td>
<td>{{book.publish}}td>
tr>
template>
但是这种方法只是传统解决办法,不是vue3.0官方解决办法。
解决方法二:
DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>v-iftitle>
<script src="../vue 初识/vue.js">script>
<style>
table,tr,th,td{
border: 1px solid red;
border-collapse: collapse;
}
th ,td{
width: 200px;
text-align: center;
height: 30px;
line-height: 30px;
}
style>
head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<div v-if="this.age > 18">
<div>成人div>
<ul>
<li>江西li>
<li>湖南li>
<li>四川li>
ul>
div>
<div v-else>
<div>儿童div>
<ul>
<li>动漫li>
<li>故事会li>
<li>武侠li>
ul>
div>
<table >
<tr>
<th>序号th>
<th>书名th>
<th>价格th>
<th>出版社th>
tr>
<tr v-for="(book,index) in filterBooks">
<td>{{index+1}}td>
<td>{{book.name}}td>
<td>{{book.price}}td>
<td>{{book.publish}}td>
tr>
table>
div>
<script>
const app={
data(){
return{
use:"liqiang" ,
age:18,
books:[
{name:"水浒传",price:3999,publish:"人民出版社"},
{name:"红楼梦",price:299,publish:"机械出版社"},
{name:"西游记",price:899,publish:"西瓜出版社"},
{name:"西厢记",price:499,publish:"香蕉出版社"}
]
}
},
methods:{
},
computed:{
//先对books的数据进行过滤计算
filterBooks(){
let newBooks = []
for (i=0;i<this.books.length;i++){
if (this.books[i].price>500){
newBooks.push(this.books[i])
}
}
console.log(newBooks)
return newBooks
}
}
}
vm=Vue.createApp(app).mount('#app')
script>
body>
html>
DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>v-iftitle>
<script src="../vue 初识/vue.js">script>
<style>
table,tr,th,td{
border: 1px solid red;
border-collapse: collapse;
}
th ,td{
width: 200px;
text-align: center;
height: 30px;
line-height: 30px;
}
style>
head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<div v-if="this.age > 18">
<div>成人div>
<ul>
<li>江西li>
<li>湖南li>
<li>四川li>
ul>
div>
<div v-else>
<div>儿童div>
<ul>
<li>动漫li>
<li>故事会li>
<li>武侠li>
ul>
div>
<table >
<tr>
<th>序号th>
<th>书名th>
<th>价格th>
<th>出版社th>
tr>
<tr v-for="(book,index) in filterBooks2">
<td>{{index+1}}td>
<td>{{book.name}}td>
<td>{{book.price}}td>
<td>{{book.publish}}td>
tr>
table>
div>
<script>
const app={
data(){
return{
use:"liqiang" ,
age:18,
books:[
{name:"水浒传",price:3999,publish:"人民出版社"},
{name:"红楼梦",price:299,publish:"机械出版社"},
{name:"西游记",price:899,publish:"西瓜出版社"},
{name:"西厢记",price:499,publish:"香蕉出版社"}
]
}
},
methods:{
},
computed:{
//先对books的数据进行过滤计算
filterBooks2(){
return this.books.filter(function (item){
// 便利所有的books,赋值给数组
console.log("item",item)
return item.price>500
})
}
}
}
vm=Vue.createApp(app).mount('#app')
script>
body>
html>
效果如下:
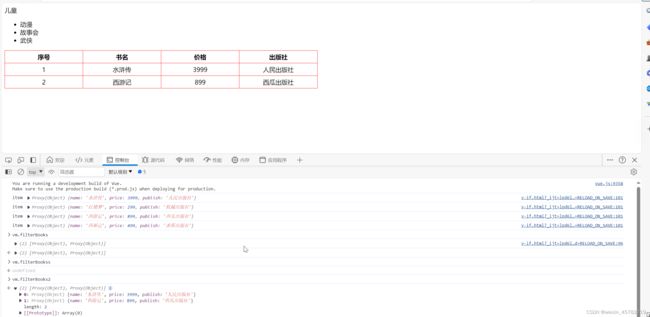
filterBooks2 是一个 Vue 实例中定义的计算属性(computed属性)。计算属性是基于它们的响应式依赖进行缓存的。只有在相关响应式依赖发生改变时,它们才会重新求值。这意味着只要 books 数组或数组内对象的 price 属性没有发生变化,filterBooks2 将不会重新计算,从而提高应用的性能。
在给出的代码段中,filterBooks2 方法通过 filter 函数过滤 books 数组,返回所有 price 大于 500 的书籍。filter 函数是 JavaScript 中的数组方法之一,它创建一个新数组,新数组中的元素是通过检查指定数组中符合条件的所有元素。条件检查是在回调函数中完成的,每个数组元素都会执行一次回调函数。
接下来,我们逐行解释一下filterBooks2:
filterBooks2(){
return this.books.filter(function (item){
console.log("item",item) // 打印当前正在处理的书籍对象
return item.price>500 // 判断当前书籍的价格是否大于500
console.log("item",item) // 这行代码不会被执行,因为return语句已经结束了函数执行
})
}
关键点解释
-
filter方法的回调函数:this.books.filter(function (item){...})中的function(item)是filter方法的回调函数,item表示数组中的当前遍历到的元素。在这个场景下,item代表books数组中的一个书籍对象。 -
判断条件
item.price>500:这是filter方法的核心判断逻辑,用来检查当前书籍对象的price属性是否大于 500。 -
返回值:
filter方法会创建一个新数组,包含所有通过测试(即函数返回true)的元素。在本例中,所有价格大于500的书籍对象会被包含在返回的新数组中。 -
console.log的位置:在return语句之后的console.log("item",item)实际上是无法到达的代码,因为return语句执行后,函数的执行已经结束了,之后的代码将不会被执行。因此,如果你在测试或调试时需要查看item的值,需要确保console.log在return语句之前。
实验二:
下面我想实现当选出的价格大于500时候,背景颜色变为橘黄色。
DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>v-iftitle>
<script src="../vue 初识/vue.js">script>
<style>
table,tr,th,td{
border: 1px solid red;
border-collapse: collapse;
}
th ,td{
width: 200px;
text-align: center;
height: 30px;
line-height: 30px;
}
.co{
background-color: orange;
}
style>
head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<div v-if="this.age > 18">
<div>成人div>
<ul>
<li>江西li>
<li>湖南li>
<li>四川li>
ul>
div>
<div v-else>
<div>儿童div>
<ul>
<li>动漫li>
<li>故事会li>
<li>武侠li>
ul>
div>
<table >
<tr>
<th>序号th>
<th>书名th>
<th>价格th>
<th>出版社th>
tr>
<tr v-for="(book,index) in filterBooks2" :class="classes">
<td>{{index+1}}td>
<td>{{book.name}}td>
<td>{{book.price}}td>
<td>{{book.publish}}td>
tr>
table>
div>
<script>
const app={
data(){
return{
use:"liqiang" ,
age:18,
books:[
{name:"水浒传",price:3999,publish:"人民出版社"},
{name:"红楼梦",price:2499,publish:"机械出版社"},
{name:"西游记",price:899,publish:"西瓜出版社"},
{name:"西厢记",price:499,publish:"香蕉出版社"}
],
classes: {co: true}
}
},
computed:{
//先对books的数据进行过滤计算
filterBooks(){
let newBooks = []
for (i=0;i<this.books.length;i++){
if (this.books[i].price>500){
newBooks.push(this.books[i])
}
}
console.log(newBooks)
return newBooks
},
filterBooks2(){
return this.books.filter(function (item){
console.log("item",item)
return item.price>500
})
}
}
}
vm=Vue.createApp(app).mount('#app')
script>
body>
html>
根据书籍价格来改变样式,直接在模板中使用条件绑定会更加直接和高效。
实验三
下面我希望显示所有书籍并且,价格大于500的背景色的为橘黄色怎么实现?这里我们采用三元运算符。
DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>v-iftitle>
<script src="../vue 初识/vue.js">script>
<style>
table,tr,th,td{
border: 1px solid red;
border-collapse: collapse;
}
th ,td{
width: 200px;
text-align: center;
height: 30px;
line-height: 30px;
}
.co{
background-color: orange;
}
style>
head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<div v-if="this.age > 18">
<div>成人div>
<ul>
<li>江西li>
<li>湖南li>
<li>四川li>
ul>
div>
<div v-else>
<div>儿童div>
<ul>
<li>动漫li>
<li>故事会li>
<li>武侠li>
ul>
div>
<table >
<tr>
<th>序号th>
<th>书名th>
<th>价格th>
<th>出版社th>
tr>
<tr v-for="(book,index) in books" :class="book.price>500?'co':''">
<td>{{index+1}}td>
<td>{{book.name}}td>
<td>{{book.price}}td>
<td>{{book.publish}}td>
tr>
table>
div>
<script>
const app={
data(){
return{
use:"liqiang" ,
age:18,
books:[
{name:"水浒传",price:99,publish:"人民出版社"},
{name:"红楼梦",price:2499,publish:"机械出版社"},
{name:"西游记",price:899,publish:"西瓜出版社"},
{name:"西厢记",price:499,publish:"香蕉出版社"}
],
classes: {co: true}
}
},
computed:{
//先对books的数据进行过滤计算
filterBooks(){
let newBooks = []
for (i=0;i<this.books.length;i++){
if (this.books[i].price>500){
newBooks.push(this.books[i])
}
}
console.log(newBooks)
return newBooks
},
filterBooks2(){
return this.books.filter(function (item){
console.log("item",item)
return item.price>500
})
}
}
}
vm=Vue.createApp(app).mount('#app')
script>
body>
html>
针对三元运算符进行详解:
在Vue.js中,使用:class绑定时候,如果条件判断需要根据结果选择不同的类名,通常会用到三元运算符,格式如下:
:class="condition ? 'trueClassName' : 'falseClassName'"
这里的condition是你要检查的条件,trueClassName是当条件为真(true)时要添加的类名,而falseClassName是条件为假(false)时要添加的类名。在这种情况下,类名是字符串类型的值,因此它们需要被引号(单引号'或双引号")包围。
在例子中:
:class="book.price>500 ? 'co' : ''"
- 当
book.price > 500为真时,将为元素添加'co'类名。这里的'co'就是一个字符串,代表某个具体的CSS类,用来改变该元素的样式。此类名外必须用引号包围,因为它是一个字符串。 - 当条件为假时,元素不会添加任何类名,因此使用一对空引号
''代表空字符串,也就是说,不添加任何类名。这对空引号同样表明这里是一个字符串类型的值,虽然它是空的。
引号的使用是因为CSS类名在JavaScript(因此也包括Vue.js模板表达式中)是作为字符串处理的,不管是具有实际名称的字符串,还是一个空字符串。不使用引号的话,JavaScript会试图将其解释为变量或其他表达式,从而引发语法或逻辑错误。
小结
通过 filterBooks2 计算属性,可以得到一个包含所有价格大于 500 的书籍的数组。这是在 Vue 应用中处理数组和展示过滤结果的一种高效方法。使用计算属性可以确保数据处理逻辑简洁且可维护,同时 Vue 的响应式系统会帮你确保数据的更新能够正确反映在 UI 上。