对象字段java clone 中的浅复制和深复制
废话就不多说了,开始。。。
什么是浅复制?
首先,浅复制会创建一个新对象,这个新的对象各个字段的值会从原始对象复制过来,如果某个字段是引用其他的对象,那么仅仅复制此对象在内存中的引用地址。
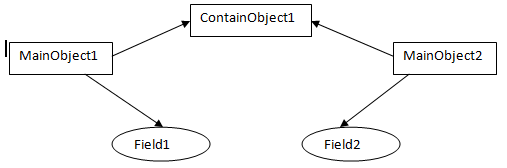
图1
如图1 所示,对象 MainObject1 有一个 int 类型的字段 Field1 和一个字段引用 ContainObject1对象,被克隆的新对象是 MainObject2, MainObject2 有一个 int 类型字段 Field2, Field2 的值是从对象MainObject1的字段 Field1 复制过来,而MainObject2的一个字段和MainObject1 中的某个字段仍然指向同一个对象ContainObject1,也就是说只要ContainObject1 产生任何变更,MainObject1 和MainObject2所引用的ContainObject1 都会用变更。
什么是深复制?
深复制也会创建一个新的对象,除了复制这个新对象里的原始类型字段的值,还要对此对象的引用字段再做克隆,而不是仅仅复制此引用字段再内存中的引用地址。
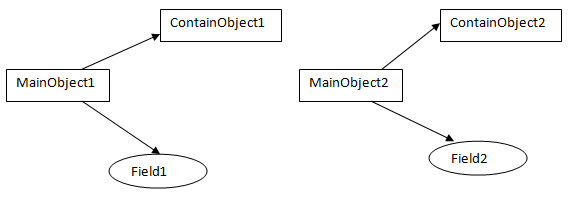
图2
如图2 所示,MainObject1 是原始对象,MainObject2 是被克隆出的对象,从图2和图1的差异可以看出,克隆对象MainObject2 字段ContainObject2和 MainObject1 里的字段 ContainObject1 指向的是不同的对象,也就是说,MainObject1 里的 ContainObject1 产生任何变更,都不会影响到 MainObject2 里的 ContainObject2。
用 java 实现浅复制示例:
class Subject {
private String name;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String s) {
name = s;
}
public Subject(String s) {
name = s;
}
}
class Student implements Cloneable {
//Contained object
private Subject subj;
private String name;
public Subject getSubj() {
return subj;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String s) {
name = s;
}
public Student(String s, String sub) {
name = s;
subj = new Subject(sub);
}
public Object clone() {
//shallow copy
try {
return super.clone();
} catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) {
return null;
}
}
}
public class CopyTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Original Object
Student stud = new Student("John", "Algebra");
System.out.println("Original Object: " + stud.getName() + " - "
+ stud.getSubj().getName());
//Clone Object
Student clonedStud = (Student) stud.clone();
System.out.println("Cloned Object: " + clonedStud.getName() + " - "
+ clonedStud.getSubj().getName());
stud.setName("Dan");
stud.getSubj().setName("Physics");
System.out.println("Original Object after it is updated: "
+ stud.getName() + " - " + stud.getSubj().getName());
System.out.println("Cloned Object after updating original object: "
+ clonedStud.getName() + " - " + clonedStud.getSubj().getName());
}
}
输出结果是:
Original Object: John - Algebra Cloned Object: John - Algebra Original Object after it is updated: Dan - Physics Cloned Object after updating original object: John - Physics
用java 实现深复制示例
只要要把上例的Student类的clone 方法修改如下:
class Student implements Cloneable {
//Contained object
private Subject subj;
private String name;
public Subject getSubj() {
return subj;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String s) {
name = s;
}
public Student(String s, String sub) {
name = s;
subj = new Subject(sub);
}
public Object clone() {
//Deep copy
Student s = new Student(name, subj.getName());
return s;
}
}
修改后运行结果如下:
Original Object: John - Algebra Cloned Object: John - Algebra Original Object after it is updated: Dan - Physics Cloned Object after updating original object: John - Algebra
使用序列化实现深复制
请看如下示例:
public class ColoredCircle implements Serializable {
private int x;
private int y;
public ColoredCircle(int x, int y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
public int getX() {
return x;
}
public void setX(int x) {
this.x = x;
}
public int getY() {
return y;
}
public void setY(int y) {
this.y = y;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "x=" + x + ",y=" + y;
}
}
public class DeepCopy {
static public void main(String[] args) {
ObjectOutputStream oos = null;
ObjectInputStream ois = null;
try {
// create original serializable object
ColoredCircle c1 = new ColoredCircle(100, 100);
// print it
System.out.println("Original = " + c1);
ColoredCircle c2 = null;
// deep copy
ByteArrayOutputStream bos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
oos = new ObjectOutputStream(bos);
// serialize and pass the object
oos.writeObject(c1);
oos.flush();
ByteArrayInputStream bin =
new ByteArrayInputStream(bos.toByteArray());
ois = new ObjectInputStream(bin);
// return the new object
c2 = (ColoredCircle) ois.readObject();
// verify it is the same
System.out.println("Copied = " + c2);
// change the original object's contents
c1.setX(200);
c1.setY(200);
// see what is in each one now
System.out.println("Original = " + c1);
System.out.println("Copied = " + c2);
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("Exception in main = " + e);
} finally {
try {
oos.close();
ois.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println(e);
}
}
}
}
程序输出结果:
Original = x=100,y=100 Copied = x=100,y=100 Original = x=200,y=200 Copied = x=100,y=100
文章结束给大家分享下程序员的一些笑话语录: IBM和波音777
波音777是有史以来第一架完全在电脑虚拟现实中设计制造的飞机,所用的设备完全由IBM公司所提供。试飞前,波音公司的总裁非常热情的邀请IBM的技术主管去参加试飞,可那位主管却说道:“啊,非常荣幸,可惜那天是我妻子的生日,So..”..
波音公司的总载一听就生气了:“胆小鬼,我还没告诉你试飞的日期呢!”