Android(java)学习笔记80:UDP协议发送数据
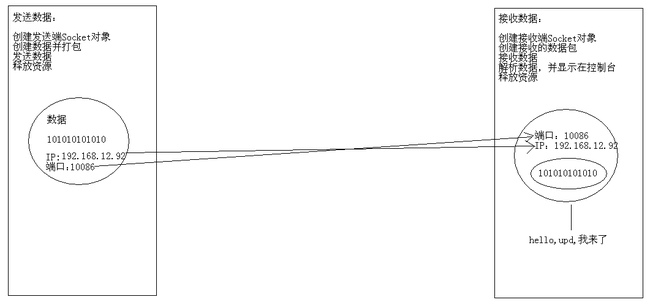
UDP协议发送数据:我们总是先运行接收端,再运行发送端
发送端:
1 package cn.itcast_02; 2 3 import java.io.IOException; 4 import java.net.DatagramPacket; 5 import java.net.DatagramSocket; 6 import java.net.InetAddress; 7 /* 8 * UDP协议发送数据: 9 * A:创建发送端Socket对象 10 * B:创建数据,并把数据打包 11 * C:调用Socket对象的发送方法发送数据包 12 * D:释放资源 13 */ 14 public class SendDemo { 15 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { 16 // 创建发送端Socket对象 17 // DatagramSocket() 18 DatagramSocket ds = new DatagramSocket(); 19 20 // 创建数据,并把数据打包 21 // DatagramPacket(byte[] buf, int length, InetAddress address, int port) 22 // 创建数据 23 byte[] bys = "hello,udp,我来了".getBytes();//转码 24 // 长度 25 int length = bys.length; 26 // IP地址对象 27 InetAddress address = InetAddress.getByName("192.168.12.92"); 28 // 端口 29 int port = 10086; 30 DatagramPacket dp = new DatagramPacket(bys, length, address, port); 31 32 // 调用Socket对象的发送方法发送数据包 33 // public void send(DatagramPacket p) 34 ds.send(dp); 35 36 // 释放资源 37 ds.close(); 38 } 39 }
接收端:
1 package cn.itcast_02; 2 3 import java.io.IOException; 4 import java.net.DatagramPacket; 5 import java.net.DatagramSocket; 6 import java.net.InetAddress; 7 8 /* 9 * UDP协议接收数据: 10 * A:创建接收端Socket对象 11 * B:创建一个数据包(接收容器) 12 * C:调用Socket对象的接收方法接收数据 13 * D:解析数据包,并显示在控制台 14 * E:释放资源 15 */ 16 public class ReceiveDemo { 17 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { 18 // 创建接收端Socket对象 19 // DatagramSocket(int port) 20 DatagramSocket ds = new DatagramSocket(10086); 21 22 // 创建一个数据包(接收容器) 23 // DatagramPacket(byte[] buf, int length) 24 byte[] bys = new byte[1024]; 25 int length = bys.length; 26 DatagramPacket dp = new DatagramPacket(bys, length); 27 28 // 调用Socket对象的接收方法接收数据 29 // public void receive(DatagramPacket p) 30 ds.receive(dp); // 阻塞式 31 32 // 解析数据包,并显示在控制台 33 // 获取对方的ip 34 // public InetAddress getAddress() 35 InetAddress address = dp.getAddress(); 36 String ip = address.getHostAddress(); 37 // public byte[] getData():获取数据缓冲区 38 // public int getLength():获取数据的实际长度 39 byte[] bys2 = dp.getData(); 40 int len = dp.getLength(); 41 String s = new String(bys2, 0, len); 42 System.out.println(ip + "传递的数据是:" + s); 43 44 // 释放资源 45 ds.close(); 46 } 47 }
这里ds.close():
java的内存回收机制,也是要等到资源达到一定限度才开始回收,也是有生命周期的。用close()可以及时回收资源,更加高效.使用close()后就可以及时释放资源,不必非等到最后资源占用完了才开始痛苦的回收过程,而且从良好的编程习惯来说,创建了对象,就应该考虑到用完后就要释放内存资源,要养成一个良好的编程习惯。
这里首先我们是运行接收端,因为如果不先运行接收端,先运行发送端的话,数据也不会接收到。但是与此同时,如果先运行接收端,可是没有接收到数据,不可能解析数据和显示数据,所以:先运行接收端,后运行发送端,同时我们也定义接收端为阻塞式,(也就是等待数据发送过来)。
UDP发送数据和接收数据图解:
UDP发送数据和接收数据代码的优化:
UDP协议发送数据:我们总是先运行接收端,再运行发送端
发送端:
1 package cn.itcast_03; 2 3 import java.io.IOException; 4 import java.net.DatagramPacket; 5 import java.net.DatagramSocket; 6 import java.net.InetAddress; 7 8 public class SendDemo { 9 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { 10 // 创建发送端的Socket对象 11 DatagramSocket ds = new DatagramSocket(); 12 13 // 创建数据并打包 14 byte[] bys = "helloworld".getBytes(); 15 DatagramPacket dp = new DatagramPacket(bys, bys.length, 16 InetAddress.getByName("192.168.12.92"), 12345); 17 18 // 发送数据 19 ds.send(dp); 20 21 // 释放资源 22 ds.close(); 23 } 24 }
接收端:
1 package cn.itcast_03; 2 3 import java.io.IOException; 4 import java.net.DatagramPacket; 5 import java.net.DatagramSocket; 6 7 /* 8 * 多次启动接收端: 9 * java.net.BindException: Address already in use: Cannot bind 10 * 端口被占用。 11 */ 12 public class ReceiveDemo { 13 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { 14 // 创建接收端的Socket对象 15 DatagramSocket ds = new DatagramSocket(12345); 16 17 // 创建一个包裹 18 byte[] bys = new byte[1024]; 19 DatagramPacket dp = new DatagramPacket(bys, bys.length); 20 21 // 接收数据 22 ds.receive(dp); 23 24 // 解析数据 25 String ip = dp.getAddress().getHostAddress(); 26 String s = new String(dp.getData(), 0, dp.getLength()); 27 System.out.println("from " + ip + " data is : " + s); 28 29 // 释放资源 30 ds.close(); 31 } 32 }
1.发送端数据来自于键盘录入的案例:(注意这里我们是如何更改上面的代码的)
发送端:
1 package cn.itcast_04; 2 3 import java.io.BufferedReader; 4 import java.io.IOException; 5 import java.io.InputStreamReader; 6 import java.net.DatagramPacket; 7 import java.net.DatagramSocket; 8 import java.net.InetAddress; 9 10 /* 11 * 数据来自于键盘录入 12 * 键盘录入数据要自己控制录入结束。 13 */ 14 public class SendDemo { 15 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { 16 // 创建发送端的Socket对象 17 DatagramSocket ds = new DatagramSocket(); 18 19 // 封装键盘录入数据 20 BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in)); 21 String line = null; 22 while ((line = br.readLine()) != null) { 23 if ("886".equals(line)) { //键盘录入数据终止符定义为:886 24 break; 25 } 26 27 // 创建数据并打包 28 byte[] bys = line.getBytes(); 29 // DatagramPacket dp = new DatagramPacket(bys, bys.length, 30 // InetAddress.getByName("192.168.12.92"), 12345);//发送给特定的用户电脑 31 DatagramPacket dp = new DatagramPacket(bys, bys.length, 32 InetAddress.getByName("192.168.12.255"), 12345);//发送给网内所有电脑 33 34 // 发送数据 35 ds.send(dp); 36 } 37 38 // 释放资源 39 ds.close(); 40 } 41 }
接收端:
1 package cn.itcast_04; 2 3 import java.io.IOException; 4 import java.net.DatagramPacket; 5 import java.net.DatagramSocket; 6 7 /* 8 * 多次启动接收端: 9 * java.net.BindException: Address already in use: Cannot bind 10 * 端口被占用。 11 */ 12 public class ReceiveDemo { 13 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { 14 // 创建接收端的Socket对象 15 DatagramSocket ds = new DatagramSocket(12345); 16 17 while (true) { 18 // 创建一个包裹 19 byte[] bys = new byte[1024]; 20 DatagramPacket dp = new DatagramPacket(bys, bys.length); 21 22 // 接收数据 23 ds.receive(dp); 24 25 // 解析数据 26 String ip = dp.getAddress().getHostAddress(); 27 String s = new String(dp.getData(), 0, dp.getLength()); 28 System.out.println("from " + ip + " data is : " + s); 29 } 30 31 // 释放资源 32 // 接收端应该一直开着等待接收数据,是不需要关闭,就好比百度服务器是一直开着着,一样的,接收端好比服务器端 33 // ds.close(); 34 } 35 }
这里我们知道如果这个程序要完成通信的话,我们就必须打开两个界面,一个发送端,一个接收端:
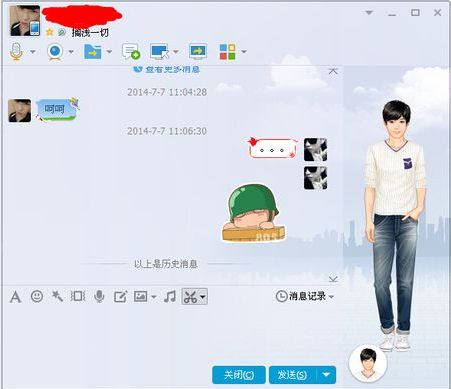
但是现实生活中我们都是在一个界面下发送和接收数据,例如如下的qq聊天界面:
于是我们这里引入对上面程序的进一步优化:这里就是利用多线程改进程序
1 package cn.itcast_05; 2 3 import java.io.IOException; 4 import java.net.DatagramSocket; 5 6 /* 7 * 通过多线程改进刚才的聊天程序,这样我就可以实现在一个窗口发送和接收数据了 8 */ 9 public class ChatRoom { 10 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { 11 DatagramSocket dsSend = new DatagramSocket(); 12 DatagramSocket dsReceive = new DatagramSocket(12306); 13 14 SendThread st = new SendThread(dsSend); 15 ReceiveThread rt = new ReceiveThread(dsReceive); 16 17 Thread t1 = new Thread(st); 18 Thread t2 = new Thread(rt); 19 20 t1.start(); 21 t2.start(); 22 } 23 }
1 package cn.itcast_05; 2 3 import java.io.IOException; 4 import java.net.DatagramPacket; 5 import java.net.DatagramSocket; 6 7 public class ReceiveThread implements Runnable { 8 private DatagramSocket ds; 9 10 public ReceiveThread(DatagramSocket ds) { 11 this.ds = ds; 12 } 13 14 @Override 15 public void run() { 16 try { 17 while (true) { 18 // 创建一个包裹 19 byte[] bys = new byte[1024]; 20 DatagramPacket dp = new DatagramPacket(bys, bys.length); 21 22 // 接收数据 23 ds.receive(dp); 24 25 // 解析数据 26 String ip = dp.getAddress().getHostAddress(); 27 String s = new String(dp.getData(), 0, dp.getLength()); 28 System.out.println("from " + ip + " data is : " + s); 29 } 30 } catch (IOException e) { 31 e.printStackTrace(); 32 } 33 } 34 35 }
1 package cn.itcast_05; 2 3 import java.io.BufferedReader; 4 import java.io.IOException; 5 import java.io.InputStreamReader; 6 import java.net.DatagramPacket; 7 import java.net.DatagramSocket; 8 import java.net.InetAddress; 9 10 public class SendThread implements Runnable { 11 12 private DatagramSocket ds; 13 14 public SendThread(DatagramSocket ds) { 15 this.ds = ds; 16 } 17 18 @Override 19 public void run() { 20 try { 21 // 封装键盘录入数据 22 BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader( 23 System.in)); 24 String line = null; 25 while ((line = br.readLine()) != null) { 26 if ("886".equals(line)) { 27 break; 28 } 29 30 // 创建数据并打包 31 byte[] bys = line.getBytes(); 32 // DatagramPacket dp = new DatagramPacket(bys, bys.length, 33 // InetAddress.getByName("192.168.12.92"), 12345); 34 DatagramPacket dp = new DatagramPacket(bys, bys.length, 35 InetAddress.getByName("192.168.12.255"), 12306); 36 37 // 发送数据 38 ds.send(dp); 39 } 40 41 // 释放资源 42 ds.close(); 43 } catch (IOException e) { 44 e.printStackTrace(); 45 } 46 } 47 48 }
执行效果图如下: