HarmonyOS学习第二章:初识ArkTs/ArkUI,常用组件(待补充)
文章目录
- 一、ArkTs
-
- 1.1 简介
- 1.2 关键特性
- 1.3 基础代码结构
-
- 1.3.1 示例:
- 1.3.2 页面组件
- 1.3.3 自定义组件
- 二、ArkUI
-
- 2.1 ArkUI介绍
- 2.2 开发范式
- 三、常用组件的使用
-
- 3.1 Text组件
- 3.2 Column 列组件
- 3.3 Row 行组件
- 3.4 Flex 以弹性方式容器组件
- 3.5 Grid 网格布局组件
- 3.6 Button 按钮组件
- 3.7 TextInput 输入框组件
- 3.8 Image 图片组件
- 3.9 Toggle 切换组件
- 3.10 Slider 滑块组件
- 3.11 progress 进度条组件
- 3.12 Stack 堆叠组件
- 3.13 Blank 组件
- 3.14 Divider 分割线组件
- 3.15 List 列表组件
- 3.16 Scroll 滚动组件
- 四、补充:在编辑器中查看组件文档
-
- 4.1 DevEco Studio编辑器内查看官方文档
一、ArkTs
1.1 简介
ArkTS是HarmonyOS的应用开发语言,它在保持
TypeScript(简称TS)基本语法风格的基础上,对TS的动态类型特性施加了更严格的约束,并引入了静态类型。
1.2 关键特性
-
声明式UI、自定义组件、动态扩展UI元素
ArkTS定义了声明式UI描述、自定义组件和动态扩展UI元素的能力,再配合ArkUI开发框架中的系统组件及其相关的事件方法、属性方法等共同构成了UI开发的主体。下面是一个示例,是一个基础的ArkTs书写的代码片段,展示了ArkTs声明式UI的能力:
@Entry @Component struct MyComponent { @State private text: string = 'Hello, HarmonyOS!'; build() { Row() { Text(this.text) .fontSize(20) .fontWeight(FontWeight.Bold) .onClick(() => { this.text = 'You clicked me!'; }); } } } -
状态管理
ArkTS提供了多维度的状态管理机制。在UI开发框架中,与UI相关联的数据可以在组件内使用,也可以在不同组件层级间传递,比如父子组件之间、爷孙组件之间,还可以在应用全局范围内传递或跨设备传递。另外,从数据的传递形式来看,可分为只读的单向传递和可变更的双向传递。开发者可以灵活地利用这些能力来实现数据和UI的联动。
-
渲染控制
ArkTS提供了渲染控制的能力。条件渲染可根据应用的不同状态,渲染对应状态下的UI内容。循环渲染可从数据源中迭代获取数据,并在每次迭代过程中创建相应的组件。数据懒加载从数据源中按需迭代数据,并在每次迭代过程中创建相应的组件。
1.3 基础代码结构
1.3.1 示例:
注意:build()函数中只能包含一个根节点
1.3.2 页面组件
// @Entry 装饰器 - 代表入口
@Entry
// @Component 装饰器 - 代表组件
@Component
// struct 声明组件 Index 表示自定义的组件名称
struct Index {
// @State 装饰器
@State message: string = '鸿蒙开发'
@State color: string = 'green'
// @Builder装饰器:自定义构建函数
build() {
// 只能包含一个根节点
// 下面的都属于UI描述器,可以理解为HTML中的元素、CSS中的属性
// Row Column Text 都属于系统组件
Row() {
Column() {
Text(this.message)
// fontSize 属性,和css中的font-size一致,用来设置文字大小,单位是VP
.fontSize(50)
// fontWeight 属性,和css中的font-weight一致,用来设置字体粗细
.fontWeight(FontWeight.Bold)
// fontColor 设置字体颜色
.fontColor(this.color)
// onClick 点击事件
.onClick(() => {
console.log('我被点击了!!!')
})
}
// 设置Column组件宽度,可以是百分数,也可以是具体数值,写具体数值时不带单位
.width('100%')
}
// 设置Row组件高度
.height('100%')
}
}
1.3.3 自定义组件
二、ArkUI
2.1 ArkUI介绍
ArkUI是一套构建分布式应用界面的声明式UI开发框架。它使用极简的UI信息语法、丰富的UI组件、以及实时界面预览工具
2.2 开发范式
ArkUI针对不同的应用场景及技术背景,提供了两种开发范式,分别是基于ArkTS的声明式开发范式(简称“声明式开发范式”)和兼容JS的类Web开发范式(简称“类Web开发范式”)。推荐使用声明式开发范式。
- 声明式开发范式:采用基于TypeScript声明式UI语法扩展而来的ArkTS语言,从组件、动画和状态管理三个维度提供UI绘制能力。
- Web开发范式:原生的html、css、js开发
三、常用组件的使用
这里列举了一些常用的组件,有前端开发经验的同学可以查看官方文档。
3.1 Text组件
文本组件,可以用于放置文本类内容
-
@Entry @Component struct TextPage { build() { Text('这是一个Text组件') } } -
@Entry @Component struct TextPage { build() { Text('这是一个Text组件') .height(150) .width('100%') .backgroundColor('blue') .fontColor('green') .fontSize(40) .border({ width: 1, color: '#f40' }) } } -
也可以插入span组件
注意:组件有两种方式书写,一种是向上面那种直接写属性、传值,一种是下面这种在组件的{}中书写内容,下面这种写法在花括号中加了span组件之后,Text组件传递的参数就不生效了@Entry @Component struct TextPage { build() { Text('这是一个Text组件') { Span('这是Span组件').height(100).width(100) } .height(150) .width('100%') .backgroundColor('blue') .fontColor('green') .fontSize(40) .border({ width: 1, color: '#f40' }) } }
3.2 Column 列组件
纵向排列的组件,主轴是Y,内部可以书写任意组件(注意build组件内只能有一个根组件)
-
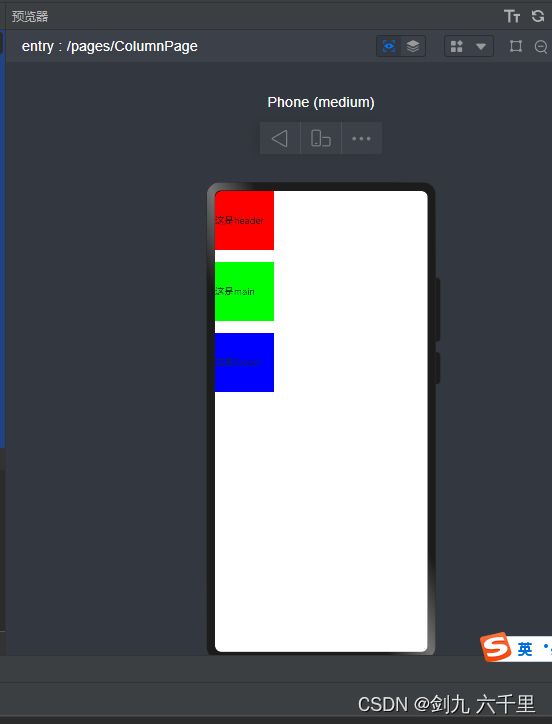
基本使用
@Entry @Component struct ColumnPage { build() { Column() { Text('这是header') .backgroundColor('red') .width(100) .height(100) Text('这是main') .backgroundColor('green') .width(100) .height(100) Text('这是footer') .backgroundColor('blue') .width(100) .height(100) } } } -
column接收参数,增加间距
@Entry @Component struct ColumnPage { build() { Column({ space: 20 }) { Text('这是header') .backgroundColor('red') .width(100) .height(100) Text('这是main') .backgroundColor('green') .width(100) .height(100) Text('这是footer') .backgroundColor('blue') .width(100) .height(100) } } } -
写一个常见的水平垂直居中布局

此处的.alignItems(HorizontalAlign.Center)和.justifyContent(FlexAlign.Center)可以理解为css中的Flex布局。Flex常用的属性都可以使用,更多使用可以查看官方文档。@Entry @Component struct ColumnPage { build() { Column({ space: 20 }) { Text('这是header') .backgroundColor('red') .width(100) .height(100) Text('这是main') .backgroundColor(Color.Green) .width(100) .height(100) Text('这是footer') .backgroundColor(Color.Blue) .width(100) .height(100) } .width('100%') .height('100%') .alignItems(HorizontalAlign.Center) // .alignItems(HorizontalAlign.Start) // .alignItems(HorizontalAlign.End) .justifyContent(FlexAlign.Center) // .justifyContent(FlexAlign.End) // .justifyContent(FlexAlign.SpaceBetween) } }
一般来说Column组件搭配Row组件一起使用,来实现一些常见的布局样式。
3.3 Row 行组件
水平排列的组件,主轴是X,内部可以书写任意组件(注意build组件内只能有一个根组件)
- 基本使用

使用方法和Column组件基本一致:@Entry @Component struct RowPage { build() { Row({ space: 20 }) { Text('这是header') .backgroundColor('red') .width(80) .height(100) Text('这是main') .backgroundColor(Color.Green) .width(80) .height(100) Text('这是footer') .backgroundColor(Color.Blue) .width(80) .height(100) } .width('100%') .height('100%') } } - 写一个常见的布局样式

flex布局常见的属性在Row组件中同样适用:@Entry @Component struct RowPage { build() { Row({ space: 20 }) { Text('这是header') .backgroundColor('red') .width(80) .height(100) Text('这是main') .backgroundColor(Color.Green) .width(80) .height(100) Text('这是footer') .backgroundColor(Color.Blue) .width(80) .height(100) } .width('100%') .height('100%') .alignItems(VerticalAlign.Center) .justifyContent(FlexAlign.Center) } }
3.4 Flex 以弹性方式容器组件
弹性盒布局,不了解弹性盒布局的同学可先学习一下css中的弹性盒布局。官方推荐使用Row和Column组件。
-
基本使用

column是一列多行展示,通过Flex组件将其一行展示:@Entry @Component struct FlexPage { build() { Flex() { Column() { Text('这是header') .backgroundColor('red') .width(80) .height(100) } Column() { Text('这是main') .backgroundColor(Color.Green) .width(80) .height(100) } Column() { Text('这是footer') .backgroundColor(Color.Blue) .width(80) .height(100) } } .width('100%') .height('100%') } } -
写一个常见的布局样式(水平垂直居中)
@Entry @Component struct FlexPage { build() { Flex({ direction: FlexDirection.Row, alignItems: ItemAlign.Center, justifyContent: FlexAlign.Center}) { Column() { Text('这是header') .backgroundColor('red') .width(80) .height(100) } Column() { Text('这是main') .backgroundColor(Color.Green) .width(80) .height(100) } Column() { Text('这是footer') .backgroundColor(Color.Blue) .width(80) .height(100) } } .width('100%') .height('100%') } }
3.5 Grid 网格布局组件
注意:Grid组件内部只能使用GridItem组件
Grid组件和css中的display:grid;属性原理基本是一致的。前端同学可以按css中的grid布局来理解这个Grid组件。
-
基本使用

columnsTemplate 写几个参数表示有几列 此处表示有两列:
fr 表示份数,此处表示将宽度等分成3份,第一列占 1/3,第二列占 2/3:
rowsTemplate 写几个参数就有几行 此处表示有四行:
fr 表示份数,此处表示将高度等分成5分,第二行占 2/5,其他行各占 1/5:@Entry @Component struct GridPage { build() { Grid() { GridItem() { Text('1') }.backgroundColor(Color.Red) GridItem() { Text('2') }.backgroundColor(Color.Blue) GridItem() { Text('3') }.backgroundColor(Color.Gray) GridItem() { Text('4') }.backgroundColor(Color.Green) GridItem() { Text('5') }.backgroundColor(Color.Orange) GridItem() { Text('6') }.backgroundColor(Color.Pink) GridItem() { Text('7') }.backgroundColor(Color.Yellow) GridItem() { Text('8') }.backgroundColor(Color.Grey) } .width('100%') .height(500) // columnsTemplate 写几个参数表示有几列 此处表示有两列 // fr 表示份数,此处表示将宽度等分成3份,第一列占 1/3,第二列占 2/3 .columnsTemplate('1fr 2fr') // rowsTemplate 写几个参数就有几行 此处表示有四行 // fr 表示份数,此处表示将高度等分成5分,第二行占 2/5,其他行各占 1/5 .rowsTemplate('1fr 2fr 1fr 1fr') // 列和列之间的间距 .columnsGap(5) // 行和行之间的间距 .rowsGap(5) } } -
写一个常见的布局样式
合并行或者合并列:
.columnStart(1).columnEnd(2) 表示第一列和第二列盒子合并,第三列会被挤到下一行去:
.rowStart(1).rowEnd(2) 表示当前行和下一行合并:@Entry @Component struct GridPage { build() { Grid() { GridItem() { Text('1') // .columnStart(1).columnEnd(2) 表示第一列和第二列盒子合并,第三列会被挤到下一行去 }.backgroundColor(Color.Red).columnStart(1).columnEnd(2) GridItem() { Text('2') }.backgroundColor(Color.Blue) GridItem() { Text('3') }.backgroundColor(Color.Gray) GridItem() { Text('4') // .rowStart(1).rowEnd(2) 表示当前行和下一行合并 }.backgroundColor(Color.Green).rowStart(1).rowEnd(2) GridItem() { Text('5') }.backgroundColor(Color.Orange) GridItem() { Text('6') }.backgroundColor(Color.Pink) GridItem() { Text('7') }.backgroundColor(Color.Yellow) GridItem() { Text('8') }.backgroundColor(Color.Grey) } .width('100%') .height('100%') // columnsTemplate 写几个参数表示有几列 此处表示有两列 // fr 表示份数,此处表示将宽度等分成3份,第一列占 1/3,第二列占 2/3 .columnsTemplate('1fr 2fr 1fr') // rowsTemplate 写几个参数就有几行 此处表示有四行 // fr 表示份数,此处表示将高度等分成5分,第二行占 2/5,其他行各占 1/5 .rowsTemplate('1fr 2fr 1fr 1fr') // 列和列之间的间距 .columnsGap(5) // 行和行之间的间距 .rowsGap(5) } }
3.6 Button 按钮组件
-
基础用法
@Entry @Component struct ButtonPage { build() { Button() { Text('登陆') } .height(100) .width(200) } } -
事件绑定(支持通用事件)

必须使用箭头函数,this指向问题:
接收一个参数,事件对象:@Entry @Component struct ButtonPage { @State message: string = '我被点击了' build() { Button() { Text('登陆') } .height(100) .width(200) .onClick(() => { // 必须使用箭头函数,this指向问题 console.log(this.message) }) } }还有很多的按钮样式属性,可以查看官方文档
3.7 TextInput 输入框组件
-
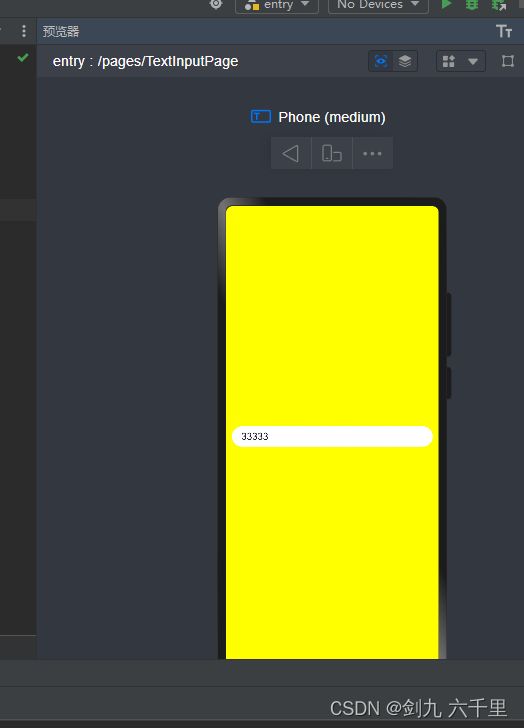
基本使用
@Entry @Component struct TextInputPage { build() { Row() { TextInput().backgroundColor(Color.White) } .height('100%') .width('100%') .backgroundColor(Color.Yellow) .padding(10) } } -
增加placeholder
@Entry @Component struct TextInputPage { build() { Row() { TextInput({ placeholder: '请输入用户名'}) .backgroundColor(Color.White) } .height('100%') .width('100%') .backgroundColor(Color.Yellow) .padding(10) } } -
@Entry @Component struct TextInputPage { build() { Row() { TextInput({ placeholder: '请输入用户名', text: 'admin'}) .backgroundColor(Color.White) } .height('100%') .width('100%') .backgroundColor(Color.Yellow) .padding(10) } } -
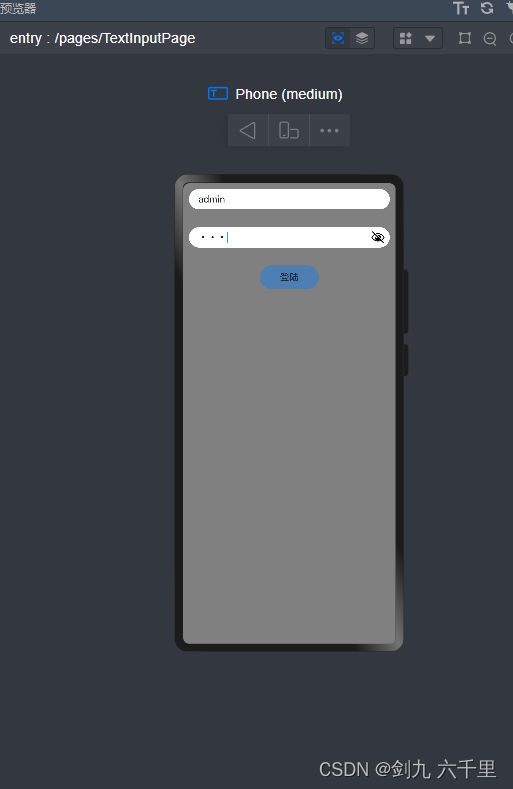
写一个基本的登陆功能

演示了基本的数据声明/数据绑定/事件绑定等:@Entry @Component struct TextInputPage { @State userName: string = '' @State password: string = '' build() { Column({space: 30}) { Row() { TextInput({ placeholder: '请输入用户名', text: 'admin'}) .backgroundColor(Color.White) .onChange(value => { this.userName = value }) } Row() { TextInput({ placeholder: '请输入密码'}) .backgroundColor(Color.White) .type(InputType.Password) .onChange(value => { this.password = value }) } Row() { Button() { Text('登陆') } .width(100) .height(40) .onClick(() => { console.log(this.userName) console.log(this.password) }) } } .height('100%') .width('100%') .backgroundColor(Color.Grey) .padding(10) } }点击登录的时候数据已经是响应式的了:
-
@Entry @Component struct TextInputPage { @State userName: string = '' @State password: string = '' validate() { return !this.userName || !this.password ? true : false } build() { Column({space: 30}) { Row() { TextInput({ placeholder: '请输入用户名', text: 'admin'}) .backgroundColor(Color.White) .onChange(value => { this.userName = value }) } Row() { TextInput({ placeholder: '请输入密码'}) .backgroundColor(Color.White) .type(InputType.Password) .onChange(value => { this.password = value }) } Row() { Button() { Text('登陆') } .width(100) .height(40) .enabled(this.validate()) .onClick(() => { if(this.userName === 'admin' && this.password === 'admin123') { AlertDialog.show({ message:"登录成功啦" }) } else { AlertDialog.show({ message:"登录失败啦" }) } }) } } .height('100%') .width('100%') .backgroundColor(Color.Grey) .padding(10) } }
3.8 Image 图片组件
3.9 Toggle 切换组件
3.10 Slider 滑块组件
3.11 progress 进度条组件
3.12 Stack 堆叠组件
3.13 Blank 组件
3.14 Divider 分割线组件
3.15 List 列表组件
3.16 Scroll 滚动组件
四、补充:在编辑器中查看组件文档
4.1 DevEco Studio编辑器内查看官方文档
鼠标悬停到组件上,在出来的弹窗中点击查询API参考: