通过.net reflector了解asp.net站点的请求与响应过程
通过.NET Reflerctor我们可以反编译看一个请求是如何被响应处理的。以下为请求被响应处理的过程涉及到的主要类
- ISAPIRuntime
- HttpRuntime
- HttpApplicationFactory
- HttpApplication
- HttpContext
- HttpModule
- HttpHanler
使用.net reflerctor读取.net 3.5 frameword类库
一、请求如何到达w3wp.exe进程
当站点已部署在IIS下时,这时有客户端请求到达,首先被www服务进程inetinfo.exe捕获,根据请求页面的后缀名由IIS配置处理程序映射的dll处理,如果是aspx页面就交由aspnet_isapi.dll处理,aspnet_isapi.dll再将请求分发给w3wp.exe进程(也就是我们在VS调试的时候附加的进程)。
二、如何创建HttpApplication管线
w3wp.exe进程先调用System.Web.Hosting下的ISAPIRuntime.ProcessRequest方法触发HttpRuntime
public int ProcessRequest(IntPtr ecb, int iWRType)
{
IntPtr zero = IntPtr.Zero;
if (iWRType == 2 )
{
zero = ecb;
ecb = UnsafeNativeMethods.GetEcb(zero);
}
ISAPIWorkerRequest wr = null ;
try
{
bool useOOP = iWRType == 1 ;
wr = ISAPIWorkerRequest.CreateWorkerRequest(ecb, useOOP);
wr.Initialize();
string appPathTranslated = wr.GetAppPathTranslated();
string appDomainAppPathInternal = HttpRuntime.AppDomainAppPathInternal;
if ((appDomainAppPathInternal == null ) || StringUtil.EqualsIgnoreCase(appPathTranslated, appDomainAppPathInternal))
{
HttpRuntime.ProcessRequestNoDemand(wr);
return 0 ;
}
HttpRuntime.ShutdownAppDomain(ApplicationShutdownReason.PhysicalApplicationPathChanged, SR.GetString( " Hosting_Phys_Path_Changed " , new object [] { appDomainAppPathInternal, appPathTranslated }));
return 1 ;
}
catch (Exception exception)
{
try
{
WebBaseEvent.RaiseRuntimeError(exception, this );
}
catch
{
}
if ((wr == null ) || ! (wr.Ecb == IntPtr.Zero))
{
throw ;
}
if (zero != IntPtr.Zero)
{
UnsafeNativeMethods.SetDoneWithSessionCalled(zero);
}
if (exception is ThreadAbortException)
{
Thread.ResetAbort();
}
return 0 ;
}
}
ISAPIRuntime生成了一个HttpWorkerRequest对象(即HttpContext.Current),并传递给HttpRuntime。接着执行HttpRuntime.ProcessRequestNoDemand方法
internal static void ProcessRequestNoDemand(HttpWorkerRequest wr)
{
RequestQueue queue = _theRuntime._requestQueue;
if (queue != null )
{
wr = queue.GetRequestToExecute(wr);
}
if (wr != null )
{
CalculateWaitTimeAndUpdatePerfCounter(wr);
wr.ResetStartTime();
ProcessRequestNow(wr);
}
}
转到HttpRuntime.ProcessRequestNow方法
internal static void ProcessRequestNow(HttpWorkerRequest wr)
{
_theRuntime.ProcessRequestInternal(wr);
}
继续调用HttpRuntime.ProcessRequestInternal方法
private void ProcessRequestInternal(HttpWorkerRequest wr)
{
HttpContext context;
try
{
context = new HttpContext(wr, false );
}
catch
{
wr.SendStatus( 400 , " Bad Request " );
wr.SendKnownResponseHeader( 12 , " text/html; charset=utf-8 " );
byte [] bytes = Encoding.ASCII.GetBytes( " <html><body>Bad Request</body></html> " );
wr.SendResponseFromMemory(bytes, bytes.Length);
wr.FlushResponse( true );
wr.EndOfRequest();
return ;
}
wr.SetEndOfSendNotification( this ._asyncEndOfSendCallback, context);
Interlocked.Increment( ref this ._activeRequestCount);
HostingEnvironment.IncrementBusyCount();
try
{
try
{
this .EnsureFirstRequestInit(context);
}
catch
{
if ( ! context.Request.IsDebuggingRequest)
{
throw ;
}
}
context.Response.InitResponseWriter();
IHttpHandler applicationInstance = HttpApplicationFactory.GetApplicationInstance(context);
if (applicationInstance == null )
{
throw new HttpException(SR.GetString( " Unable_create_app_object " ));
}
if (EtwTrace.IsTraceEnabled( 5 , 1 ))
{
EtwTrace.Trace(EtwTraceType.ETW_TYPE_START_HANDLER, context.WorkerRequest, applicationInstance.GetType().FullName, " Start " );
}
if (applicationInstance is IHttpAsyncHandler)
{
IHttpAsyncHandler handler2 = (IHttpAsyncHandler) applicationInstance;
context.AsyncAppHandler = handler2;
handler2.BeginProcessRequest(context, this ._handlerCompletionCallback, context);
}
else
{
applicationInstance.ProcessRequest(context);
this .FinishRequest(context.WorkerRequest, context, null );
}
}
catch (Exception exception)
{
context.Response.InitResponseWriter();
this .FinishRequest(wr, context, exception);
}
}
该方法创建了我们在后面经常用到的HttpContext上下文(请求与响应信息),接着通过 HttpApplicationFactory获取HttpApplication实例。
仔细看一下IHttpHandler
applicationInstance = HttpApplicationFactory.GetApplicationInstance(context) 方法
internal static IHttpHandler GetApplicationInstance(HttpContext context)
{
if (_customApplication != null )
{
return _customApplication;
}
if (context.Request.IsDebuggingRequest)
{
return new HttpDebugHandler();
}
_theApplicationFactory.EnsureInited();
_theApplicationFactory.EnsureAppStartCalled(context);
return _theApplicationFactory.GetNormalApplicationInstance(context);
}
如果HttpApplication实例存在就直接返回,不存就先执行_theApplicationFactory.EnsureInited();
private void EnsureInited()
{
if ( ! this ._inited)
{
lock ( this )
{
if ( ! this ._inited)
{
this .Init();
this ._inited = true ;
}
}
}
}
调用HttpApplicationFactory的Init方法(HttpApplicationFactory是单例模式)
private void Init()
{
if (_customApplication == null )
{
try
{
try
{
this ._appFilename = GetApplicationFile();
this .CompileApplication();
}
finally
{
this .SetupChangesMonitor();
}
}
catch
{
throw ;
}
}
}
主要看两个方法
internal static string GetApplicationFile()
{
return Path.Combine(HttpRuntime.AppDomainAppPathInternal, " global.asax " );
}
private void SetupChangesMonitor()
{
FileChangeEventHandler callback = new FileChangeEventHandler( this .OnAppFileChange);
HttpRuntime.FileChangesMonitor.StartMonitoringFile( this ._appFilename, callback);
if ( this ._fileDependencies != null )
{
foreach ( string str in this ._fileDependencies)
{
HttpRuntime.FileChangesMonitor.StartMonitoringFile(HostingEnvironment.MapPathInternal(str), callback);
}
}
}
读取global.asax文件(很熟悉吧,应用程序的全局配置文件),并添加事件监视。
再回到GetApplicationInstance方法中,执行_theApplicationFactory.GetNormalApplicationInstance(context) 从_freeList读取HttpApplication实例
或者通过反射创建新的HttpApplication实例。
private HttpApplication GetNormalApplicationInstance(HttpContext context)
{
HttpApplication application = null ;
lock ( this ._freeList)
{
if ( this ._numFreeAppInstances > 0 )
{
application = (HttpApplication) this ._freeList.Pop();
this ._numFreeAppInstances -- ;
if ( this ._numFreeAppInstances < this ._minFreeAppInstances)
{
this ._minFreeAppInstances = this ._numFreeAppInstances;
}
}
}
if (application == null )
{
application = (HttpApplication) HttpRuntime.CreateNonPublicInstance( this ._theApplicationType);
using ( new ApplicationImpersonationContext())
{
application.InitInternal(context, this ._state, this ._eventHandlerMethods);
}
}
return application;
}
三、何时加载HttpModule
当HttpApplication首次被创建的时候,我们可以看到上面的方法的实例化调用了HttpApplication的方法
application.InitInternal(context,
this._state,
this._eventHandlerMethods),这个方法将首先将HttpApplication实例绑到
HttpContext.ApplicationInstance 上,这样我们通过上下文可以找到HttpApplication实例。接着又调用了
this.InitModules()
去加载配置文件中的HttpModule
private void InitModules()
{
this ._moduleCollection = RuntimeConfig.GetAppConfig().HttpModules.CreateModules();
this .InitModulesCommon();
}
private void InitModulesCommon()
{
int count = this ._moduleCollection.Count;
for ( int i = 0 ; i < count; i ++ )
{
this ._currentModuleCollectionKey = this ._moduleCollection.GetKey(i);
this ._moduleCollection[i].Init( this );
}
this ._currentModuleCollectionKey = null ;
this .InitAppLevelCulture();
}
Module被反射加载后,在InitMoulesCommon中会调会HttpModule的Init方法。
我们来看一配置文件,Module加载是按照配置文件的顺序,所以事件被触发也是按照这个顺序。另外.net 的module是优先加载的,例如Session等。
< httpModules >
< add name = " ScriptModule " type = " System.Web.Handlers.ScriptModule, System.Web.Extensions, Version=3.5.0.0, Culture=neutral, PublicKeyToken=31BF3856AD364E35 " />
< add name = " UrlRoutingModule " type = " System.Web.Routing.UrlRoutingModule, System.Web.Routing, Version=3.5.0.0, Culture=neutral, PublicKeyToken=31BF3856AD364E35 " />
</ httpModules >
我们再回HttpApplication的 InitInternal方法,当 InitModules()创建HttpModuleCollection后,在HookupEventHandlersForApplicationAndModules方法中绑定Module的事件处理
接着就是HttpApplication的管线事件和HttpHandler的有序绑定。
接着就是HttpApplication的管线事件和HttpHandler的有序绑定。
if (HttpRuntime.UseIntegratedPipeline)
{
this ._stepManager = new PipelineStepManager( this );
}
else
{
this ._stepManager = new ApplicationStepManager( this );
}
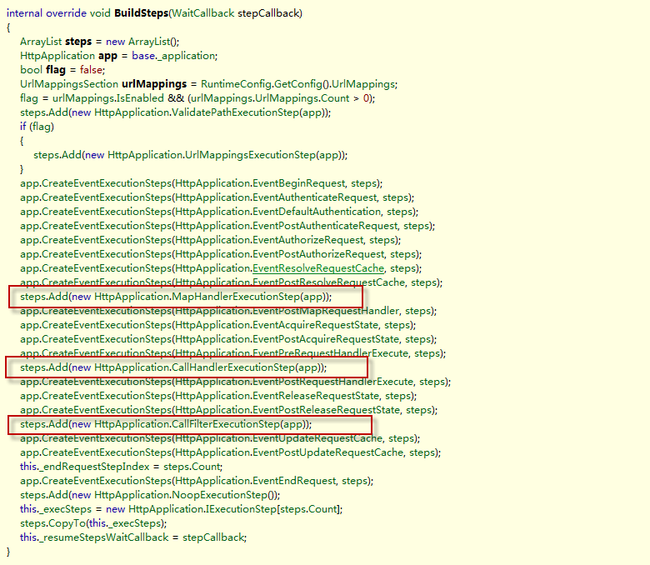
this ._stepManager.BuildSteps( this ._resumeStepsWaitCallback);
ApplicationManager和PipelineStepManager都继随自HttpApplication.StepManager。SetpManager主HttpApplication的内部调度类,主要负责HttpApplication管线的事件和HttpHandler有序绑定和执行工作。
题外话:HttpApplication本身不对请求做任何处理,而是交由HttpModule与HttpHandler,而HttpModule不仅决定了使用什么HttpHandler,并且还可以修改请求和响应信息。当HttpModule把处理权交给HttpHandler后,HttpHandler才能从上下文取出请求做相应处理。(WebForm与MVC差别从这里开始不同了)。
四、HttpHandler
HttpHandler是我们真正.net 程序处理代码的位置(Page,Controller,Session操作等等)
里只是建立了好管线事件的触发顺序以及HttpHandler的加载与执行句柄等,但是直正触发管道执行的,还是要回到HttpRuntime的
ProcessRequestInternal的方法中。
steps.
Add(
new HttpApplication.MapHandlerExecutionStep(app))添加加载反射HttpHandler的MapHandlerExecutionSte到Steps中;注意他的Execute方法是加载。
internal class MapHandlerExecutionStep : HttpApplication.IExecutionStep
{
// Fields
private HttpApplication _application;
// Methods
internal MapHandlerExecutionStep(HttpApplication app)
{
this ._application = app;
}
void HttpApplication.IExecutionStep.Execute()
{
HttpContext context = this ._application.Context;
HttpRequest request = context.Request;
if (EtwTrace.IsTraceEnabled( 5 , 1 ))
{
EtwTrace.Trace(EtwTraceType.ETW_TYPE_MAPHANDLER_ENTER, context.WorkerRequest);
}
context.Handler = this ._application.MapHttpHandler(context, request.RequestType, request.FilePathObject, request.PhysicalPathInternal, false );
if (EtwTrace.IsTraceEnabled( 5 , 1 ))
{
EtwTrace.Trace(EtwTraceType.ETW_TYPE_MAPHANDLER_LEAVE, context.WorkerRequest);
}
}
// Properties
bool HttpApplication.IExecutionStep.CompletedSynchronously
{
get
{
return true ;
}
}
bool HttpApplication.IExecutionStep.IsCancellable
{
get
{
return false ;
}
}
}
steps.Add(
new HttpApplication.CallHandlerExecutionStep(app));这个CallHandlerExecutionStep是触发HttpHandler的Step,我们来看一下他的Exectue方法
internal class CallHandlerExecutionStep : HttpApplication.IExecutionStep
{
// Fields
private HttpApplication _application;
private AsyncCallback _completionCallback;
private IHttpAsyncHandler _handler;
private bool _sync;
// Methods
internal CallHandlerExecutionStep(HttpApplication app)
{
this ._application = app;
this ._completionCallback = new AsyncCallback( this .OnAsyncHandlerCompletion);
}
private void OnAsyncHandlerCompletion(IAsyncResult ar)
{
if ( ! ar.CompletedSynchronously)
{
HttpContext context = this ._application.Context;
Exception error = null ;
try
{
try
{
this ._handler.EndProcessRequest(ar);
}
finally
{
context.Response.GenerateResponseHeadersForHandler();
}
}
catch (Exception exception2)
{
if ((exception2 is ThreadAbortException) || ((exception2.InnerException != null ) && (exception2.InnerException is ThreadAbortException)))
{
this ._application.CompleteRequest();
}
else
{
error = exception2;
}
}
if (EtwTrace.IsTraceEnabled( 4 , 4 ))
{
EtwTrace.Trace(EtwTraceType.ETW_TYPE_HTTPHANDLER_LEAVE, context.WorkerRequest);
}
this ._handler = null ;
context.SetStartTime();
this .ResumeStepsWithAssert(error);
}
}
[PermissionSet(SecurityAction.Assert, Unrestricted = true )]
private void ResumeStepsWithAssert(Exception error)
{
this ._application.ResumeStepsFromThreadPoolThread(error);
}
void HttpApplication.IExecutionStep.Execute()
{
HttpContext context = this ._application.Context;
IHttpHandler handler = context.Handler;
if (EtwTrace.IsTraceEnabled( 4 , 4 ))
{
EtwTrace.Trace(EtwTraceType.ETW_TYPE_HTTPHANDLER_ENTER, context.WorkerRequest);
}
if ((handler != null ) && HttpRuntime.UseIntegratedPipeline)
{
IIS7WorkerRequest workerRequest = context.WorkerRequest as IIS7WorkerRequest;
if ((workerRequest != null ) && workerRequest.IsHandlerExecutionDenied())
{
this ._sync = true ;
HttpException exception = new HttpException( 0x193 , SR.GetString( " Handler_access_denied " ));
exception.SetFormatter( new PageForbiddenErrorFormatter(context.Request.Path, SR.GetString( " Handler_access_denied " )));
throw exception;
}
}
if (handler == null )
{
this ._sync = true ;
}
else if (handler is IHttpAsyncHandler)
{
IHttpAsyncHandler handler2 = (IHttpAsyncHandler) handler;
this ._sync = false ;
this ._handler = handler2;
IAsyncResult result = handler2.BeginProcessRequest(context, this ._completionCallback, null );
if (result.CompletedSynchronously)
{
this ._sync = true ;
this ._handler = null ;
try
{
handler2.EndProcessRequest(result);
}
finally
{
context.Response.GenerateResponseHeadersForHandler();
}
if (EtwTrace.IsTraceEnabled( 4 , 4 ))
{
EtwTrace.Trace(EtwTraceType.ETW_TYPE_HTTPHANDLER_LEAVE, context.WorkerRequest);
}
}
}
else
{
this ._sync = true ;
context.SyncContext.SetSyncCaller();
try
{
handler.ProcessRequest(context);
}
finally
{
context.SyncContext.ResetSyncCaller();
if (EtwTrace.IsTraceEnabled( 4 , 4 ))
{
EtwTrace.Trace(EtwTraceType.ETW_TYPE_HTTPHANDLER_LEAVE, context.WorkerRequest);
}
context.Response.GenerateResponseHeadersForHandler();
}
}
}
// Properties
bool HttpApplication.IExecutionStep.CompletedSynchronously
{
get
{
return this ._sync;
}
}
bool HttpApplication.IExecutionStep.IsCancellable
{
get
{
return ! ( this ._application.Context.Handler is IHttpAsyncHandler);
}
}
}
注意Execute方法调用了HttpHandler的BeginProcessRequest或ProcessRequst。这就HttpHandler的直正接手处理请求的入口,但这里都StepManager的准备工作。
它的触发过程:->HttpRuntime获取到HttpApplication,并调用的HttpApplication.BeginProcessRequest->HttpApplication.StepManager.ResumeSteps
->HttpApplication.StepManager._execSteps[i].Execute ->HttpHandler.ProcessRequest
当通过IHttpHandler
applicationInstance = HttpApplicationFactory.GetApplicationInstance(context); 获取实例后,HttpRuntime开始触发application的请求处理
即调用HttpApplication的BeginProcessRequest方法
if (applicationInstance is IHttpAsyncHandler)
{
IHttpAsyncHandler handler2 = (IHttpAsyncHandler) applicationInstance;
context.AsyncAppHandler = handler2;
handler2.BeginProcessRequest(context, this ._handlerCompletionCallback, context);
}
else
{
applicationInstance.ProcessRequest(context);
this .FinishRequest(context.WorkerRequest, context, null );
}
看一下BeginProcessRequest方法
IAsyncResult IHttpAsyncHandler.BeginProcessRequest(HttpContext context, AsyncCallback cb, object extraData)
{
this ._context = context;
this ._context.ApplicationInstance = this ;
this ._stepManager.InitRequest();
this ._context.Root();
HttpAsyncResult result = new HttpAsyncResult(cb, extraData);
this .AsyncResult = result;
if ( this ._context.TraceIsEnabled)
{
HttpRuntime.Profile.StartRequest( this ._context);
}
this .ResumeSteps( null );
return result;
}
void IHttpHandler.ProcessRequest(HttpContext context)
{
throw new HttpException(SR.GetString( " Sync_not_supported " ));
}
BeginProcessRequest方法调用
StepManager的InitRequest(初始化执行顺序的参数),然后接着调用了最重要的
ResumeSteps方法,此方法将按顺序执行
StepManager中保存HttpApplication绑定的事件及HttpHandler。
分析一下
ResumeSteps 方法
[DebuggerStepperBoundary]
internal override void ResumeSteps(Exception error)
{
bool flag = false ;
bool completedSynchronously = true ;
HttpApplication application = base ._application;
HttpContext context = application.Context;
HttpApplication.ThreadContext context2 = null ;
AspNetSynchronizationContext syncContext = context.SyncContext;
lock ( base ._application)
{
try
{
context2 = application.OnThreadEnter();
}
catch (Exception exception)
{
if (error == null )
{
error = exception;
}
}
try
{
try
{
Label_0040:
if (syncContext.Error != null )
{
error = syncContext.Error;
syncContext.ClearError();
}
if (error != null )
{
application.RecordError(error);
error = null ;
}
if (syncContext.PendingOperationsCount > 0 )
{
syncContext.SetLastCompletionWorkItem( this ._resumeStepsWaitCallback);
}
else
{
if (( this ._currentStepIndex < this ._endRequestStepIndex) && ((context.Error != null ) || base ._requestCompleted))
{
context.Response.FilterOutput();
this ._currentStepIndex = this ._endRequestStepIndex;
}
else
{
this ._currentStepIndex ++ ;
}
if ( this ._currentStepIndex >= this ._execSteps.Length)
{
flag = true ;
}
else
{
this ._numStepCalls ++ ;
context.SyncContext.Enable();
error = application.ExecuteStep( this ._execSteps[ this ._currentStepIndex], ref completedSynchronously);
if (completedSynchronously)
{
this ._numSyncStepCalls ++ ;
goto Label_0040;
}
}
}
}
finally
{
if (context2 != null )
{
try
{
context2.Leave();
}
catch
{
}
}
}
}
catch
{
throw ;
}
}
if (flag)
{
context.Unroot();
application.AsyncResult.Complete( this ._numStepCalls == this ._numSyncStepCalls, null , null );
application.ReleaseAppInstance();
}
}
留意代码会发现
Label_0040
this._currentStepIndex++;
error = application.ExecuteStep(
this._execSteps[
this._currentStepIndex],
ref completedSynchronously);
goto Label_0040;
每执行完
StepManager中_execSteps保存事件或httpHandler就+1 goto 到下一次的事件或httpHandler。
ExecuteStep调用了 step.Execute(),接着Execute又执行了HttpHandler的ProecessRequest方法。这个时候请求就直正交到了HttpHandler手里处理了。
以下HttpApplication管线执行先后顺序,订阅事件,HttpModule,HttpHanlder加载与执行位置(参照博文:
ASP.NET MVC Preview生命周期分析)
HttpApplication 管线会依次处理下面的请求:
-
对请求进行验证,将检查浏览器发送的信息,并确定其是否包含潜在恶意标记。
-
如果已在 Web.config 文件的 UrlMappingsSection 节中配置了任何 URL,则执行 URL 映射。
-
引发 BeginRequest 事件。
-
引发 AuthenticateRequest 事件。
-
引发 PostAuthenticateRequest 事件。
-
引发 AuthorizeRequest 事件。
-
引发 PostAuthorizeRequest 事件。
-
引发 ResolveRequestCache 事件。
-
引发 PostResolveRequestCache 事件。通知HttpModule根据请求选择对应的HttpHnadler加载至上下文中。
-
根据所请求资源的文件扩展名(在应用程序的配置文件中映射),选择实现 IHttpHandler 的类,对请求进行处理。如果该请求针对从 Page 类派生的对象(页),并且需要对该页进行编译,则 ASP.NET 会在创建该页的实例之前对其进行编译。(除了配置文件中的,还有上下文中的HttpHnadler)
-
引发 PostMapRequestHandler 事件。继续通知HttpModule确定要使用哪个HttpHandler用以处理请求。
-
引发 AcquireRequestState 事件。
-
引发 PostAcquireRequestState 事件。
-
引发 PreRequestHandlerExecute 事件。
-
为该请求调用合适的 IHttpHandler 类的 ProcessRequest 方法(或异步版 BeginProcessRequest)。例如,如果该请求针对某页,则当前的页实例将处理该请求。
-
引发 PostRequestHandlerExecute 事件。
-
引发 ReleaseRequestState 事件。
-
引发 PostReleaseRequestState 事件。
-
如果定义了 Filter 属性,则执行响应筛选。
-
引发 UpdateRequestCache 事件。
-
引发 PostUpdateRequestCache 事件。
-
引发 EndRequest 事件。
小结:
理一下前后的过程
ISAPIRuntime 调用至HttpRuntime , HttpRuntime 通过HttpApplicationFactory 获取HttpApplication,HttpApplication在生成的同时加载了所有的HttpMoudule,并且通过StepManager完
成对管线事件绑定及HttpHandler的加载。然后HttpRuntime 触发HttpApplication 的BeginProcessRequest开始了真正的HttpRequest请求的处理过程。
HttpApplication按照管线StepManager事先设定好的事件触发顺序,当被HttpModule订阅的事件发生,HttpModule根据请求的信息加载对应的HttpHandler到上下文中,并把控制权还给管线。
HttpApplication继续按照管线进行,将所有的HttpHandler加载进来。之后过程中通过HttpModule确定使用哪个HttpHandler处理请求,直到管线调用这个 HttpHandler的ProcessRequest,这个时候HttpHandler才开始着手处理上下文中的请求,比如查找请求的具体页面地址,调用请求的方法,绘制视图等等。
HttpHandler 处理完后,HttpApplication管线又将上下文的控制交还给HttpModule,HttpModule对请求最后处理后,又把控制权还给管线继续处理下面的事件,直到HttpRuntime 结束请求返回客户端。
以上是为.net MVC 实现机制分析做的铺垫。