7.1.5 选项卡结合案例详解
选项卡是通过TabHost和TabActivity一起实现的,TabHost是Android中很常用的布局之一,它的标签可以有文本和文本图片样式。点击不同标签还可以切换标签。TabHost类的继承图如下:
java.lang.Object
↳android.view.View
↳android.view.ViewGroup
↳android.widget.FrameLayout
↳android.widget.TabHost
android.widget.TabHost继承了android.widget.FrameLayout框架布局类。下面是一个文本图片选项卡例子,如图7-10所示。
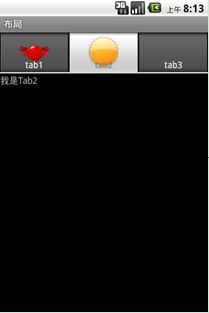
图7-10 TabHost1
代码请参考代码清单7-11,完整代码请参考chapter7_1工程中Tab1代码部分。
【代码清单7-11】
选项卡屏幕的Activity必须继承TabActivity,通过基类TabActivity提供的方法getTabHost()可以获得TabHost对象。下面的代码实现了为TabHost指定布局文件:
LayoutInflater.from(this).inflate(R.layout.tab1_layout,
tabHost.getTabContentView(), true);
addTab(TabHost.TabSpec tabSpec)方法可以添加选项卡的标签,本例中有三个标签。TabHost.TabSpec调用setIndicator()设置标签样式,有三个setIndicator ()方法:
• setIndicator(CharSequence label) 指定标签的文本信息;
• setIndicator(CharSequence label, Drawable icon) 指定文本图片标签;
• setIndicator(View view) 使用一个View指定标签。
TabHost.TabSpec调用setContent ()设置各个选项卡容纳的内容,有三个setContent ()方法:
• setContent(TabHost.TabContentFactory contentFactory) 通过TabHost.TabContentFactory工厂类创建选项卡的内容;
• setContent(int viewId) 通过一个id指定选项卡内容;
• setContent(Intent intent) 通过一个Intent指定选择选项卡跳转到一个Activity。
布局文件请参考代码清单7-12,完整代码请参考chapter7_1工程中tab1_layout.xml代码部分(chapter7_1/res/layout/tab1_layout.xml)。
【代码清单7-12】
下面的例子是指定一个Intent的选项卡跳转到一个Activity的例子,如图7-11所示,有两个选项卡:城市列表和城市展示。
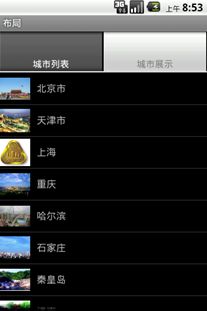
图7-11 TabHost2
代码请参考代码清单7-13,完整代码请参考chapter7_1工程中Tab2代码部分。
【代码清单7-13】
通过setContent方法设置Intent,当用户点击了选项卡的标签后,选项卡的内容会跳转。跳转之后的ListView_1和ListViewIcon_3是两个ListView展示城市信息,这两个ListView在第6章已经介绍了,这里就不再介绍了。
出自《Android开发案例驱动教程》第七章
java.lang.Object
↳android.view.View
↳android.view.ViewGroup
↳android.widget.FrameLayout
↳android.widget.TabHost
android.widget.TabHost继承了android.widget.FrameLayout框架布局类。下面是一个文本图片选项卡例子,如图7-10所示。

图7-10 TabHost1
代码请参考代码清单7-11,完整代码请参考chapter7_1工程中Tab1代码部分。
【代码清单7-11】
public class Tab1 extends TabActivity {
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
TabHost tabHost = getTabHost();
LayoutInflater.from(this).inflate(R.layout.tab1_layout,
tabHost.getTabContentView(), true);
tabHost.addTab(tabHost.newTabSpec("tab1").setIndicator("tab1",
getResources().getDrawable(R.drawable.redimage)).setContent(
R.id.view1));
tabHost.addTab(tabHost.newTabSpec("tab3").setIndicator("tab2",
getResources().getDrawable(R.drawable.yellowimage)).setContent(
R.id.view2));
tabHost.addTab(tabHost.newTabSpec("tab3").setIndicator("tab3")
.setContent(R.id.view3));
}
}
选项卡屏幕的Activity必须继承TabActivity,通过基类TabActivity提供的方法getTabHost()可以获得TabHost对象。下面的代码实现了为TabHost指定布局文件:
LayoutInflater.from(this).inflate(R.layout.tab1_layout,
tabHost.getTabContentView(), true);
addTab(TabHost.TabSpec tabSpec)方法可以添加选项卡的标签,本例中有三个标签。TabHost.TabSpec调用setIndicator()设置标签样式,有三个setIndicator ()方法:
• setIndicator(CharSequence label) 指定标签的文本信息;
• setIndicator(CharSequence label, Drawable icon) 指定文本图片标签;
• setIndicator(View view) 使用一个View指定标签。
TabHost.TabSpec调用setContent ()设置各个选项卡容纳的内容,有三个setContent ()方法:
• setContent(TabHost.TabContentFactory contentFactory) 通过TabHost.TabContentFactory工厂类创建选项卡的内容;
• setContent(int viewId) 通过一个id指定选项卡内容;
• setContent(Intent intent) 通过一个Intent指定选择选项卡跳转到一个Activity。
布局文件请参考代码清单7-12,完整代码请参考chapter7_1工程中tab1_layout.xml代码部分(chapter7_1/res/layout/tab1_layout.xml)。
【代码清单7-12】
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
>
<TextView android:id="@+id/view1"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:text="@string/tab1"/>
<TextView android:id="@+id/view2"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:text="@string/tab2"/>
<TextView android:id="@+id/view3"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:text="@string/tab3"/>
</LinearLayout>
下面的例子是指定一个Intent的选项卡跳转到一个Activity的例子,如图7-11所示,有两个选项卡:城市列表和城市展示。

图7-11 TabHost2
代码请参考代码清单7-13,完整代码请参考chapter7_1工程中Tab2代码部分。
【代码清单7-13】
public class Tab2 extends TabActivity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
TabHost tabHost = getTabHost();
tabHost.addTab(tabHost.newTabSpec("tab1").setIndicator("城市列表")
.setContent(new Intent(this, ListView_1.class)));
tabHost.addTab(tabHost.newTabSpec("tab3").setIndicator("城市展示")
.setContent(
new Intent(this, ListViewIcon_3.class)
.addFlags(Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_CLEAR_TOP)));
}
}
通过setContent方法设置Intent,当用户点击了选项卡的标签后,选项卡的内容会跳转。跳转之后的ListView_1和ListViewIcon_3是两个ListView展示城市信息,这两个ListView在第6章已经介绍了,这里就不再介绍了。
出自《Android开发案例驱动教程》第七章