IO流即输入输出流,流是一组有顺序的,有起点和终点的字节结合,是对数据传输的总称。即数据在两设备间的传输称为流,流的本质是数据传输。
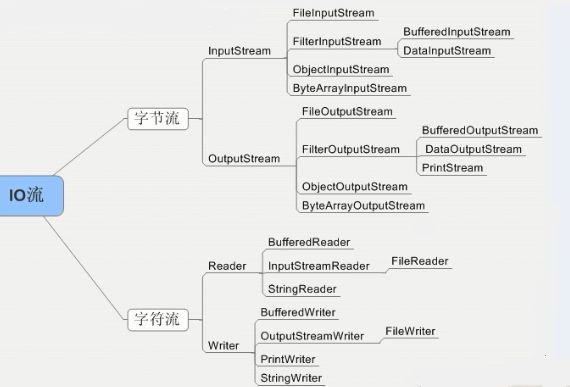
IO流可以分为字节流和字符流。给出相应的IO结构图:
在接下来的一段时间里,将会慢慢介绍各种流的使用,本篇博客先介绍字节流的FileOutputStream和相对应的FileInputStream。
一.FileOutputStream(文件输出流)
OutputStream是一个抽象类,抽象类必须通过子类实现。现在要向文件里输出就要用FileOutputStream。
FileOutputStream有四个构造方法,分别为
1.FileOutputStream(File file)-------------向File对象的文件写入数据
2.FileOutputStream(File file,boolean append);------向File对象的文件追加写入数据
3.FileOutputStream(String path)-------------向指定文件写入数据
4.FileOutputStream(String path,boolean append);--------向指定文件追加写入数据
当append的值为true时,向文件中写入的数据会追加到原数据的后面,否则会重写该文件的数据。默认为false。
写入方法1:一个个字节写入
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
//创建一个文件字节输出流对象
OutputStream os=new FileOutputStream("L:\\io.txt");
//写入的数据
String string="hello IO Stream";
byte[]bytes=string.getBytes();//转化为字节数组
for(int i=0;i<bytes.length;i++){
//向文件输出
os.write(bytes[i]);
}
os.close();//关闭流
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
方法二:全部一次写入
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
//创建一个文件字节输出流对象
OutputStream os=new FileOutputStream("L:\\io.txt",true);//追加
//写入的数据
String string="hello IO Stream";
byte[]bytes=string.getBytes();//转化为字节数组
os.write(bytes);//全部写入
//os.write(bytes,0,5)表示从0开始,写入长度为5个字节
os.close();//关闭流
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
一.FileInputStream(文件输入流)
FileInputStream是从系统的某个文件中获得输入字节,有两个构造方法
1.FileInputStream(File file)
2.FileInputStream(String path)
读取字节方法1:一个个字节读取
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
//创建一个字节输入流对象
InputStream is=new FileInputStream("L:\\io.txt");
int b=-1;
while((b=is.read())!=-1)//字节读取,当为-1时读取完毕
{
System.out.print((char)b);//转化为字符输出
}
is.close();//关闭流
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
输出结果为:hello IO Stream。这样一个一个字节读取,速度很慢。
读取字节方法2:一次性读取全部字节
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
File file=new File("L:\\io.txt");
//创建一个字节输入流对象
InputStream is=new FileInputStream(file);
//根据文件大小来创建字节数组
byte[]bytes=new byte[(int)file.length()] ;
int len=is.read(bytes);//返回读取字节的长度
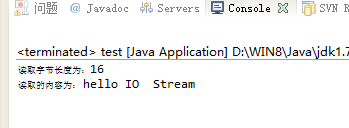
System.out.println("读取字节长度为:"+len);
System.out.println("读取的内容为: "+new String(bytes));//构建成字符串输出
is.close();//关闭流
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
运行结果:
这种读取方法主要缺点是要构建一个和文件大小一样大的字节数组,文件小的时候还可以,当文件很大,内存可能无法构架出如此大的字节数组。所以,这种方法只适合小文件。
读取字节方法3:每次读取指定长度(最常用的方法)
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
//创建一个字节输入流对象
InputStream is=new FileInputStream("L:\\io.txt");
//指定每次读取的大小--可根据性能字节修改
byte[]bytes=new byte[8] ;
StringBuffer sb=new StringBuffer();
int len=-1;//每次读取的实际长度
while((len=is.read(bytes))!=-1)
{
sb.append(new String(bytes,0,len));
}
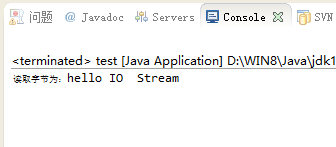
System.out.println("读取字节为:"+sb);
is.close();//关闭流
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
输出结果: