WPF开发基于导航的WINDOWS程序
随着.net framework3.5的发布,在新的操作系统下(如VISTA、WIN7)中我们看到了大量炫丽的软件界面设计,使传统的WINFORM程序和WEB程序的界限变得模糊。
主要内容 使用WPF开发基于导航的WINDOWS程序
技术问题 PAGE 切换
WPF中使用NavigationWindow容器来放置Page,关于NavigationWindow的使用不在本篇的讲解范围;
1.1 WPF中Page切换三种方法
1.Page调用NavigationService.Navigate;
2.XAML中使用Hyperlinks标签;
3.NavigationWindow的导航日志;
一、Page调用NavigationService.Navigate
1.新建一个项目;
2.在XAML中添加一个NavigationWindow;
3.NavigationWindow 中 Source指向Page1.xaml;
如下:
<NavigationWindow x:Class="WpfApplication1.MainWindow"
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"
Title="PC集控系统" Height="250" Width="1000" ShowsNavigationUI="False" Source="Page1.xaml" ResizeMode="CanMinimize" WindowStartupLocation="CenterScreen" WindowStyle="SingleBorderWindow">
</NavigationWindow>
4.新建一个名为Page1.xaml和Page2.xaml的文件,在Page1中构建界面元素,如图:
Page2雷同;
5.右击菜单View code进入代码界面,如图:
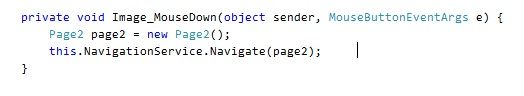
在Image鼠标事件中new一个Page2的对象,使用NavigationService.Navigate专至Page2
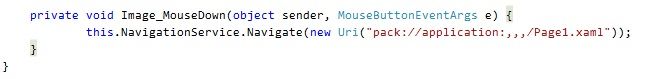
也可以使用URI的方法,如图:
在 Image鼠标事件中NavigationService.Navigate一个URI专至Page1
效果:
点击前:
点击后:
二、XAML中使用Hyperlinks标签
和HTML一样htperlinks提供已知的简单的链接,用法和HTML雷同,这里不做详细阐述;
用法:<Hyperlink NavigateUri="page1.xaml">转向到PAGE1</Hyperlink>
三、NavigationWindow的导航日志
返回上一页:this.NavigationService.GoBack
向前下一页:this.NavigationService.GoForward
1.2 Page数据传递
同样也有三种传递方法
1.通过NavigationService.Navigate传递参数
2.通过构造函数传递参数
3.通过Application.Properties的全局数据
一、通过NavigationService.Navigate传递参数
1.首先new一个page对象:
Page2 page2 = new Page2();
2.通过NavigationService.Navigate传递参数
this.NavigationService.Navigate(page2,"frompage1");
3.在Page2,处理NavigationWindow的LoadCompleted事件
this.NavigationService.LoadCompleted += new LoadCompletedEventHandler(page2_LoadCompleted);
4.在page2_LoadCompleted方法里获取传递过来的参数
void page2_LoadCompleted(object sender,NavigationEventArgs e)
{
if(e.ExtraData != null)
{
string args = e.ExtraData.toString();
}
}
二、通过构造函数传递参数
首先new一个page对象并用NavigationService.Navigate转向
Page2 page2 = new Page2("frompage1");
this.NavigationService.Navigate(page2);
在page2中定义构造函数
public Page2(string args)
{
string args2 = args;
}
三、通过Application.Properties的全局数据
用实例或URI导航到页面
Application.Properties["Args"] = "frompage2";
Page2 page2 = new Page2();
this.NavigationService.Navigate(page2);
在page2页面检查参数值
if(Application.Properties["Args"] != null)
{
string arg = Application.Properties["Args"];
}
2.1 Page与UC的比较
1.UC可以寄主在UIElement类下的任何容器类中,灵活性比较强;Page只能在NavigationWinodow下使用,可以把NavigationWinodow看成一个弱浏览器;
2.UC不具备导航功能;Page具备导航功能,可以把PAGE的历史保存在Cache、Properties中供容器定位页面;
3.UC和Page一样可以做为其他构件的容器;
4.从定义上说PageFunction和UC雷同;
5.在应用层面:
Page配合NavigationWinodow用于开发软件业务流程关注界面流程框架;
UC把多次出现的重复功能提取构成一个控件,关注于实现具体业务功能,理想的状态是一个系统由构件库的不同构件叠加而成(建筑行业的预制体系);
2.2 需要局部翻页的设计架构
Page可以在NavigationWinodow和Frame中,Frame用于局部翻页,NavigationWinodow用于整体翻页;
设计架构:
整体为一个Window对象包含一个UC和一个Frame,点击UC上的元素按钮对Frame进行翻页;
Window XAML code:
2 xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
3 xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"
4 xmlns:m="clr-namespace:WpfApplication1"
5 Title="Window2" Height="768" Width="1024" ResizeMode="CanMinimize" WindowStartupLocation="CenterScreen" Loaded="Window_Loaded">
6 <StackPanel>
7 <m:Menu x:Name="menuuc"></m:Menu>
8 <Frame x:Name="frame1" NavigationUIVisibility="Hidden"></Frame>
9 </StackPanel>
10 </Window>
Window CS code:
2 public partial class Window2 : Window {
3 public Window2() {
4 InitializeComponent();
5 }
6
7 private void Window_Loaded(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e) {
8 this.menuuc.MenuClicked += (o1, e1) => {
9 string uc = o1 as string ;
10 switch (uc) {
11 case "page1" :
12 this.frame1.NavigationService.Navigate(new Uri("pack://application:,,,/Page1.xaml" ));
13 break ;
14 case "page2" :
15 this.frame1.NavigationService.Navigate(new Uri("pack://application:,,,/Page2.xaml" ));
16
17 break ;
18 default :
19 break ;
20 }
21 };
22 }
23 }
24 }
UC CS code:
2 /// <summary>
3 /// Menu.xaml 的交互逻辑
4 /// </summary>
5 public partial class Menu : UserControl, INotifyPropertyChanged {
6 public event EventHandler MenuClicked;
7 public event PropertyChangedEventHandler PropertyChanged;
8 private string titletext = string .Empty;
9
10 public Menu() {
11 InitializeComponent();
12 }
13
14 ......
15
16 private void Image_MouseDown(object sender, MouseButtonEventArgs e) {
17 if (MenuClicked != null ) {
18 MenuClicked((e.Source as Image).Name, EventArgs.Empty);
19 ......
20 }
21 }
22
23
24 ......
25 }
26 }
转载时,请注明本文来源:www.cnblogs.com/tmywu
作者邮箱:[email protected]