Java Web 编码问题三:URL和URI以及QueryString的编码问题
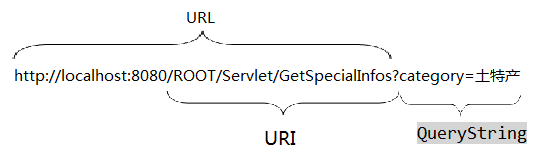
在问题之前我们先来了解一下什么是URL,URI以及QueryString,如下图1所示:
图1:URL-URI-QueryString
URL:是全球资源定位符的英文缩写,如上 其中localhost:是指Domain(IP或者主机名),8080:是端口 Web服务一般是80,8080是自己测试是候用的,避免和和浏览器的端口冲突。
ROOT:是ContentPath,就是虚拟路径,如果是tomcat服务器对象的是servlet.xml配置文件中的<Context path=”/ROOT” /> 如果没有配置这一个tomcat默认的是path就是ROOT。
Servlet:就是ServletPath的信息,就是和web.xml中的<url-pattern>相对应的,用来查找Servlet。
GetSpecialInfos:就是要请求的文件了。
category=土特产:就是QueryString,相当于用get提交的参数。
URI(Universal Resource Identifier, 简称"URI"):是Web上可用的每种资源。通过URI进行定位。一般是服务器自己使用。
知道了URL,URI和QueryString,我们就可以来试一试他们的编码问题了,看下面一个Java Servlet程序:
import java.io.IOException;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import org.apache.logging.log4j.LogManager;
import org.apache.logging.log4j.Logger;
import org.wl.util.SpecialInfoToJson;
import org.wl.util.StringUtils;
/**
* Servlet implementation class GetSpecialInfo
*/
public class GetSpecialInfos extends HttpServlet {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
private static final Logger log = LogManager.getLogger();
/**
* @see HttpServlet#HttpServlet()
*/
public GetSpecialInfos() {
super();
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
/**
* @see HttpServlet#doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
*/
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
doPost(request, response);
}
/**
* @see HttpServlet#doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
*/
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
response.setContentType("text/html;charset=utf-8");
log.info(request.getCharacterEncoding());
request.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
log.info(request.getCharacterEncoding());
log.info(request.getQueryString());
System.out.println();
String category = request.getParameter("category");
if(StringUtils.isNullOrEmpty(category))
{
response.getWriter().append("category is null");
return;
}
log.info(category);
// category = new String(category.getBytes("iso-8859-1"),"utf-8");
// category = new String(category.getBytes("iso-8859-1"),"gbk");
// log.info(category);
response.getWriter().append(SpecialInfoToJson.getCategoryInfo(category));
}
}
我用的是tomcat服务器,如果要进行简单测试,可以把log语句换为System.out.println();输出直接到控制台,避免配置log4j2。可以把最后的response.getWriter().append(SpecialInfoToJson.getCategoryInfo(category));去掉。
直接通过浏览器访问:http://localhost:8080/market/GetSpecialInfos?category=土特产
把market换为您的工程名字。
通过IE浏览器访问控制台的输出:
null
22:02:58.492 INFO org.wl.app.GetSpecialInfos 44 doPost - utf-8
22:02:58.492 INFO org.wl.app.GetSpecialInfos 45 doPost - category=ÍÁÌزú
22:02:58.492 INFO org.wl.app.GetSpecialInfos 52 doPost - ÍÁÌزú
通过Firefox或者Google浏览器访问控制台的输出(忽略了部分输出):
null
utf-8
category=%E5%9C%9F%E7%89%B9%E4%BA%A7
åç¹äº§
现在还暂时猜测不出是什么意思,没有关系我们先把把被注释掉的代码
category = new String(category.getBytes("iso-8859-1"),"utf-8");去掉注释,在重新运行。
发现用Firefox或者Google浏览器访问的控制台的输出为:
null
utf-8
category=%E5%9C%9F%E7%89%B9%E4%BA%A7
åç¹äº§
土特产
用IE访问控制台的输出为:
null
22:43:56.614 INFO org.wl.app.GetSpecialInfos 44 doPost - utf-8
22:43:56.614 INFO org.wl.app.GetSpecialInfos 45 doPost - category=ÍÁÌزú
22:43:56.614 INFO org.wl.app.GetSpecialInfos 53 doPost - ÍÁÌزú
22:43:56.614 INFO org.wl.app.GetSpecialInfos 56 doPost - ���ز�
说明Firefox和Google对于QueryString的编码格式是utf-8。而IE对于QueryString的编码肯定不是utf-8。
我们在把category = new String(category.getBytes("iso-8859-1"),"utf-8");注释掉。
把 category = new String(category.getBytes("iso-8859-1"),"gbk");的注释去掉。重新运行,然后通过IE
Firefox、Google浏览器来访问。
控制台的输出为IE正常了,Firefox和Google乱码了。说明IE用的是gbk或者以其兼容的编码方式(gb2312等)
对QueryString进行编码的。
下面我们重新来看一看这一句:category = new String(category.getBytes("iso-8859-1"),"utf-8");
我们为什么要category.getBytes("iso-8859-1"),用iso-8859-1这一编码来得到字节数组。是因为对于QueryString来说,如果没有中请求头(header)中设置contentType,在tomcat的servlet.xml配置文件中也没有设置<Connector URIEncoding=”utf-8” uesBodyEncodingForURI=”true” />这样的配置。那么就会使用iso-8859-1对QueryString进行编码。我们的request.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");这一句一直输出的是null,说明浏览器并没有设置contentType。我们也没有配置服务器,所以就使用的是iso-8859-1对QueryString进行的编码。
同时我们发现request.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");这一句好像没有用,对于get方式提交的(包括,url参数,和表单通过get方法提交)的确没有作用,但是对于post提交的是用用的。如果有兴趣可以试一试。
注意:必须同时设定了contentType和uesBodyEncodingForURI=”true”才会使用contentType的方式对QueryString就像解码。