【Twitter Storm系列】 Storm简单实例讲解
实例来自书籍《Oreilly.Getting.Started.with.Storm.Aug.2012》
先讲下我们这次所需涉及到的概念:Topology、Spout、Blot
Topology:Storm的运行单位,相当于Hadoop中的job,一个topology是spouts和bolts组成的图, 通过stream groupings将图中的spouts和bolts连接起来
Spout:消息源,topology里面的消息生产者,一般来说消息源会从一个外部源读取数据并且向topology里面发出消息:tuple。
Blot:所有的消息处理逻辑被封装在bolts里面。Bolts可以做很多事情:过滤,聚合,查询数据库等等。
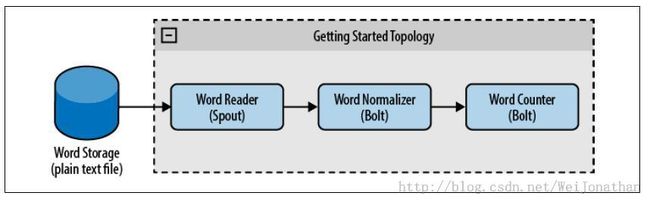
一下是实例的流程图
words.txt--将要执行wordcount操作的文件
storm test are great is an storm simple application but very powerfull really StOrm is great
1、Topology的创建
//Topology definition
TopologyBuilder builder = new TopologyBuilder();
builder.setSpout("word-reader",new WordReader());
builder.setBolt("word-normalizer", new WordNormalizer())
.shuffleGrouping("word-reader");
builder.setBolt("word-counter", new WordCounter(),1)
.fieldsGrouping("word-normalizer", new Fields("word"));
//Configuration
Config conf = new Config();
conf.put("wordsFile", args[0]);
conf.setDebug(false);
//Topology run
conf.put(Config.TOPOLOGY_MAX_SPOUT_PENDING, 1);
LocalCluster cluster = new LocalCluster();
cluster.submitTopology("Getting-Started-Toplogie", conf, builder.createTopology());
Thread.sleep(1000);
cluster.shutdown();从上面代码我们可以看到,Topology是通过TopologyBuilder的createTopology来创建。通过TopologyBuilder对象设置Spout以及Blot。
Config对象用于设置集群计算所需的参数,这里的参数是要执行wordcount操作的文件路径。
例子是以本地集群方式运行。
Topology提交通过cluster对象的submitTopology方法来提交。参数包括任务名、配置、以及Topology对象。
注:我们可以看下这里的TopologyBuilder对象的创建。
TopologyBuilder builder = new TopologyBuilder();
builder.setSpout("word-reader",new WordReader());
builder.setBolt("word-normalizer", new WordNormalizer())
.shuffleGrouping("word-reader");
builder.setBolt("word-counter", new WordCounter(),1)
.fieldsGrouping("word-normalizer", new Fields("word"));可以看出,这里有一个流程的执行关系。也可以说是一定订阅关系。第一个blot设置了shuffleGrouping的名称为Spout的名称,而第二个blot则指定了第一个blot的名称。就如我们上面的流程图执行流程一致。
2、Spout(WordReader)
package spouts;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.util.Map;
import backtype.storm.spout.SpoutOutputCollector;
import backtype.storm.task.TopologyContext;
import backtype.storm.topology.OutputFieldsDeclarer;
import backtype.storm.topology.base.BaseRichSpout;
import backtype.storm.tuple.Fields;
import backtype.storm.tuple.Values;
public class WordReader extends BaseRichSpout {
private SpoutOutputCollector collector;
private FileReader fileReader;
private boolean completed = false;
public void ack(Object msgId) {
System.out.println("OK:"+msgId);
}
public void close() {}
public void fail(Object msgId) {
System.out.println("FAIL:"+msgId);
}
/**
* The only thing that the methods will do It is emit each
* file line
*/
public void nextTuple() {
/**
* The nextuple it is called forever, so if we have been readed the file
* we will wait and then return
*/
if(completed){
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
//Do nothing
}
return;
}
String str;
//Open the reader
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(fileReader);
try{
//Read all lines
while((str = reader.readLine()) != null){
/**
* By each line emmit a new value with the line as a their
*/
this.collector.emit(new Values(str),str);
}
}catch(Exception e){
throw new RuntimeException("Error reading tuple",e);
}finally{
completed = true;
}
}
/**
* We will create the file and get the collector object
*/
public void open(Map conf, TopologyContext context,
SpoutOutputCollector collector) {
try {
this.fileReader = new FileReader(conf.get("wordsFile").toString());
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
throw new RuntimeException("Error reading file ["+conf.get("wordFile")+"]");
}
this.collector = collector;
}
/**
* Declare the output field "line"
*/
public void declareOutputFields(OutputFieldsDeclarer declarer) {
declarer.declare(new Fields("line"));
}
}* declareOutputFields方法用于定义输出字段名
* 首先集群提交Topology之后,会先调用open方法,open内部使用config对象获取文件并获取fileReader对象。
* nextTuple()方法通过BufferReader读取到fileReader数据之后,读取每一行数据,然后通过emit方法发送数据到订阅了数据的blot上。
3、第一个Blot(拆分出所有的wordcount传入下一个blot)
package bolts;
import backtype.storm.topology.BasicOutputCollector;
import backtype.storm.topology.OutputFieldsDeclarer;
import backtype.storm.topology.base.BaseBasicBolt;
import backtype.storm.tuple.Fields;
import backtype.storm.tuple.Tuple;
import backtype.storm.tuple.Values;
public class WordNormalizer extends BaseBasicBolt {
public void cleanup() {}
/**
* The bolt will receive the line from the
* words file and process it to Normalize this line
*
* The normalize will be put the words in lower case
* and split the line to get all words in this
*/
public void execute(Tuple input, BasicOutputCollector collector) {
String sentence = input.getString(0);
String[] words = sentence.split(" ");
for(String word : words){
word = word.trim();
if(!word.isEmpty()){
word = word.toLowerCase();
collector.emit(new Values(word));
}
}
}
/**
* The bolt will only emit the field "word"
*/
public void declareOutputFields(OutputFieldsDeclarer declarer) {
declarer.declare(new Fields("word"));
}
}这个blot基本上没做什么事情,只是在execute方法中将words切分然后emit到下一个blot
4、第二个blot(执行单词统计)
package bolts;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import backtype.storm.task.TopologyContext;
import backtype.storm.topology.BasicOutputCollector;
import backtype.storm.topology.OutputFieldsDeclarer;
import backtype.storm.topology.base.BaseBasicBolt;
import backtype.storm.tuple.Tuple;
public class WordCounter extends BaseBasicBolt {
Integer id;
String name;
Map<String, Integer> counters;
/**
* At the end of the spout (when the cluster is shutdown
* We will show the word counters
*/
@Override
public void cleanup() {
System.out.println("-- Word Counter ["+name+"-"+id+"] --");
for(Map.Entry<String, Integer> entry : counters.entrySet()){
System.out.println(entry.getKey()+": "+entry.getValue());
}
}
/**
* On create
*/
@Override
public void prepare(Map stormConf, TopologyContext context) {
this.counters = new HashMap<String, Integer>();
this.name = context.getThisComponentId();
this.id = context.getThisTaskId();
}
@Override
public void declareOutputFields(OutputFieldsDeclarer declarer) {}
@Override
public void execute(Tuple input, BasicOutputCollector collector) {
String str = input.getString(0);
/**
* If the word dosn't exist in the map we will create
* this, if not We will add 1
*/
if(!counters.containsKey(str)){
counters.put(str, 1);
}else{
Integer c = counters.get(str) + 1;
counters.put(str, c);
}
}
}
这里定义了一个HashMap counters用于存储单词的统计结果。在execute方法中执行单词统计。
转载请注明来源地址:http://blog.csdn.net/weijonathan/article/details/17399077