动态凸包问题
对于动态凸包添加的问题的一般做法:
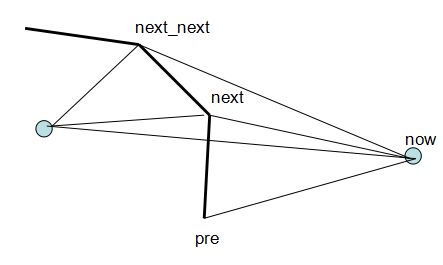
如上图。我们知道,如果能够有一种数据结构可以维护一下凸包上的顶点与原点的角度,对于插入一个点now的时候,我们就可以二分出点的位置,然后找到比他角度小的上一个顶点pre以及比他角度大的下一个顶点next,通过判断now跟next,pre的叉积正负来判断点now是否在凸包内。
对于需要插入不在凸包中的点时,我们找出了pre,next之后,需要分别通过维护上凸包以及下凸包,把多余的点从平衡树中删掉。例如上图中,由于next_next可以被now“看见”,所以next需要被删掉,删掉next之后继续判断next_next是否需要删掉,直到不能够删掉为止。对于下凸包同样进行这样的操作。
由于我们使用atan2(y,x)这样的方式来维护极角序,不可避免的存在极角相同的情况,可能存在精度误差使得找出的pre,next不是真正意义上的pre,next,所以我们需要在插入前三个点的时候用随机数乘上三个点的坐标,然后以该坐标的加权平均数作为原点。具体可以看代码。
如果可以用long long,最好直接用long long表示点的坐标,因为用double的精度可能不够,而判断叉积正负的时候可以直接用原坐标来判断。
题目:
现在有两种操作:
1.把(x,y)加到凸包中
2.问(x,y)是否在凸包中
现在给出n个操作,对于操作二,输出
分析:
这题的数据比较强,所以强烈推荐做一下。
#include <set>
#include <map>
#include <cmath>
#include <queue>
#include <stack>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef unsigned long long ull;
#define debug puts("here")
#define rep(i,n) for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
#define rep1(i,n) for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
#define REP(i,a,b) for(int i=a;i<=b;i++)
#define foreach(i,vec) for(unsigned i=0;i<vec.size();i++)
#define pb push_back
#define RD(n) scanf("%d",&n)
#define RD2(x,y) scanf("%d%d",&x,&y)
#define RD3(x,y,z) scanf("%d%d%d",&x,&y,&z)
#define RD4(x,y,z,w) scanf("%d%d%d%d",&x,&y,&z,&w)
#define All(vec) vec.begin(),vec.end()
#define MP make_pair
#define PII pair<int,int>
/******** program ********************/
const double eps = 1e-8;
double ox,oy;
struct node{
int x,y;
double angle;
int op;
friend bool operator < (node a,node b){
return a.angle-b.angle<0;
}
inline void rd(){
scanf("%d%d%d",&op,&x,&y);
}
inline void ch(){
angle = atan2(y-oy,x-ox);
}
inline void od(){
cout<<op<<" "<<x<<" "<<y<<" "<<atan2(y,x)<<endl;
}
};
set<node> s;
inline node getPre(node now){ // 得到前驱
if(s.count(now)>0)
return now;
set<node>::iterator it = s.lower_bound(now );
if(it==s.begin())
it = s.end();
return *--it;
}
inline node getNext(node now){ // 得到后继
set<node>::iterator it = s.upper_bound( now );
if(it==s.end())
it = s.begin();
return *it;
}
inline ll det(node a,node b,node o){
return ll(a.x-o.x)*(b.y-o.y)-ll(b.x-o.x)*(a.y-o.y);
}
inline bool in(node now){ // 判断点是否在凸包内
if(s.size()<3)
return false;
node p = getPre(now);
node n = getNext(now);
return det(p,n,now)>=0;
}
inline void add(node now){ // 添加
if(in(now)) return;
while(1){
node n = getNext(now);
s.erase(n);
node nn = getNext(now);
if(det(now,nn,n)<0){
s.insert(n);
break;
}
}
while(1){
node p = getPre(now);
s.erase(p);
node pp = getPre(now);
if(det(pp,now,p)<0){
s.insert(p);
break;
}
}
s.insert(now);
}
int main(){
#ifndef ONLINE_JUDGE
freopen("sum.in","r",stdin);
//freopen("sum.out","w",stdout);
#endif
int n;
while(~RD(n)){
node a[5];
ox = oy = 0;
double t[] = {0,0.49214632134, 0.2348329743213, 0.9854827427182};
double sum = 0;
rep1(i,3){
a[i].rd();
ox += a[i].x*t[i];
oy += a[i].y*t[i];
sum += t[i];
}
s.clear();
ox /= sum, oy /= sum;
rep1(i,3){
a[i].ch();
s.insert(a[i]);
}
node now;
n -= 3;
while(n--){
now.rd();
now.ch();
if(now.op==1)
add(now);
else
in(now)?puts("YES"):puts("NO");
}
}
return 0;
}
题目:
先给出三个点,保证三个点不共线。
现在添加k个点,问添加第i个点时,现有的点所形成的凸包面积的两倍
分析:
动态凸包添加点计算面积的问题。
我们先判断点是否在凸包内。
不在的话,把三角形(next,pre,now)加上。
然后对于上半部分,判断next是否需要删掉,需要删掉的话,面积加上三角形(next,next_next,now),
继续判断下一个点。
对于下半部分进行同样的操作即可。
#include <set>
#include <map>
#include <cmath>
#include <queue>
#include <stack>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef unsigned long long ull;
#define debug puts("here")
#define rep(i,n) for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
#define rep1(i,n) for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
#define REP(i,a,b) for(int i=a;i<=b;i++)
#define foreach(i,vec) for(unsigned i=0;i<vec.size();i++)
#define pb push_back
#define RD(n) scanf("%d",&n)
#define RD2(x,y) scanf("%d%d",&x,&y)
#define RD3(x,y,z) scanf("%d%d%d",&x,&y,&z)
#define RD4(x,y,z,w) scanf("%d%d%d%d",&x,&y,&z,&w)
#define All(vec) vec.begin(),vec.end()
#define MP make_pair
#define PII pair<int,int>
/******** program ********************/
ll area;
struct node{
ll x,y;
double ang;
node(){}
node(ll _x,ll _y):x(_x),y(_y){}
node(ll _x,ll _y,double _a):x(_x),y(_y),ang(_a){}
void rd(){
int _x,_y;
RD2(_x,_y);
x = _x;
y = _y;
}
void od(){
cout<<x<<" "<<y<<" "<<ang<<endl;
}
friend bool operator < (node a,node b){
return a.ang<b.ang;
}
friend node operator - (node a,node b){
return node(a.x-b.x,a.y-b.y);
}
};
set<node> s;
ll det(node a,node b){
return a.x*b.y-a.y*b.x;
}
ll det(node a,node b,node o){
return det(a-o,b-o);
}
node getPre(node now){
if(s.count(now)>0)
return now;
set<node>::iterator it = s.lower_bound(now);
if(it==s.begin())
it = s.end();
return *--it;
}
node getNext(node now){
set<node>::iterator it = s.upper_bound(now);
if(it==s.end())
it = s.begin();
return *it;
}
bool in(node now){
node p = getPre(now);
node n = getNext(now);
return det(now,n,p)<=0;
}
void add(node now){
if(in(now)) return;
area += abs( det(now,getNext(now),getPre(now)) );
while(true){
node p = getPre(now);
s.erase(p);
node pp = getPre(now);
if(det(now,pp,p)>=0){
s.insert(p);
break;
}
area += abs(det(now,pp,p));
}
while(true){
node n = getNext(now);
s.erase(n);
node nn = getNext(now);
if(det(now,nn,n)<=0){
s.insert(n);
break;
}
area += abs(det(n,nn,now));
}
s.insert(now);
}
int main(){
#ifndef ONLINE_JUDGE
freopen("sum.in","r",stdin);
//freopen("sum.out","w",stdout);
#endif
node a[5];
double t[] = {0.49214632134, 0.2348329743213, 0.9854827427182};
double sum = 0;
double ox = 0 , oy = 0;
rep(i,3){
a[i].rd();
ox += a[i].x*t[i];
oy += a[i].y*t[i];
sum += t[i];
}
ox /= sum;
oy /= sum;
s.clear();
rep(i,3)
s.insert(node(a[i].x,a[i].y,atan2(a[i].y-oy,a[i].x-ox)));
area = abs( det(a[0],a[1],a[2]) );
int n;
RD(n);
int x,y;
rep(i,n){
RD2(x,y);
add( node(x,y,atan2(y-oy,x-ox)) );
printf("%I64d\n",area);
}
return 0;
}