基于注解管理bean
文章目录
- 一、标记与扫描
-
- 1、标记
- 2、扫描
- 组件的beanName
- 二、自动装配
- 三、纯注解开发模式
-
-
-
- 1、创建配置类(SpringConfig)
- 2、加载配置类
- 3、测试
- 加载第三方配置文件.properties
- 使用@Bean配置第三方Bean
-
-
- 四、bean的作用范围与生命周期管理
一、标记与扫描
1、标记
①使用@Component注解标记的普通组件
②使用@Controller注解标记的控制器组件
③使用@Service注解标记的业务逻辑组件
④使用@Repository注解标记的持久化层组件
@Controller、@Service、@Repository这三个注解只是在@Component注解的基础上起了三个新的名字。
对于Spring使用IOC容器管理这些组件来说没有区别。所以@Controller、@Service、@Repository这三个注解只是给开发人员看的,让我们能够便于分辨组件的作用。
注意:虽然它们本质上一样,但是为了代码的可读性,为了程序结构严谨我们肯定不能随便胡乱标记。
2、扫描
①情况一:最基本的扫描方式[常用]
<context:component-scan base-package="com.iflytek">context:component-scan>
②情况二:指定匹配模式
这种模式只会扫描com.iflytek下的文件,不会扫描子包
<context:component-scan base-package="com.iflytek" resource-pattern="Book*.class">context:component-scan>
③情况三:指定要排除的组件
排除了使用@Controller注解注入的bean
<context:component-scan base-package="com.iflytek">
<context:exclude-filter type="annotation" expression="org.springframework.stereotype.Controller"/>
context:component-scan>
④情况四:仅扫描指定组件
<context:component-scan base-package="com.iflytek" use-default-filters="false">
<context:include-filter type="annotation" expression="org.springframework.stereotype.Controller"/>
context:component-scan>
组件的beanName
在我们使用XML方式管理bean的时候,每个bean都有一个唯一标识,便于在其他地方引用。现在使用注解后,每个组件仍然应该有一个唯一标识。
①默认情况
类名首字母小写就是bean的id。例如:SoldierController类对应的bean的id就是soldierController。
②使用value属性指定
eg:@Controller(value = (“bookController”))
二、自动装配
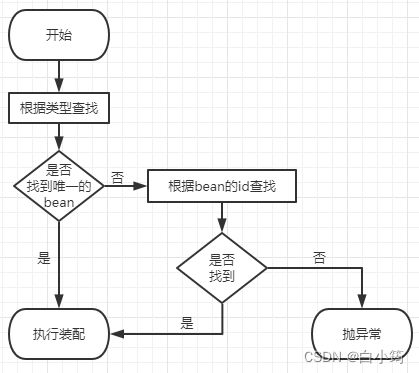
@Autowired:先根据类型装配,如果有多个相同类型的bean,再根据id装配
@Qualifier:指定名称,按照名称来查找,通常和@Autowired注解搭配使用
@Resource:默认按照名称自动装配,如果名称找不到的话,就按照类型动装配
1.定义一个service接口和两个实现类
public interface BookService {
void getBook();
}
@Service
public class BookServiceImpl implements BookService {
@Override
public void getBook() {
System.out.println("获取书本");
}
}
@Service
public class BookServiceImpl2 implements BookService {
@Override
public void getBook() {
System.out.println("获取书本2");
}
}
2、在BookController中注入这个BookService
@Controller
public class BookController {
@Autowired
private BookService bookService;
public void getBook(){
bookService.getBook();
}
}
这里肯定是注入失败的,因为有两个BookService的实现类
解决办法:① @Autowired+@Qualifie注解
@Controller
public class BookController {
@Autowired
@Qualifier(value = "bookServiceImpl2")
private BookService bookService;
public void getBook(){
bookService.getBook();
}
}
②修改其中一个Service的id
@Service(value = "bookService")
public class BookServiceImpl implements BookService {
@Override
public void getBook() {
System.out.println("获取书本");
}
}
@Service(value = "bookService2")
public class BookServiceImpl2 implements BookService {
@Override
public void getBook() {
System.out.println("获取书本2");
}
}
@Autowired注解其他细节
①标记在其他位置
[1]构造器
@Controller(value = "tianDog")
public class SoldierController {
private SoldierService soldierService;
@Autowired
public SoldierController(SoldierService soldierService) {
this.soldierService = soldierService;
}
[2]setXxx()方法
@Controller(value = "tianDog")
public class SoldierController {
private SoldierService soldierService;
@Autowired
public void setSoldierService(SoldierService soldierService) {
this.soldierService = soldierService;
}
三、纯注解开发模式
没有配置文件ApplicationContext.xml文件
1、创建配置类(SpringConfig)
等同于ApplicationContext.xml文件
@Configuration
@ComponentScan("com.itheima.service.impl")
public class SpringConfig {
}
使用@Configuration注解消除配置文件中的下面这段代码
使用@ComponentScan消除消除配置文件中的下面这段代码
@Configuration注解用于设定当前类为配置类
@ComponentScan注解用于设定扫描路径,此注解只能添加一次,多个数据请用数组格式
2、加载配置类
使用配置文件时:
ApplicationContext applicationContext=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
使用纯注解开发后:
ApplicationContext ctx=new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfig.class);
3、测试
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext applicationContext=new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfig.class);
BookService bean = applicationContext.getBean(BookService.class);
bean.save();
}
加载第三方配置文件.properties
使用@PropertySource
在配置类中
如果要加载多个Properties文件
设置为集合的格式
@PropertySource({"jdbc2.properties"})
使用@Bean配置第三方Bean
并且不要写在SpringCongfig配置类中
创建一个JdbcConfig类
public class JdbcConfig {
//1.定义一个方法获得要管理的对象
//2.添加@Bean,表示当前方法的返回值是一个bean
@Bean
public DataSource dataSource(){
DruidDataSource ds=new DruidDataSource();
ds.setDriverClassName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
ds.setUrl("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/spring_db");
ds.setUsername("root");
ds.setPassword("20020630");
return ds;
}
}
在配置类SpringConfig类中使用@Import导入这个类
@Configuration
@Import(JdbcConfig.class)
public class SpringConfig {
}
四、bean的作用范围与生命周期管理
@Scope(“singleton”)单例模式
@Scope(“prototype”)非单例模式
生命周期:
@PostConstruct初始化
@PreDestroy销毁
注意:使用JDK11需要导入依赖坐标
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.annotationgroupId>
<artifactId>javax.annotation-apiartifactId>
<version>1.3.2version>
dependency>
使用举例:
@Component
public class BookServiceImpl implements BookService {
public void save() {
System.out.println("BookService!");
}
@PostConstruct
public void init(){
System.out.println("初始化");
}
@PreDestroy
public void destory(){
System.out.println("销毁前");
}
}