Android学习笔记26:图片切换控件ImageSwitcher的使用
在Windows操作系统中,要查看多张图片,可以通过使用“Windows照片查看器”在“上一张”和“下一张”之间切换,进行多张图片的浏览。
在Android中,可以通过使用图片切换控件ImageSwitcher来实现浏览多张图片的功能。下面我们就通过一个实际的例子来说明图片切换控件ImageSwitcher的使用方法。
1.界面布局
在xml布局文件中,我们使用LinearLayout对整个界面进行垂直布局。在界面的顶端设置了一个水平居中的ImageSwitcher控件,用来显示多张图片。在ImageSwitcher控件的下面使用LinearLayout水平布局设置四个ImageButton按钮,在点击这些按钮时分别用于实现右旋图片、显示上一张图片、显示下一张图片、左旋图片效果。整个布局文件很简单,具体源码如下:
1 <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" 2 xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" 3 android:orientation="vertical" 4 android:layout_width="match_parent" 5 android:layout_height="match_parent" > 6 7 <ImageSwitcher 8 android:id="@+id/imageSwitcher" 9 android:layout_marginTop="5dp" 10 android:layout_gravity="center" 11 android:layout_width="wrap_content" 12 android:layout_height="wrap_content" ></ImageSwitcher> 13 14 <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" 15 xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" 16 android:orientation="horizontal" 17 android:layout_marginTop="5dp" 18 android:layout_width="match_parent" 19 android:layout_height="match_parent" > 20 21 <!-- 右旋箭头 --> 22 <ImageButton 23 android:id="@+id/rightrotatearrow" 24 android:layout_marginLeft="30dp" 25 android:layout_width="wrap_content" 26 android:layout_height="wrap_content" 27 android:src="@drawable/rightrotatearrow" ></ImageButton> 28 29 <!-- 前一个箭头 --> 30 <ImageButton 31 android:id="@+id/forwardarrow" 32 android:layout_width="wrap_content" 33 android:layout_height="wrap_content" 34 android:src="@drawable/forwardarrow" ></ImageButton> 35 36 <!-- 下一个箭头 --> 37 <ImageButton 38 android:id="@+id/nextarrow" 39 android:layout_width="wrap_content" 40 android:layout_height="wrap_content" 41 android:src="@drawable/nextarrow" ></ImageButton> 42 43 <!-- 左旋箭头 --> 44 <ImageButton 45 android:id="@+id/liftrotatearrow" 46 android:layout_width="wrap_content" 47 android:layout_height="wrap_content" 48 android:src="@drawable/liftrotatearrow" ></ImageButton> 49 50 </LinearLayout> 51 52 </LinearLayout>
程序运行后的效果如图1所示。
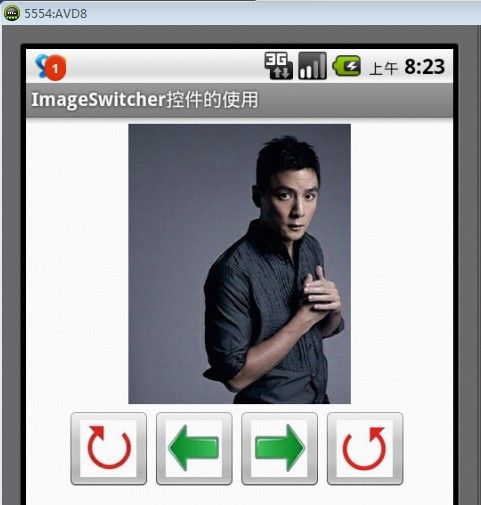
图1 主界面
2.ViewFactory接口
要将图片显示在ImageSwitcher控件中,必须为ImageSwitcher类设置一个ViewFactory,用来将显示的图片和父窗口区分开来。这可以通过如下方法来实现:
mImageSwitcher.setFactory();
此外,我们还需要实现ViewSwitcher.ViewFactory接口中的makeView()抽象方法,通过该方法可以返回一个ImageView对象,所有图片都将通过该ImageView对象来进行显示。具体实现方法如下:
1 /* 2 * Function : makeView() 3 * Describe : 将所有图片通过ImageView来显示 4 * Author : 博客园-依旧淡然 5 */ 6 public View makeView() { 7 return new ImageView(this); 8 }
3.存储图片资源
在《Android学习笔记25:画廊控件Gallery的使用》(http://www.cnblogs.com/menlsh/archive/2013/02/26/2934434.html)中,我们是通过使用一个继承自BaseAdapter类的派生类ImageAdapter来存储图片资源的。
在该实例中,我们将新建一个ArrayList对象来存储图片资源,方法如下:
List<Drawable> list = new ArrayList<Drawable>();
然后,可以使用list.add()方法将图片资源加载到该ArrayList对象中,具体方法如下:
1 //将图片资源加载到ArrayList中 2 list.add(getResources().getDrawable(R.drawable.image1)); 3 list.add(getResources().getDrawable(R.drawable.image2)); 4 list.add(getResources().getDrawable(R.drawable.image3)); 5 list.add(getResources().getDrawable(R.drawable.image4));
在该实例中,我们往ArrayList中加载了4张资源图片。
4.获取图片资源
当我们点击“上一张”和“下一张”按钮时,需要获取图片资源进行显示,这该如何实现呢?
通过查看ImageSwitcher的API帮助文档(http://developer.android.com/reference/android/widget/ImageSwitcher.html),我们可以看出向ImageSwitcher加载图片有以下三种方式:
(1)public void setImageDrawable(Drawable drawable);
(2)public void setImageResource(int resid);
(3)public void setImageURI(Uri uri);
其中,setImageDrawable()方法通过Drawable对象来获取图片资源;setImageResource()方法通过图片资源Id来获取图片资源;setImageURI()方法通过图片的Uri路径来获取图片资源。
在该实例中,我们选择使用setImageDrawable()方法来获取图片资源,这也就是为什么我们往ArrayList对象中存储图片时使用Drawable对象的原因。
5.按键处理
在该实例中,我们还需要实现OnClickListener接口的onClick()方法,对四个按键进行事件监听,具体实现方法如下:
1 /* 2 * Function : 事件监听处理 3 * Author : 博客园-依旧淡然 4 */ 5 public void onClick(View v) { 6 switch (v.getId()) { 7 case R.id.forwardarrow: //向前箭头按钮按键处理 8 index--; 9 if (index < 0) { 10 index = list.size() - 1; 11 } 12 mImageSwitcher.setImageDrawable(list.get(index)); 13 break; 14 case R.id.nextarrow: //向后箭头按钮按键处理 15 index++; 16 if (index >= list.size()) { 17 index = 0; 18 } 19 mImageSwitcher.setImageDrawable(list.get(index)); 20 break; 21 case R.id.liftrotatearrow: //左旋箭头按钮按键处理 22 //TO DO 23 break; 24 case R.id.rightrotatearrow: //右旋箭头按钮按键处理 25 //TO DO 26 break; 27 } 28 }
其中,变量index用于对图片进行索引,实现图片的循环显示,即当显示到最后一张图片时,再次点击“下一张”,则将图片索引号重置为0,然后重新显示第一张图片;当显示第一张图片时,再次点击“上一张”,则将图片的索引号重置为最大,然后显示最后一张图片。
在该实例中,并未对“左旋”和“右旋”按钮进行按键处理。要实现图片的旋转效果,请见博文《Android学习笔记11:图像的平移、旋转及缩放》(http://www.cnblogs.com/menlsh/archive/2012/12/02/2798802.html)。