委托Delegate深入总结
1.1 委托的基本概念
委托是一种引用方法的类型。一旦为委托分配了方法,委托将与该方法具有完全相同的行为。委托方法的调用可以像其他任何方法一样,具有参数和返回值,如下面的示例所示:
| C# |
|
| public delegate int Calculation(int x, int y);
|
|
与委托的签名(由返回类型和参数组成)匹配的任何可访问类或结构中的任何方法都可以分配给该委托。方法可以是静态方法,也可以是实例方法。这样就可以通过编程方式来更改方法调用,还可以向现有类中插入新代码。只要知道委托的签名,便可以分配自己的委托方法。
| 注意: |
| 在方法重载的上下文中,方法的签名不包括返回值。但在委托的上下文中,签名的确包括返回值。 |
将方法作为参数进行引用的能力使委托成为定义回调方法的理想选择。例如,可以向排序算法传递对比较两个对象的方法的引用.分离比较代码使得可以采用更通用的方式编写算法。
委托概述
委托具有以下特点:
委托类似于 C++ 函数指针,但它们是类型安全的。
委托允许将方法作为参数进行传递。
委托可用于定义回调方法。
委托可以链接在一起;例如,可以对一个事件调用多个方法。
方法不必与委托签名完全匹配。
1.2 Delegate使用三部曲
delegate是面向对象、类型安全、可靠的受控(managed)对象。也就是说,runtime能够保证delegate指向一个有效的方法,你无须担心delegate会指向无效地址或者越界地址。
实现一个delegate是很简单的,通过以下3个步骤即可实现一个delegate:
1. 声明一个delegate对象,它应当与你想要传递的方法具有相同的参数和返回值类型。
声明一个代理的例子:
public delegate void MyDelegate(string name);
2. 创建delegate对象,并将你想要传递的函数作为参数传入。
创建代理对象的方法:
1). MyDelegate myDelegate = new MyDelegate(实例名.方法名);
2). MyDelegate myDelegate = new MyDelegate(类名.方法名);
注:如果需要代理的方法是一个static静态方法的话,采用第2种方式,否则采用第1种方式。
3. 在要实现异步调用的地方,通过上一步创建的对象来调用方法。
可以直接使用代理调用代理所指向的方法:
myDelegate(向方法传递的参数);
具体的代码示例如下:

 代码
代码
{
// 步骤1,声明delegate对象
public delegate void MyDelegate( string name);
/// / 这是我们欲传递的方法,它与MyDelegate具有相同的参数和返回值类型
public static void MyDelegateMethod( string name)
{
Console.WriteLine( " Hello,{0} " , name);
}
public static void Main()
{
// 步骤2,创建delegate对象
MyDelegate md = new MyDelegate(MyDelegateTest.MyDelegateMethod);
// 步骤3,调用delegate
md( " Michael " );
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
1.3 委托在CLR中的实现本质
利用ILDasm.exe来查看生成的程序集(assembly),如下图所示。
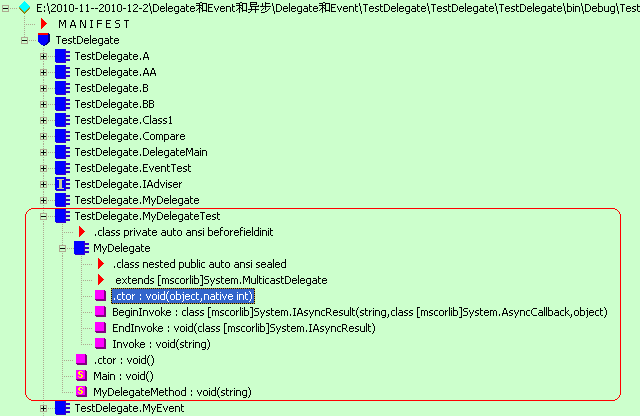
在这个例子中,编译器定义了一个类,名为MyDelegateTest, 委托MyDelegate继承自System.MulticastDelegate 类型(所有委托类型都继承自 MulticastDelegate)。
由于委托继承自System.MulticastDelegate类,自然也继承MulticastDelegate类的字段、属性和方法。这些成员中,最重要的当属三个非公共字段,如下表所示:
| 字段名称 |
字段类型 |
描述 |
| _target |
System.Object |
该字段指明委托所调用的方法所在的实例类型。如果委托调用的为静态方法,该字段为null;如果为实例方法则为该方法所在的对象。 |
| _methodPtr |
System.IntPtr |
一个内部的整数值,CLR用它标识要回调的方法。 |
| _invocationList |
System.Object |
在构建委托链时指向一个委托数组,在委托刚刚构建时通常为null。 |
委托有Public可见性 ,因为委托在源代码中被声明为Public类。我们应该知道,委托类可以在一个类型内部(即嵌套在另一个类型内)或在全局范围内定义。简单地说,因为委托本质上就是一个是类,在可以定义类的任何地方,都可以定义委托。
1.4 匿名委托
 代码
代码
{
private delegate void MyDelegate( string name);
public static void Main()
{
MyDelegate myDelegate = delegate ( string name)
{
Console.WriteLine(name);
};
myDelegate( " Mydelegate " );
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
例如,如果创建方法所需的系统开销是不必要的,则指定代码块(而不是委托)可能非常有用。启动新线程即是一个很好的示例。无需为委托创建更多方法,线程类即可创建一个线程并且包含该线程执行的代码。
 代码
代码
{
System.Threading.Thread t1 = new System.Threading.Thread
( delegate ()
{
System.Console.Write( " Hello, " );
System.Console.WriteLine( " World! " );
});
t1.Start();
}
匿名方法不能访问外部范围的 ref 或 out 参数。
在“匿名方法块”中不能访问任何不安全代码。
在 is 运算符的左侧不允许使用匿名方法。
1.5 委托中的协变和逆变
将方法签名与委托类型匹配时,协变和逆变可以提供一定程度的灵活性。协变允许方法具有的派生返回类型比委托中定义的更多。逆变允许方法具有的派生参数类型比委托类型中的更少。
协变示例代码
 代码
代码
{
}
class Dogs : Mammals
{
}
class Program
{
// Define the delegate.
public delegate Mammals HandlerMethod();
public static Mammals FirstHandler()
{
return null ;
}
public static Dogs SecondHandler()
{
return null ;
}
static void Main()
{
HandlerMethod handler1 = FirstHandler;
// Covariance allows this delegate.
HandlerMethod handler2 = SecondHandler;
}
}
逆变示例代码:
 代码
代码
public Form1()
{
InitializeComponent();
lastActivity = new System.DateTime();
this .textBox1.KeyDown += this .MultiHandler; // works with KeyEventArgs
this .button1.MouseClick += this .MultiHandler; // works with MouseEventArgs
}
// Event hander for any event with an EventArgs or
// derived class in the second parameter
private void MultiHandler( object sender, System.EventArgs e)
{
lastActivity = System.DateTime.Now;
}
1.6 多播委托与委托数组
委托对象的一个用途在于,可以使用 + 运算符将它们分配给一个要成为多路广播委托的委托实例。组合的委托可调用组成它的那两个委托。只有相同类型的委托才可以组合。- 运算符可用来从组合的委托移除组件委托。(如下msdn示例)
 代码
代码
class TestClass
{
static void Hello( string s)
{
System.Console.WriteLine( " Hello, {0}! " , s);
}
static void Goodbye( string s)
{
System.Console.WriteLine( " Goodbye, {0}! " , s);
}
static void Main()
{
Del a, b, c, d;
// Create the delegate object a that references
// the method Hello:
a = Hello;
// Create the delegate object b that references
// the method Goodbye:
b = Goodbye;
// The two delegates, a and b, are composed to form c:
c = a + b;
// Remove a from the composed delegate, leaving d,
// which calls only the method Goodbye:
d = c - a;
System.Console.WriteLine( " Invoking delegate a: " );
a( " A " );
System.Console.WriteLine( " Invoking delegate b: " );
b( " B " );
System.Console.WriteLine( " Invoking delegate c: " );
c( " C " );
System.Console.WriteLine( " Invoking delegate d: " );
d( " D " );
}
}
输出的结果:
Hello, A !
Invoking delegate b:
Goodbye, B !
Invoking delegate c:
Hello, C !
Goodbye, C !
Invoking delegate d:
Goodbye, D !
如果对于多播委托中的委托的返回类型并不是void的时候,如果返回的类型为string的话,多播委托链c的调用的返回值并不是两个委托的值相加,而是仅返回Goodbye, C!
在委托对象被调用时,挂接于委托对象之上的方法会按照多个方法挂接的先后顺序依次对其执行。这便是所谓的多路广播委托
具体的上述代码改为如下所示:
 代码
代码
{
delegate string Del( string s);
static string Hello( string s)
{
return string .Format( " Hello, {0}! " , s);
}
static string Goodbye( string s)
{
return string .Format( " Goodbye, {0}! " , s);
}
static void Main()
{
Del a, b, c, d;
// Create the delegate object a that references
// the method Hello:
a = Hello;
// Create the delegate object b that references
// the method Goodbye:
b = Goodbye;
// The two delegates, a and b, are composed to form c:
c = a + b;
// Remove a from the composed delegate, leaving d,
// which calls only the method Goodbye:
d = c - a;
System.Console.WriteLine( " Invoking delegate a: " );
Console.WriteLine(a( " A " ));
System.Console.WriteLine( " Invoking delegate b: " );
Console.WriteLine(b( " B " ));
System.Console.WriteLine( " Invoking delegate c: " );
Console.WriteLine(c( " C " ));
System.Console.WriteLine( " Invoking delegate d: " );
Console.WriteLine(d( " D " ));
Console.Read();
}
}
具体的输出结果为:
Hello, A !
Invoking delegate b:
Goodbye, B !
Invoking delegate c:
Goodbye, C !
Invoking delegate d:
Goodbye, D !
如果要获取两个值,这个时候只能采取变通的方法,构建为委托数组的方式,通过遍历的方式,获取每个委托的值进行组合获取自己想要的值
 代码
代码
{
// 声明委托数组
Del[] del = new Del[ 2 ];
// 为数组中的多个对象分别挂载不同的方法
del[ 0 ] = new Del(Hello);
del[ 1 ] = new Del(Goodbye);
// 通过下标分别调用不同委托对象中的不同方法
for ( int i = 0 ; i < 2 ; i ++ )
{
Console.WriteLine( " 调用方法[{0}]: " , i);
Console.WriteLine( " 所得结果:{0} " , del[i]( " C " ));
}
Console.ReadLine();
}
输出结果为:
所得结果: Hello, C !
调用方法[ 1 ]:
所得结果: Goodbye, C !