《Algorithms 4th Edition》读书笔记——2.4 优先队列(priority queue)-Ⅴ
命题Q。对于一个含有N个元素的基于堆叠优先队列,插入元素操作只需要不超过(lgN + 1)次比较,删除最大元素的操作需要不超过2lgN次比较。
证明。由命题P可知,两种操作都需要在根节点和堆底之间移动元素,而路径的长度不超过lgN。对于路径上的每个节点,删除最大元素需要两次比比较(除了堆底元素),一次用来找出较大的子节点,一次用来确定该子节点是否需要上浮。
对于需要大量混杂的插入和删除最大元素操作的典型应用来说,命题Q意味着一个重要的性能突破(详见优先队列增长数量级表)。使用有序或是无序数组的优先队列的初级实现总是需要线性时间来完成其中一种操作,但基于堆底实现则能够抱枕在对数时间内完成他们。这种差别使得我们能够解决以前无法解决的问题。
2.4.4.3 多叉堆
基于用数组表示的完全三叉树构造堆并修改相应的代码并不困难。对于数组中1 至N 的N个元素,位置k的结点大于等于位于3k - 1、3k和3k + 1的结点,小于等于位于[(k + 1) / 3 (d)]的结点。甚至对于给定的d,将其修改为任意的d叉树也并不困难。我们需要在树高(logaN)和在每个节点的d个子节点找到最大者的代价之间找到折中,这取决于实现的细节以及不同操作的预期相对频繁程度。堆上的优先队列操作如右图。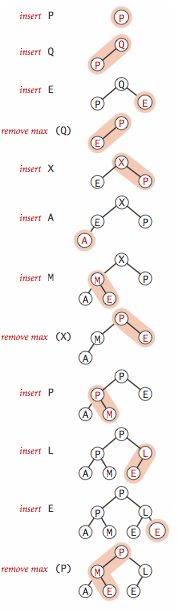
2.4.4.4 调整数组大小
我们可以添加一个没有参数的构造函数,在insert()中添加将数组长度加倍的代码,在delMax()中添加将数组长度减半的代码,就像栈那样。这样,算法的用例就无需管组各种队列大小的限制。当有限队列的数组大小可以跳帧、队列长度可以是任意值时,命题Q指出的对数时间复杂度上限就只是针对一般性的队列长度N而言了。
2.4.4.5 元素的不可变性
有限队列存储了用例创建的对象,但同时假设用例代码不会改变他们(改变他们就可能打破堆的有序性)。我们可以将这个假设为强制条件,但程序员通常不会这么做,因为增加代码的复杂性会降低性能。
2.4.4.6 索引优先队列
在很多应用中,允许用例引用已经进入有限队列中的元素是有必要的。做到这一点的一种简单方法是用例已经有了总量为N的多个元素,而且可能还同时使用了多个(平行)数组(Parallel Array)来存储这些元素的信息。此时,其他无关的用例代码可能已经在使用一个整数索引来引用这些元素了。这些考虑引导我们设计了下表。

理解这种数据结构的一个较好方法是将它看成一个能够快速访问其中最小元素的数组。事实上它还要更好——它能够快速访问数组的一个特定子集中的最小元素(指所有被插入的元素)。换句话说,可以将名为pq的IndexMinPQ优先队列看做数组pq[0..N - 1]中的一部分元素的代表。将pq.insert(k, item)看做将k加入这个子集并使pq[k] = item, pq.change(k, item)则代表令pq[k] = item。这两种操作没有改变其他操作所依赖的数据结构,其中最重要的就是delMin()(删除最小元素并返回它的索引)和change()(改变数据结构中的某个元素的索引——即pq[i] = item)。这些操作在许多应用中都很重要并且依赖于对元素的引用(索引)。一般来说,当堆发生变化时,我们会用下沉(元素减小时)或上浮(元素变大时)操作来恢复堆的有序性。在这些操作中,我们可以用索引查找元素。能够定位堆中的任意元素也使我们能够在API中加入一个delete()操作。
命题Q(续)。在一个大小为N的索引优先队列中,插入元素(insert)、改变优先级(change)、删除(delete)和删除最大小元素(remove the minimum)操作所需的比较次数和logN成正比(如后表)
证明。已知堆中所有路径最长即为~lgN,从代码中很容易得到这个结论。
| 操作 | 比较次数的增长数量级 |
| insert() | logN |
| change() | logN |
| contains() | 1 |
| delete() | logN |
| min() | 1 |
| minIndex() | 1 |
| delMin | logN |
这段讨论针对的是找好粗最小元素的队列;以下是《alg4》书中实现的一个找出最大元素的版本IndexMaxPQ。

1 import java.util.Iterator; 2 import java.util.NoSuchElementException; 3 4 /** 5 * The <tt>IndexMaxPQ</tt> class represents an indexed priority queue of generic keys. 6 * It supports the usual <em>insert</em> and <em>delete-the-maximum</em> 7 * operations, along with <em>delete</em> and <em>change-the-key</em> 8 * methods. In order to let the client refer to items on the priority queue, 9 * an integer between 0 and NMAX-1 is associated with each key—the client 10 * uses this integer to specify which key to delete or change. 11 * It also supports methods for peeking at a maximum key, 12 * testing if the priority queue is empty, and iterating through 13 * the keys. 14 * <p> 15 * This implementation uses a binary heap along with an array to associate 16 * keys with integers in the given range. 17 * The <em>insert</em>, <em>delete-the-maximum</em>, <em>delete</em>, 18 * <em>change-key</em>, <em>decrease-key</em>, and <em>increase-key</em> 19 * operations take logarithmic time. 20 * The <em>is-empty</em>, <em>size</em>, <em>max-index</em>, <em>max-key</em>, and <em>key-of</em> 21 * operations take constant time. 22 * Construction takes time proportional to the specified capacity. 23 * <p> 24 * For additional documentation, see <a href="http://algs4.cs.princeton.edu/24pq">Section 2.4</a> of 25 * <i>Algorithms, 4th Edition</i> by Robert Sedgewick and Kevin Wayne. 26 * 27 * @author Robert Sedgewick 28 * @author Kevin Wayne 29 */ 30 public class IndexMaxPQ<Key extends Comparable<Key>> implements Iterable<Integer> { 31 private int N; // number of elements on PQ 32 private int[] pq; // binary heap using 1-based indexing 33 private int[] qp; // inverse of pq - qp[pq[i]] = pq[qp[i]] = i 34 private Key[] keys; // keys[i] = priority of i 35 36 /** 37 * Initializes an empty indexed priority queue with indices between 0 and NMAX-1. 38 * @param NMAX the keys on the priority queue are index from 0 to NMAX-1 39 * @throws java.lang.IllegalArgumentException if NMAX < 0 40 */ 41 public IndexMaxPQ(int NMAX) { 42 keys = (Key[]) new Comparable[NMAX + 1]; // make this of length NMAX?? 43 pq = new int[NMAX + 1]; 44 qp = new int[NMAX + 1]; // make this of length NMAX?? 45 for (int i = 0; i <= NMAX; i++) qp[i] = -1; 46 } 47 48 /** 49 * Is the priority queue empty? 50 * @return true if the priority queue is empty; false otherwise 51 */ 52 public boolean isEmpty() { return N == 0; } 53 54 /** 55 * Is i an index on the priority queue? 56 * @param i an index 57 * @throws java.lang.IndexOutOfBoundsException unless (0 ≤ i < NMAX) 58 */ 59 public boolean contains(int i) { 60 return qp[i] != -1; 61 } 62 63 /** 64 * Returns the number of keys on the priority queue. 65 * @return the number of keys on the priority queue 66 */ 67 public int size() { 68 return N; 69 } 70 71 /** 72 * Associate key with index i. 73 * @param i an index 74 * @param key the key to associate with index i 75 * @throws java.lang.IndexOutOfBoundsException unless 0 ≤ i < NMAX 76 * @throws java.util.IllegalArgumentException if there already is an item associated with index i 77 */ 78 public void insert(int i, Key key) { 79 if (contains(i)) throw new IllegalArgumentException("index is already in the priority queue"); 80 N++; 81 qp[i] = N; 82 pq[N] = i; 83 keys[i] = key; 84 swim(N); 85 } 86 87 /** 88 * Returns an index associated with a maximum key. 89 * @return an index associated with a maximum key 90 * @throws java.util.NoSuchElementException if priority queue is empty 91 */ 92 public int maxIndex() { 93 if (N == 0) throw new NoSuchElementException("Priority queue underflow"); 94 return pq[1]; 95 } 96 97 /** 98 * Return a maximum key. 99 * @return a maximum key 100 * @throws java.util.NoSuchElementException if priority queue is empty 101 */ 102 public Key maxKey() { 103 if (N == 0) throw new NoSuchElementException("Priority queue underflow"); 104 return keys[pq[1]]; 105 } 106 107 /** 108 * Removes a maximum key and returns its associated index. 109 * @return an index associated with a maximum key 110 * @throws java.util.NoSuchElementException if priority queue is empty 111 */ 112 public int delMax() { 113 if (N == 0) throw new NoSuchElementException("Priority queue underflow"); 114 int min = pq[1]; 115 exch(1, N--); 116 sink(1); 117 qp[min] = -1; // delete 118 keys[pq[N+1]] = null; // to help with garbage collection 119 pq[N+1] = -1; // not needed 120 return min; 121 } 122 123 /** 124 * Returns the key associated with index i. 125 * @param i the index of the key to return 126 * @return the key associated with index i 127 * @throws java.lang.IndexOutOfBoundsException unless 0 ≤ i < NMAX 128 * @throws java.util.NoSuchElementException no key is associated with index i 129 */ 130 public Key keyOf(int i) { 131 if (!contains(i)) throw new NoSuchElementException("index is not in the priority queue"); 132 else return keys[i]; 133 } 134 135 /** 136 * Change the key associated with index i to the specified value. 137 * @param i the index of the key to change 138 * @param key change the key assocated with index i to this key 139 * @throws java.lang.IndexOutOfBoundsException unless 0 ≤ i < NMAX 140 * @deprecated Replaced by changeKey() 141 */ 142 @Deprecated public void change(int i, Key key) { 143 changeKey(i, key); 144 } 145 146 /** 147 * Change the key associated with index i to the specified value. 148 * @param i the index of the key to change 149 * @param key change the key assocated with index i to this key 150 * @throws java.lang.IndexOutOfBoundsException unless 0 ≤ i < NMAX 151 */ 152 public void changeKey(int i, Key key) { 153 if (!contains(i)) throw new NoSuchElementException("index is not in the priority queue"); 154 keys[i] = key; 155 swim(qp[i]); 156 sink(qp[i]); 157 } 158 159 160 /** 161 * Increase the key associated with index i to the specified value. 162 * @param i the index of the key to increase 163 * @param key increase the key assocated with index i to this key 164 * @throws java.lang.IndexOutOfBoundsException unless 0 ≤ i < NMAX 165 * @throws java.lang.IllegalArgumentException if key ≤ key associated with index i 166 * @throws java.util.NoSuchElementException no key is associated with index i 167 */ 168 public void increaseKey(int i, Key key) { 169 if (!contains(i)) throw new NoSuchElementException("index is not in the priority queue"); 170 if (keys[i].compareTo(key) >= 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Calling increaseKey() with given argument would not strictly increase the key"); 171 172 173 keys[i] = key; 174 swim(qp[i]); 175 } 176 177 /** 178 * Decrease the key associated with index i to the specified value. 179 * @param i the index of the key to decrease 180 * @param key decrease the key assocated with index i to this key 181 * @throws java.lang.IndexOutOfBoundsException unless 0 ≤ i < NMAX 182 * @throws java.lang.IllegalArgumentException if key ≥ key associated with index i 183 * @throws java.util.NoSuchElementException no key is associated with index i 184 */ 185 public void decreaseKey(int i, Key key) { 186 if (!contains(i)) throw new NoSuchElementException("index is not in the priority queue"); 187 if (keys[i].compareTo(key) <= 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Calling decreaseKey() with given argument would not strictly decrease the key"); 188 189 keys[i] = key; 190 sink(qp[i]); 191 } 192 193 /** 194 * Remove the key associated with index i. 195 * @param i the index of the key to remove 196 * @throws java.lang.IndexOutOfBoundsException unless 0 ≤ i < NMAX 197 * @throws java.util.NoSuchElementException no key is associated with index i 198 */ 199 public void delete(int i) { 200 if (!contains(i)) throw new NoSuchElementException("index is not in the priority queue"); 201 int index = qp[i]; 202 exch(index, N--); 203 swim(index); 204 sink(index); 205 keys[i] = null; 206 qp[i] = -1; 207 } 208 209 210 /************************************************************** 211 * General helper functions 212 **************************************************************/ 213 private boolean less(int i, int j) { 214 return keys[pq[i]].compareTo(keys[pq[j]]) < 0; 215 } 216 217 private void exch(int i, int j) { 218 int swap = pq[i]; pq[i] = pq[j]; pq[j] = swap; 219 qp[pq[i]] = i; qp[pq[j]] = j; 220 } 221 222 223 /************************************************************** 224 * Heap helper functions 225 **************************************************************/ 226 private void swim(int k) { 227 while (k > 1 && less(k/2, k)) { 228 exch(k, k/2); 229 k = k/2; 230 } 231 } 232 233 private void sink(int k) { 234 while (2*k <= N) { 235 int j = 2*k; 236 if (j < N && less(j, j+1)) j++; 237 if (!less(k, j)) break; 238 exch(k, j); 239 k = j; 240 } 241 } 242 243 244 /*********************************************************************** 245 * Iterators 246 **********************************************************************/ 247 248 /** 249 * Returns an iterator that iterates over the keys on the 250 * priority queue in descending order. 251 * The iterator doesn't implement <tt>remove()</tt> since it's optional. 252 * @return an iterator that iterates over the keys in descending order 253 */ 254 public Iterator<Integer> iterator() { return new HeapIterator(); } 255 256 private class HeapIterator implements Iterator<Integer> { 257 // create a new pq 258 private IndexMaxPQ<Key> copy; 259 260 // add all elements to copy of heap 261 // takes linear time since already in heap order so no keys move 262 public HeapIterator() { 263 copy = new IndexMaxPQ<Key>(pq.length - 1); 264 for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++) 265 copy.insert(pq[i], keys[pq[i]]); 266 } 267 268 public boolean hasNext() { return !copy.isEmpty(); } 269 public void remove() { throw new UnsupportedOperationException(); } 270 271 public Integer next() { 272 if (!hasNext()) throw new NoSuchElementException(); 273 return copy.delMax(); 274 } 275 } 276 277 /** 278 * Unit tests the <tt>IndexMaxPQ</tt> data type. 279 */ 280 public static void main(String[] args) { 281 // insert a bunch of strings 282 String[] strings = { "it", "was", "the", "best", "of", "times", "it", "was", "the", "worst" }; 283 284 IndexMaxPQ<String> pq = new IndexMaxPQ<String>(strings.length); 285 for (int i = 0; i < strings.length; i++) { 286 pq.insert(i, strings[i]); 287 } 288 289 // print each key using the iterator 290 for (int i : pq) { 291 StdOut.println(i + " " + strings[i]); 292 } 293 294 StdOut.println(); 295 296 // increase or decrease the key 297 for (int i = 0; i < strings.length; i++) { 298 if (StdRandom.uniform() < 0.5) 299 pq.increaseKey(i, strings[i] + strings[i]); 300 else 301 pq.decreaseKey(i, strings[i].substring(0, 1)); 302 } 303 304 // delete and print each key 305 while (!pq.isEmpty()) { 306 String key = pq.maxKey(); 307 int i = pq.delMax(); 308 StdOut.println(i + " " + key); 309 } 310 StdOut.println(); 311 312 // reinsert the same strings 313 for (int i = 0; i < strings.length; i++) { 314 pq.insert(i, strings[i]); 315 } 316 317 // delete them in random order 318 int[] perm = new int[strings.length]; 319 for (int i = 0; i < strings.length; i++) 320 perm[i] = i; 321 StdRandom.shuffle(perm); 322 for (int i = 0; i < perm.length; i++) { 323 String key = pq.keyOf(perm[i]); 324 pq.delete(perm[i]); 325 StdOut.println(perm[i] + " " + key); 326 } 327 328 } 329 }
2.4.4.7 索引有限队列用例
下面的用例调用了IndexMinPQ的代码Multiway解决了多项归并问题:它将多个有序的输入流归并成一个有序的输出流。许多应用中都会遇到这个问题。输入可能你来自多种科学仪器的输出(按照时间排序),或是来自多个音乐或电影网站的信息列表(按名称或艺术家名字排列),或是商业交易(按账号或时间排序),或者其他。如果有足够的空间,你可以把它们简单地读入一个数组并排序,但如果用例优先队列,无论输入有多长你都可以把它们全部读入并排序。

1 /** 2 * The <tt>Multiway</tt> class provides a client for reading in several 3 * sorted text files and merging them together into a single sorted 4 * text stream. 5 * This implementation uses a {@link IndexMinPQ} to perform the multiway 6 * merge. 7 * <p> 8 * For additional documentation, see <a href="http://algs4.cs.princeton.edu/24pq">Section 2.4</a> 9 * of <i>Algorithms, 4th Edition</i> by Robert Sedgewick and Kevin Wayne. 10 * 11 * @author Robert Sedgewick 12 * @author Kevin Wayne 13 */ 14 15 public class Multiway { 16 17 // This class should not be instantiated. 18 private Multiway() { } 19 20 // merge together the sorted input streams and write the sorted result to standard output 21 private static void merge(In[] streams) { 22 int N = streams.length; 23 IndexMinPQ<String> pq = new IndexMinPQ<String>(N); 24 for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) 25 if (!streams[i].isEmpty()) 26 pq.insert(i, streams[i].readString()); 27 28 // Extract and print min and read next from its stream. 29 while (!pq.isEmpty()) { 30 StdOut.print(pq.minKey() + " "); 31 int i = pq.delMin(); 32 if (!streams[i].isEmpty()) 33 pq.insert(i, streams[i].readString()); 34 } 35 StdOut.println(); 36 } 37 38 39 /** 40 * Reads sorted text files specified as command-line arguments; 41 * merges them together into a sorted output; and writes 42 * the results to standard output. 43 * Note: this client does not check that the input files are sorted. 44 */ 45 public static void main(String[] args) { 46 int N = args.length; 47 In[] streams = new In[N]; 48 for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) 49 streams[i] = new In(args[i]); 50 merge(streams); 51 } 52 }
这段代码调用了IndexMinPQ()来将作为命令行参数输入的多行有序字符串归并为一行有序的输出。每个输入流的索引都关联着一个元素(输入中的下个字符串)。初始化之后,代码进入一个循环,删除并打印出队列中最小的字符串,然后将该输入的下一个字符串添加为一个元素。
