- Android UI:ViewTree中的事件传递
liufeismart2024
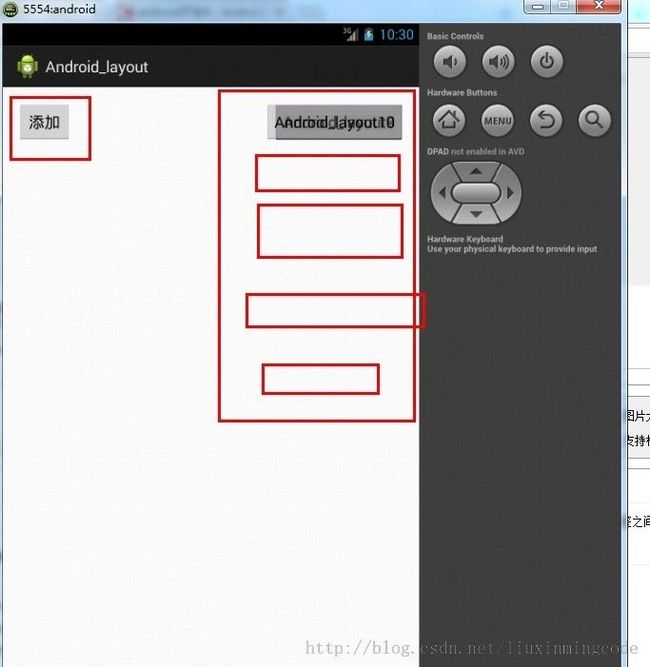
androidui
文章目录ViewTree:组合模式measure事件的传递事件传递:View/ViewGroup的measure和onMeasureLinearLayout重写onMeasureRelativeLayout重写onMeasurelayout事件的传递事件传递:View/ViewGroup的layout和onLayoutLinearLayout重写onLayoutRelativeLayout重写on
- 2019-07-28
落叶飞花
使用Androidstudio完成一个菜单栏的功能:步骤:1.在RelativeLayout布局2.用ImageView插入图片并且修改图标数值,添加状态3.创建一个数组将所有的图片都排好号4.用变量(isopen)设计图标动态
- Android开发-UI布局的使用
IM不知
前言常用五种布局方式,分别是:FrameLayout(框架布局),LinearLayout(线性布局),AbsoluteLayout(绝对布局),RelativeLayout(相对布局)TableLayout(表格布局)。View和ViewGroup1.View在Andorid应用程序中,UI元素称为View,它们都继承了android.view.View类。View有众多的子类,包括ViewGr
- android.widget.RelativeLayout.onMeasure出现的java.lang.NullPointerException错误
ljd1991
Android学习androidrelativelayoutmeasure方法
在手动计算ListView高度时出现了以下错误:04-2314:46:05.828:E/AndroidRuntime(3355):FATALEXCEPTION:main04-2314:46:05.828:E/AndroidRuntime(3355):java.lang.NullPointerException04-2314:46:05.828:E/AndroidRuntime(3355):atan
- Android: NullPointerException when using RelativeLayout with measure()
barryhappy
Androidandroidtips移动开发
使用measure()方法计算view的高度时,如果view中含有RelativeLayout布局,就有可能出现这样的错误:07-1313:18:34.330:E/AndroidRuntime(12098):java.lang.NullPointerException07-1313:18:34.330:E/AndroidRuntime(12098):atandroid.widget.Relativ
- 布局优化
崽子猪
布局优化的思想很简单,就是尽量减少布局文件的层级,这个道理很浅显的,布局中的层级少了,这就意味着Android绘制是的工作量减少了,那么程序的性能自然就提高了。如何进行布局优化呢?首先删除布局中无用的空间和层级,其次有选择地使用性能较低的ViewGroup,比如RelativeLayout。如果布局中既可以使用LinearLayout也可以使用RelativeLayout,那么就采用LinearL
- Android Studio六大基本布局的概览和每个布局的关键特性以及实例分析
特创数字科技
日常分享androidstudioandroidide
1.线性布局(LinearLayout)描述:线性布局是一种按指定方向(水平或垂直)排列其子视图的布局容器。通过android:orientation属性可设置为horizontal或vertical。关键属性:android:orientation:指定布局方向。android:layout_weight:子视图权重,用于分配剩余空间。示例:2.相对布局(RelativeLayout)描述:相对
- Android横竖屏切换View设置不同尺寸或等比例缩放的自定义View的onMeasure解决方案(2)
zhangphil
Androidandroid
Android横竖屏切换View设置不同尺寸或等比例缩放的自定义View的onMeasure解决方案(2)附录文章1以xml布局文件方式实现了一个view在横竖屏切换时候的大小尺寸缩放,实现这种需求,也可以使用自定义View的onMeasure方法实现。比如,写一个自定义的ScaleRelativeLayout相对布局:注意在Avtivity中定义configChanges属性:android:c
- 学习Android的第三天
世俗ˊ
Android学习android
目录AndroidLinearLayout线性布局XML属性LinearLayout几个重要的XML属性LinearLayout.LayoutParamsXML属性divider(分割线)AndroidRelativeLayout相对布局RelativeLayout布局属性TableLayout(表格布局)TableRow子控件的主要属性AndroidLinearLayout线性布局LinearL
- RelativeLayout中GONE导致布局错乱
风___________
针对RelativeLayout有一点需要注意,因为它内部是通过多个View之间的关系而确定的框架,那么当其中某一个View因为某些需要调用GONE来完全隐藏掉后,会影响与其相关联的Views。**Android为我们提供了一个属性**alignWithParentIfMissing用于解决类似问题,当某一个View无法找到与其相关联的Views后将依据alignWithParentIfMissi
- 安卓相对布局RelativeLayout
猪八戒1.0
安卓android
- RelativeLayout.LayoutParams详解
虫小宝
安卓开发
RelativeLayout.LayoutParams详解大家好,我是免费搭建查券返利机器人赚佣金就用微赚淘客系统3.0的小编,也是冬天不穿秋裤,天冷也要风度的程序猿!今天,我们将深入研究Android开发中的一个关键类——RelativeLayout.LayoutParams,解析它的功能、用法以及在实际布局中的应用场景。什么是RelativeLayout.LayoutParams?在Andro
- 安卓APP(3)——安卓布局控件
阿杰在线送代码
安卓APPandroid
嵌入式之路,贵在日常点滴---阿杰在线送代码目录一、布局的种类二、布局和页面的关系三、显示一张美女图控件的宽度和高度四、布局背景颜色,背景图,显示两个美女关于控件ID五、常用布局之相对布局RelativeLayout中子控件常用属性关于控件ID使用注意点六、基础控件之Button,TextView,EditText,ImageView控件布局通过拖拽通过代码编写七、padding和margin内边
- Android studio 六大基本布局详解
诗雅颂
androidapp安卓移动端安全
1.线性布局(LinearLayout)线性布局是一种按照水平或垂直方向排列子视图的布局,可以通过设置权重来调整子视图的大小比例。2.相对布局(RelativeLayout)相对布局是一种基于子视图之间相对位置关系进行定位的布局,可以根据其他子视图的位置来确定子视图的位置。3.帧布局(FrameLayout)帧布局是一种将子视图叠加在一起的布局,每个子视图都可以控制显示在最上面。4.表格布局(Ta
- 安卓自动缩放布局
Afison
AndroidJavaandroid
AutoScalingLayout适用于Android的自动缩放布局。替换布局:我们只需要替换根布局所需的自动缩放,子布局也将实现自动缩放。原始布局AutoScalingLayout相对布局ASRelativeLayout线性布局ASLinearLayoutFrameLayout(框架布局)ASFrameLayout目前支持上述三种布局。添加属性:designWidth和designHeight是
- 安卓常用布局
老A94
Android中常用的5大布局方式有以下几种:线性布局(LinearLayout):按照垂直或者水平方向布局的组件帧布局(FrameLayout):组件从屏幕左上方布局组件表格布局(TableLayout):按照行列方式布局组件相对布局(RelativeLayout):相对其它组件的布局方式绝对布局(AbsoluteLayout):按照绝对坐标来布局组件1.线性布局(LinearLayout)线性
- 鸿蒙开发笔记(十六): 相对布局 RelativeContainer,栅格布局 GridRow/GridCol,媒体查询 mediaquery
ZWaruler
鸿蒙开发harmonyos鸿蒙开发移动开发
1.相对布局RelativeContainer–RelativeLayoutRelativeContainer为采用相对布局的容器,支持容器内部的子元素设置相对位置关系。子元素支持指定兄弟元素作为锚点,也支持指定父容器作为锚点,基于锚点做相对位置布局。下图是一个RelativeContainer的概念图,图中的虚线表示位置的依赖关系。锚点:通过锚点设置当前元素基于哪个元素确定位置。对齐方式:通过对
- 相对布局RelativeLayout
lcannal
Androidandroid
- View事件分发(一) - 基础知识
世道无情
1.什么是View?1>:View是所有控件的基类,不管是TextView、Button还是LinearLayout、RelativeLayout,前者继承View,后者继承ViewGroup,但是ViewGroup也是继承View;2>:ViewGroup是控件组,表示一组View,由于ViewGroup继承View,所以View可以是单个控件,也可以是多个控件组成的控件组;2.View的位置参
- Android NestedScrollView悬浮固定顶部
吕氏春秋i
android悬浮ScrollViewandroid滑动吸顶
前言项目中有页面涉及到多个元素组需要NestedScrollView包裹来上下滑动接到需求一些标题在滑动到顶部时需要置顶我之前做过关于AndroidBehavior之ViewPager+Fragment+RecyclerView实现吸顶效果大概就是这种效果只不过这次是随意的组件比如TextView或布局组件RelativeLayout等废话不多说来看下实现效果动态效果图关于标题title勘测信息这
- ConstraintLayout约束布局详解
微语博客
ConstraintLayout可以翻译为约束布局,它是Jetpack的一部分,使用ConstraintLayout需要添加Jetpack依赖。ConstraintLayout约束布局可以无嵌套的创建复杂的大型布局,它与RelativeLayou相似,其中所有的视图均根据同级视图与父布局之间的关系进行布局,但其灵活性要高于RelativeLayout,并且更易于与AndroidStudio的布局编
- RelativeLayout把指定控件位于最上层
自带BGM的青春
控件的层等级和布局里的上下顺序也是有关系的
- Android中 ScrollView嵌套RecyclerView展示不完全问题(华为手机或者某些7.0手机)
原来是图哥
Bug记录Android显示不完全华为7.0
ScrollView在嵌套RecyclerView使用的时候,在如下手机出现了recyclerview显示不全的问题:手机型号HUAWEIMLA-AL10手机版本号7.0手机型号SLA-TL10手机版本号7.0手机型号HUAWWIP9手机版本号8.0解决方案:1.在RecycleView的外层嵌套一个RelativeLayout2.并且在RelativeLayout里面添加android:desc
- RelativeLayout 和 LinearLayout 性能比较
WaterYuan
层级数相同时LinearLayout性能优于RelativeLayout,但相对于LinearLayout,RelativeLayout一般能减少层级数从而优化整体性能RelativeLayout和LinearLayout性能比较RelativeLayout和LinearLayout是Android中常用的布局,两者的使用会极大的影响程序生成每一帧的性能,因此,正确的使用它们是提升程序性能的重要工
- 布局
W的北城
LinearLayout,RelativeLayout,GardLayout写线性布局是加一行布局方式:android:orientation="vertical"控件match_parentwrap_content匹配内容
- android RelativeLayout中android:layout_marginBottom的不起作用问题
hauler~
笔记Android
RelativeLayout布局中:1、当设置为android:layout_height="wrap_content"时,最下面的控件layout_marginBottom属性无效,如果其他控件使用layout_above让自己处于最下面的控件之上,那么layout_marginBottom属性有效。2、当设置为android:layout_height="match_parent"时,或者高度
- 6.相对布局RelativeLayout
jerry9590
Androidandroid-studio
子view可以有的属性:(1).相对位置:layout_below/layout_above/layout_toLeftOf/layout_toRightOf(2).在父容器中的位置:layout_centerInParent/layout_centerHorizontal/layout_centerVerticallayout_centerInParent:layout_centerHorizo
- Android基础教程(非常详细)从零基础入门到精通,看完这一篇就够了
程序员_大白
互联网网络安全程序员androidjvm
文章目录一、开发环境搭建二、简单控件1.文本显示2.按钮3.常用布局(1)线性布局LinearLayout(3)相对布局RelativeLayout(3)网格布局GridLayout4.图像显示(1)图像的缩放问题:(2)图像按钮ImageButton:三、Activity1.Activity的启动和结束2.Activity的生命周期3.Activity的启动模式(1)静态设置(2)动态设置4.A
- Android View的requestLayout和invalidate区别
在岁月中远行
首先来看一个布局文件:RelativeLayoutrelativeLayout1里面有TextView,RelativeLayoutrelativeLayout2里面有Button。当我调用TextView的requestLayout方法时,那么此布局中的哪些控件会重新测量和布局呢?relativeLayout1,relativeLayout2还是Button呢?下面我们从View的request
- APP
天竺鼠车车
页面布局框架布局FrameLayout——所有控件都被放置在最左上的区域;下一个子控件会重叠覆盖上一个控件线性布局LinearLayout——控件的排序方式:垂直/水平绝对布局AbsoluteLayout——采用坐标轴的方式定位控件;安卓坐标系统中,左上角为原点,往右x轴递增,往下y轴递增相对布局RelativeLayout——根据参照物(某控件)的位置,来确定控件的位置表格布局TableLayo
- 继之前的线程循环加到窗口中运行
3213213333332132
javathreadJFrameJPanel
之前写了有关java线程的循环执行和结束,因为想制作成exe文件,想把执行的效果加到窗口上,所以就结合了JFrame和JPanel写了这个程序,这里直接贴出代码,在窗口上运行的效果下面有附图。
package thread;
import java.awt.Graphics;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util
- linux 常用命令
BlueSkator
linux命令
1.grep
相信这个命令可以说是大家最常用的命令之一了。尤其是查询生产环境的日志,这个命令绝对是必不可少的。
但之前总是习惯于使用 (grep -n 关键字 文件名 )查出关键字以及该关键字所在的行数,然后再用 (sed -n '100,200p' 文件名),去查出该关键字之后的日志内容。
但其实还有更简便的办法,就是用(grep -B n、-A n、-C n 关键
- php heredoc原文档和nowdoc语法
dcj3sjt126com
PHPheredocnowdoc
<!doctype html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>Current To-Do List</title>
</head>
<body>
<?
- overflow的属性
周华华
JavaScript
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-transitional.dtd">
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml&q
- 《我所了解的Java》——总体目录
g21121
java
准备用一年左右时间写一个系列的文章《我所了解的Java》,目录及内容会不断完善及调整。
在编写相关内容时难免出现笔误、代码无法执行、名词理解错误等,请大家及时指出,我会第一时间更正。
&n
- [简单]docx4j常用方法小结
53873039oycg
docx
本代码基于docx4j-3.2.0,在office word 2007上测试通过。代码如下:
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import ja
- Spring配置学习
云端月影
spring配置
首先来看一个标准的Spring配置文件 applicationContext.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi=&q
- Java新手入门的30个基本概念三
aijuans
java新手java 入门
17.Java中的每一个类都是从Object类扩展而来的。 18.object类中的equal和toString方法。 equal用于测试一个对象是否同另一个对象相等。 toString返回一个代表该对象的字符串,几乎每一个类都会重载该方法,以便返回当前状态的正确表示.(toString 方法是一个很重要的方法) 19.通用编程:任何类类型的所有值都可以同object类性的变量来代替。
- 《2008 IBM Rational 软件开发高峰论坛会议》小记
antonyup_2006
软件测试敏捷开发项目管理IBM活动
我一直想写些总结,用于交流和备忘,然都没提笔,今以一篇参加活动的感受小记开个头,呵呵!
其实参加《2008 IBM Rational 软件开发高峰论坛会议》是9月4号,那天刚好调休.但接着项目颇为忙,所以今天在中秋佳节的假期里整理了下.
参加这次活动是一个朋友给的一个邀请书,才知道有这样的一个活动,虽然现在项目暂时没用到IBM的解决方案,但觉的参与这样一个活动可以拓宽下视野和相关知识.
- PL/SQL的过程编程,异常,声明变量,PL/SQL块
百合不是茶
PL/SQL的过程编程异常PL/SQL块声明变量
PL/SQL;
过程;
符号;
变量;
PL/SQL块;
输出;
异常;
PL/SQL 是过程语言(Procedural Language)与结构化查询语言(SQL)结合而成的编程语言PL/SQL 是对 SQL 的扩展,sql的执行时每次都要写操作
- Mockito(三)--完整功能介绍
bijian1013
持续集成mockito单元测试
mockito官网:http://code.google.com/p/mockito/,打开documentation可以看到官方最新的文档资料。
一.使用mockito验证行为
//首先要import Mockito
import static org.mockito.Mockito.*;
//mo
- 精通Oracle10编程SQL(8)使用复合数据类型
bijian1013
oracle数据库plsql
/*
*使用复合数据类型
*/
--PL/SQL记录
--定义PL/SQL记录
--自定义PL/SQL记录
DECLARE
TYPE emp_record_type IS RECORD(
name emp.ename%TYPE,
salary emp.sal%TYPE,
dno emp.deptno%TYPE
);
emp_
- 【Linux常用命令一】grep命令
bit1129
Linux常用命令
grep命令格式
grep [option] pattern [file-list]
grep命令用于在指定的文件(一个或者多个,file-list)中查找包含模式串(pattern)的行,[option]用于控制grep命令的查找方式。
pattern可以是普通字符串,也可以是正则表达式,当查找的字符串包含正则表达式字符或者特
- mybatis3入门学习笔记
白糖_
sqlibatisqqjdbc配置管理
MyBatis 的前身就是iBatis,是一个数据持久层(ORM)框架。 MyBatis 是支持普通 SQL 查询,存储过程和高级映射的优秀持久层框架。MyBatis对JDBC进行了一次很浅的封装。
以前也学过iBatis,因为MyBatis是iBatis的升级版本,最初以为改动应该不大,实际结果是MyBatis对配置文件进行了一些大的改动,使整个框架更加方便人性化。
- Linux 命令神器:lsof 入门
ronin47
lsof
lsof是系统管理/安全的尤伯工具。我大多数时候用它来从系统获得与网络连接相关的信息,但那只是这个强大而又鲜为人知的应用的第一步。将这个工具称之为lsof真实名副其实,因为它是指“列出打开文件(lists openfiles)”。而有一点要切记,在Unix中一切(包括网络套接口)都是文件。
有趣的是,lsof也是有着最多
- java实现两个大数相加,可能存在溢出。
bylijinnan
java实现
import java.math.BigInteger;
import java.util.regex.Matcher;
import java.util.regex.Pattern;
public class BigIntegerAddition {
/**
* 题目:java实现两个大数相加,可能存在溢出。
* 如123456789 + 987654321
- Kettle学习资料分享,附大神用Kettle的一套流程完成对整个数据库迁移方法
Kai_Ge
Kettle
Kettle学习资料分享
Kettle 3.2 使用说明书
目录
概述..........................................................................................................................................7
1.Kettle 资源库管
- [货币与金融]钢之炼金术士
comsci
金融
自古以来,都有一些人在从事炼金术的工作.........但是很少有成功的
那么随着人类在理论物理和工程物理上面取得的一些突破性进展......
炼金术这个古老
- Toast原来也可以多样化
dai_lm
androidtoast
Style 1: 默认
Toast def = Toast.makeText(this, "default", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT);
def.show();
Style 2: 顶部显示
Toast top = Toast.makeText(this, "top", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT);
t
- java数据计算的几种解决方法3
datamachine
javahadoopibatisr-languer
4、iBatis
简单敏捷因此强大的数据计算层。和Hibernate不同,它鼓励写SQL,所以学习成本最低。同时它用最小的代价实现了计算脚本和JAVA代码的解耦,只用20%的代价就实现了hibernate 80%的功能,没实现的20%是计算脚本和数据库的解耦。
复杂计算环境是它的弱项,比如:分布式计算、复杂计算、非数据
- 向网页中插入透明Flash的方法和技巧
dcj3sjt126com
htmlWebFlash
将
Flash 作品插入网页的时候,我们有时候会需要将它设为透明,有时候我们需要在Flash的背面插入一些漂亮的图片,搭配出漂亮的效果……下面我们介绍一些将Flash插入网页中的一些透明的设置技巧。
一、Swf透明、无坐标控制 首先教大家最简单的插入Flash的代码,透明,无坐标控制: 注意wmode="transparent"是控制Flash是否透明
- ios UICollectionView的使用
dcj3sjt126com
UICollectionView的使用有两种方法,一种是继承UICollectionViewController,这个Controller会自带一个UICollectionView;另外一种是作为一个视图放在普通的UIViewController里面。
个人更喜欢第二种。下面采用第二种方式简单介绍一下UICollectionView的使用。
1.UIViewController实现委托,代码如
- Eos平台java公共逻辑
蕃薯耀
Eos平台java公共逻辑Eos平台java公共逻辑
Eos平台java公共逻辑
>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>
蕃薯耀 2015年6月1日 17:20:4
- SpringMVC4零配置--Web上下文配置【MvcConfig】
hanqunfeng
springmvc4
与SpringSecurity的配置类似,spring同样为我们提供了一个实现类WebMvcConfigurationSupport和一个注解@EnableWebMvc以帮助我们减少bean的声明。
applicationContext-MvcConfig.xml
<!-- 启用注解,并定义组件查找规则 ,mvc层只负责扫描@Controller -->
<
- 解决ie和其他浏览器poi下载excel文件名乱码
jackyrong
Excel
使用poi,做传统的excel导出,然后想在浏览器中,让用户选择另存为,保存用户下载的xls文件,这个时候,可能的是在ie下出现乱码(ie,9,10,11),但在firefox,chrome下没乱码,
因此必须综合判断,编写一个工具类:
/**
*
* @Title: pro
- 挥洒泪水的青春
lampcy
编程生活程序员
2015年2月28日,我辞职了,离开了相处一年的触控,转过身--挥洒掉泪水,毅然来到了兄弟连,背负着许多的不解、质疑——”你一个零基础、脑子又不聪明的人,还敢跨行业,选择Unity3D?“,”真是不自量力••••••“,”真是初生牛犊不怕虎•••••“,••••••我只是淡淡一笑,拎着行李----坐上了通向挥洒泪水的青春之地——兄弟连!
这就是我青春的分割线,不后悔,只会去用泪水浇灌——已经来到
- 稳增长之中国股市两点意见-----严控做空,建立涨跌停版停牌重组机制
nannan408
对于股市,我们国家的监管还是有点拼的,但始终拼不过飞流直下的恐慌,为什么呢?
笔者首先支持股市的监管。对于股市越管越荡的现象,笔者认为首先是做空力量超过了股市自身的升力,并且对于跌停停牌重组的快速反应还没建立好,上市公司对于股价下跌没有很好的利好支撑。
我们来看美国和香港是怎么应对股灾的。美国是靠禁止重要股票做空,在
- 动态设置iframe高度(iframe高度自适应)
Rainbow702
JavaScriptiframecontentDocument高度自适应局部刷新
如果需要对画面中的部分区域作局部刷新,大家可能都会想到使用ajax。
但有些情况下,须使用在页面中嵌入一个iframe来作局部刷新。
对于使用iframe的情况,发现有一个问题,就是iframe中的页面的高度可能会很高,但是外面页面并不会被iframe内部页面给撑开,如下面的结构:
<div id="content">
<div id=&quo
- 用Rapael做图表
tntxia
rap
function drawReport(paper,attr,data){
var width = attr.width;
var height = attr.height;
var max = 0;
&nbs
- HTML5 bootstrap2网页兼容(支持IE10以下)
xiaoluode
html5bootstrap
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head lang="zh-CN">
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">