android:fitSystemWindows详解
从Android 4.4开始,Android系统加入了一个比较酷的功能,就是我们可以设置状态栏的的颜色了,有个这个功能,状态栏就不再是黑乎乎的了,我们就可以根据我们应用的主色去设置状态栏的颜色,使得应用体验变得好一些,所以我们通过如下方式设置状态栏透明。
window.setFlags(WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_TRANSLUCENT_STATUS, WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_TRANSLUCENT_STATUS); window.setFlags(WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_TRANSLUCENT_NAVIGATION, WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_TRANSLUCENT_NAVIGATION);
但是设置了状态栏和导航栏透明之后,发现Activity的contentView超出了ActionBar,那么我们就要使用fitSystemWindws来解决这个问题,关于具体如何解决这个问题,在Android4.4新的特性,在应用内开启透明状态栏和透明虚拟按钮这篇博客中有详细介绍。
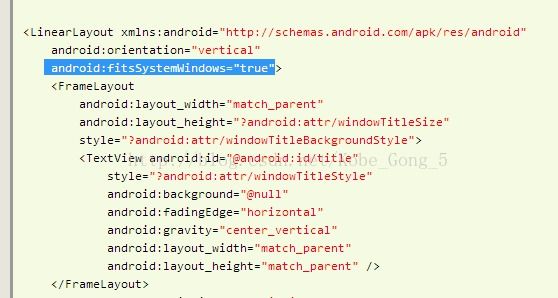
那么android:fitSystemWindows到底是什么东西啊,它是怎样计算的?
在Android Framework的源代码中查看View.java,有这几个重要方法,如下:
dispatchApplyWindowInsets
onApplyWindowInsets
fitSystemWindows
是一个自定义的View,并且覆盖View的这三个方法,打印出Log,可以发现这三个方法的调用顺序是
dispatchApplyWindowInsets
onApplyWindowInsets
fitSystemWindows
这里我们通过代码调试的方法来查看Android Framework的方法调用堆栈,如图:
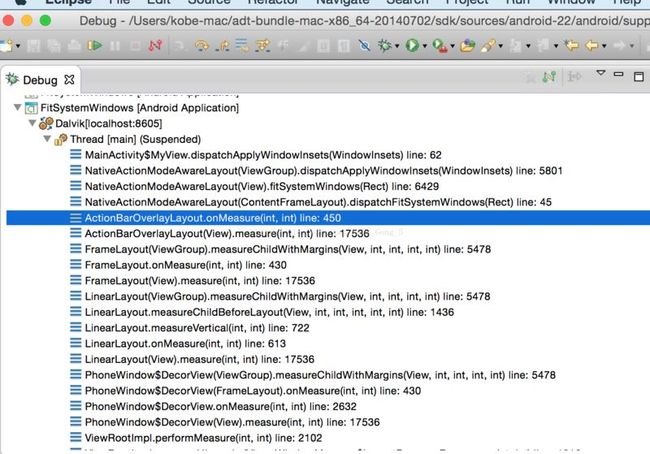
根据堆栈可以发现,dispatchApplyWindowInsets方法是在ViewRootImpl.performMeasure(int,int)方法中调用的。也就是说,dispatchApplyWindowInsets是在整个View Hierarchy的measure过程中调用的。
在从layout文件中解释到fitSystemWindows为true设置标志位。那这个标志为在什么时候起的作用。
case com.android.internal.R.styleable.View_fitsSystemWindows:
if (a.getBoolean(attr, false)) {
viewFlagValues |= FITS_SYSTEM_WINDOWS;viewFlagMasks |= FITS_SYSTEM_WINDOWS;}break;
再看上面那幅堆栈图,在ActionBarOverlayLayout.measure()中开始调用fitSystemWindows的相关方法,进入ActionBarOverlayLayout的源码。
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {//通过findViewById方法,得到布局文件中的viewpullChildren();int maxHeight = 0;int maxWidth = 0;int childState = 0;int topInset = 0;int bottomInset = 0;//测量ActionBar的高度和宽度measureChildWithMargins(mActionBarTop, widthMeasureSpec, 0, heightMeasureSpec, 0);
LayoutParams lp = (LayoutParams) mActionBarTop.getLayoutParams();
maxWidth = Math.max(maxWidth,
mActionBarTop.getMeasuredWidth() + lp.leftMargin + lp.rightMargin);
maxHeight = Math.max(maxHeight,
mActionBarTop.getMeasuredHeight() + lp.topMargin + lp.bottomMargin);
childState = ViewUtils.combineMeasuredStates(childState,
ViewCompat.getMeasuredState(mActionBarTop));// xlarge screen layout doesn't have bottom action bar.//测量ActionBar底部区域的高度和宽度if (mActionBarBottom != null) {
measureChildWithMargins(mActionBarBottom, widthMeasureSpec, 0, heightMeasureSpec, 0);
lp = (LayoutParams) mActionBarBottom.getLayoutParams();
maxWidth = Math.max(maxWidth,
mActionBarBottom.getMeasuredWidth() + lp.leftMargin + lp.rightMargin);
maxHeight = Math.max(maxHeight,
mActionBarBottom.getMeasuredHeight() + lp.topMargin + lp.bottomMargin);
childState = ViewUtils.combineMeasuredStates(childState,
ViewCompat.getMeasuredState(mActionBarBottom));
}final int vis = ViewCompat.getWindowSystemUiVisibility(this);final boolean stable = (vis & SYSTEM_UI_FLAG_LAYOUT_STABLE) != 0;if (stable) {// This is the standard space needed for the action bar. For stable measurement,// we can't depend on the size currently reported by it -- this must remain constant.topInset = mActionBarHeight;//考虑到ActionbarTab的高度,计算topInsetif (mHasNonEmbeddedTabs) {final View tabs = mActionBarTop.getTabContainer();if (tabs != null) {// If tabs are not embedded, increase space on top to account for them.topInset += mActionBarHeight;
}
}
} else if (mActionBarTop.getVisibility() != GONE) {// This is the space needed on top of the window for all of the action bar// and tabs.topInset = mActionBarTop.getMeasuredHeight();
}//如果ActionBar是split模式,考虑底部的高度,计算insetBottomif (mDecorToolbar.isSplit()) {// If action bar is split, adjust bottom insets for it.if (mActionBarBottom != null) {if (stable) {
bottomInset = mActionBarHeight;
} else {
bottomInset = mActionBarBottom.getMeasuredHeight();
}
}
}// If the window has not requested system UI layout flags, we need to// make sure its content is not being covered by system UI... though it// will still be covered by the action bar if they have requested it to// overlay.mContentInsets.set(mBaseContentInsets);
mInnerInsets.set(mBaseInnerInsets);if (!mOverlayMode && !stable) {
mContentInsets.top += topInset;
mContentInsets.bottom += bottomInset;
} else {
mInnerInsets.top += topInset;
mInnerInsets.bottom += bottomInset;
}//在ActionBar为非Overlay模式下,应用计算好的ContentInsetsapplyInsets(mContent, mContentInsets, true, true, true, true);//if (!mLastInnerInsets.equals(mInnerInsets)) {// If the inner insets have changed, we need to dispatch this down to// the app's fitSystemWindows(). We do this before measuring the content// view to keep the same semantics as the normal fitSystemWindows() call.mLastInnerInsets.set(mInnerInsets);//Overlay模式下,将InnerInsets分发到子View中。 mContent.dispatchFitSystemWindows(mInnerInsets);}
measureChildWithMargins(mContent, widthMeasureSpec, 0, heightMeasureSpec, 0);
lp = (LayoutParams) mContent.getLayoutParams();
maxWidth = Math.max(maxWidth,
mContent.getMeasuredWidth() + lp.leftMargin + lp.rightMargin);
maxHeight = Math.max(maxHeight,
mContent.getMeasuredHeight() + lp.topMargin + lp.bottomMargin);
childState = ViewUtils.combineMeasuredStates(childState,
ViewCompat.getMeasuredState(mContent));// Account for padding toomaxWidth += getPaddingLeft() + getPaddingRight();
maxHeight += getPaddingTop() + getPaddingBottom();// Check against our minimum height and widthmaxHeight = Math.max(maxHeight, getSuggestedMinimumHeight());
maxWidth = Math.max(maxWidth, getSuggestedMinimumWidth());
setMeasuredDimension(
ViewCompat.resolveSizeAndState(maxWidth, widthMeasureSpec, childState),
ViewCompat.resolveSizeAndState(maxHeight, heightMeasureSpec,
childState << MEASURED_HEIGHT_STATE_SHIFT));
}
根据上面的堆栈图知道mContent是NativeActionModeAwareLayout类型,而NativeActionModeAwareLayout,没有dispatchFitSystemWindows方法,那么查看其父类的dispatchFitSystemWindows方法。NativeActionModeAwareLayout的父类是ContentFrameLayout类型,看它的dispatchFitSystemWindows方法。
public void dispatchFitSystemWindows(Rect insets) {
fitSystemWindows(insets);
}
它直接调用View的fitSystemWindows方法。看View的fitSystemWindows方法。
protected boolean fitSystemWindows(Rect insets) {if ((mPrivateFlags3 & PFLAG3_APPLYING_INSETS) == 0) {if (insets == null) {// Null insets by definition have already been consumed.// This call cannot apply insets since there are none to apply,// so return false.return false;
}try {
mPrivateFlags3 |= PFLAG3_FITTING_SYSTEM_WINDOWS;return dispatchApplyWindowInsets(new WindowInsets(insets)).isConsumed();
} finally {
mPrivateFlags3 &= ~PFLAG3_FITTING_SYSTEM_WINDOWS;
}
} else {return fitSystemWindowsInt(insets);
}
}
由于第一次调用,这里的mPrivateFlags3 的PFLAG3_APPLYING_INSETS标志为不为1,所以进入if条件。进入dispatchApplyWindowInsets方法。并将mPrivateFlags3 的PFLAG3_APPLYING_INSETS标志为置为1。由于ContentFrameLayout继承了Framelayout ,所以进入了ViewGroup的dispatchApplyWindowInsets方法。
@Overridepublic WindowInsets dispatchApplyWindowInsets(WindowInsets insets) {
insets = super.dispatchApplyWindowInsets(insets);if (!insets.isConsumed()) {final int count = getChildCount();for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
insets = getChildAt(i).dispatchApplyWindowInsets(insets);if (insets.isConsumed()) {break;
}
}
}return insets;
}
首先调用了 super.dispatchApplyWindowInsets方法,也就是View的 dispatchApplyWindowInsets,
然后如果insets没有被消费掉的话,分别调用每个view child的dispatchApplyWindowInsets方法,让子view去消费它,如果子view消费了,那么到此结束。先执行 super.dispatchApplyWindowInsets方法。
下面是View.dispatchApplyWindowInsets方法。
public WindowInsets dispatchApplyWindowInsets(WindowInsets insets) {try {
mPrivateFlags3 |= PFLAG3_APPLYING_INSETS;if (mListenerInfo != null && mListenerInfo.mOnApplyWindowInsetsListener != null) {return mListenerInfo.mOnApplyWindowInsetsListener.onApplyWindowInsets(this, insets);
} else {return onApplyWindowInsets(insets);
}
} finally {
mPrivateFlags3 &= ~PFLAG3_APPLYING_INSETS;
}
}
在此方法中首先将mPrivateFlags3 的PFLAG3_APPLYING_INSETS标志位置为1,然后如果开发者设置了listener的话就调用listener,否则调用onApplyWindowInsets方法。
public WindowInsets onApplyWindowInsets(WindowInsets insets) {if ((mPrivateFlags3 & PFLAG3_FITTING_SYSTEM_WINDOWS) == 0) {if (fitSystemWindows(insets.getSystemWindowInsets())) {return insets.consumeSystemWindowInsets();
}
} else {if (fitSystemWindowsInt(insets.getSystemWindowInsets())) {return insets.consumeSystemWindowInsets();
}
}return insets;
}
在第一次调用fitSystemWindows方法后,mPrivateFlags3 得 PFLAG3_FITTING_SYSTEM_WINDOWS标志为被置位1了,所以进入fitSystemWindowsInt方法。
private boolean fitSystemWindowsInt(Rect insets) {if ((mViewFlags & FITS_SYSTEM_WINDOWS) == FITS_SYSTEM_WINDOWS) {
mUserPaddingStart = UNDEFINED_PADDING;
mUserPaddingEnd = UNDEFINED_PADDING;
Rect localInsets = sThreadLocal.get();if (localInsets == null) {
localInsets = new Rect();
sThreadLocal.set(localInsets);
}
boolean res = computeFitSystemWindows(insets, localInsets);
mUserPaddingLeftInitial = localInsets.left;
mUserPaddingRightInitial = localInsets.right;
internalSetPadding(localInsets.left, localInsets.top,
localInsets.right, localInsets.bottom);return res;
}return false;
}
在这个方法中,两个关键函数
computeFitSystemWindows
internalSetPadding
先看computeFitSystemWindows。官方解释是,计算insets应该被此view消费掉还是继续传递。
protected boolean computeFitSystemWindows(Rect inoutInsets, Rect outLocalInsets) {if ((mViewFlags & OPTIONAL_FITS_SYSTEM_WINDOWS) == 0|| mAttachInfo == null|| ((mAttachInfo.mSystemUiVisibility & SYSTEM_UI_LAYOUT_FLAGS) == 0&& !mAttachInfo.mOverscanRequested)) {
outLocalInsets.set(inoutInsets);
inoutInsets.set(0, 0, 0, 0);return true;
} else {// The application wants to take care of fitting system window for// the content... however we still need to take care of any overscan here.final Rect overscan = mAttachInfo.mOverscanInsets;
outLocalInsets.set(overscan);
inoutInsets.left -= overscan.left;
inoutInsets.top -= overscan.top;
inoutInsets.right -= overscan.right;
inoutInsets.bottom -= overscan.bottom;return false;
}
}
再看internalSetPadding
此方法是设置view的padding。
protected void internalSetPadding(int left, int top, int right, int bottom) {
mUserPaddingLeft = left;
mUserPaddingRight = right;
mUserPaddingBottom = bottom;final int viewFlags = mViewFlags;boolean changed = false;// Common case is there are no scroll bars.if ((viewFlags & (SCROLLBARS_VERTICAL|SCROLLBARS_HORIZONTAL)) != 0) {if ((viewFlags & SCROLLBARS_VERTICAL) != 0) {final int offset = (viewFlags & SCROLLBARS_INSET_MASK) == 0? 0 : getVerticalScrollbarWidth();switch (mVerticalScrollbarPosition) {case SCROLLBAR_POSITION_DEFAULT:if (isLayoutRtl()) {
left += offset;
} else {
right += offset;
}break;case SCROLLBAR_POSITION_RIGHT:
right += offset;break;case SCROLLBAR_POSITION_LEFT:
left += offset;break;
}
}if ((viewFlags & SCROLLBARS_HORIZONTAL) != 0) {
bottom += (viewFlags & SCROLLBARS_INSET_MASK) == 0? 0 : getHorizontalScrollbarHeight();
}
}if (mPaddingLeft != left) {
changed = true;
mPaddingLeft = left;
}if (mPaddingTop != top) {
changed = true;
mPaddingTop = top;
}if (mPaddingRight != right) {
changed = true;
mPaddingRight = right;
}if (mPaddingBottom != bottom) {
changed = true;
mPaddingBottom = bottom;
}if (changed) {
requestLayout();
}
}