构建高性能服务(一)ConcurrentSkipListMap和链表构建高性能Java Memcached
场景
缓存服务器是互联网后端服务中常用的基础设施。
场景(一)图片服务器上存储了大量图片,为了提高图片服务的吞吐量,希望把热门的图片加载到内存中。
场景(二)分布式存储服务,为提高访问吞吐,把大量的meta信息存储在内存中。
问题
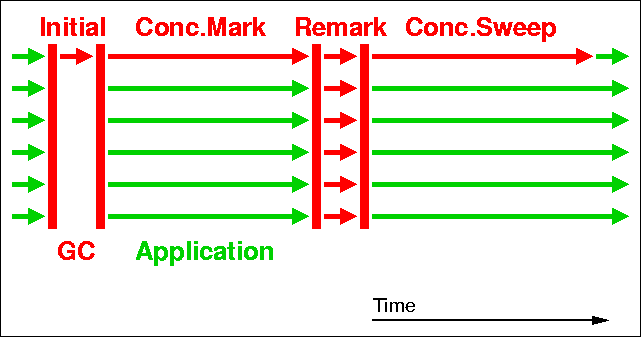
但是使用Java语言开发缓存服务,不可避免的遇到GC问题。无论使用ehcache是基于Map实现的缓存,都会产生大量Minor GC无法回收的对象,最终导致CMS或Full GC,对系统吞吐造成影响。通过观察这类服务产生的GC日志,可以观察到频繁的CMS。这里简单介绍下CMS的过程即对系统的影响,CMS两阶段标记,减少stop the world的时间,如图红色部分为STW(stop the world)。
CMS日志如下:
9.780: [GC [1 CMS-initial-mark: 507883K(507904K)] 521962K(521984K), 0.0029230 secs] [Times: user=0.00 sys=0.00, real=0.01 secs]
Total time for which application threads were stopped: 0.0029970 seconds
CMS第一次标记,stop the world。以下各个步骤则不影响Java Threads工作,即并发模式。
9.783: [CMS-concurrent-mark-start]
9.913: [CMS-concurrent-mark: 0.130/0.130 secs] [Times: user=0.26 sys=0.00, real=0.13 secs]
9.913: [CMS-concurrent-preclean-start]
9.914: [CMS-concurrent-preclean: 0.001/0.001 secs] [Times: user=0.00 sys=0.00, real=0.00 secs]
9.914: [CMS-concurrent-abortable-preclean-start]
9.914: [CMS-concurrent-abortable-preclean: 0.000/0.000 secs] [Times: user=0.00 sys=0.00, real=0.00 secs]
Application time: 0.1317920 seconds
9.914: [GC[YG occupancy: 14079 K (14080 K)]9.914: [Rescan (parallel) , 0.0023580 secs]9.917: [weak refs processing, 0.0000060 secs]
[1 CMS-remark: 507883K(507904K)] 521962K(521984K), 0.0024100 secs] [Times: user=0.01 sys=0.00, real=0.00 secs]
Total time for which application threads were stopped: 0.0025420 seconds
Rescan为第二次标记,STW。
解决方案
构造和Memcached slab/chunk类似的Java内存管理方式。为缓存的对象分配一组chunck,相同Size的Chunk合成一组Slab。初始slab设为100B,如果缓存对象小于100B,放入100B slab,如果大于100B,小于 100B * Growth Factor = 1.27 = 127B,则放入127B slab。因此需要一个快速排序的数据结构来实现slab。我用ConcurrentSkipListMap实现slab,查找插入时间复杂度和二叉树一致,但实现更简单。代码如下,
public boolean put(K key, byte[] value) {
Map.Entry<Float, LocalMCSlab> entry = null;
Float theSize = Float.valueOf(value.length);
Stat.set("CacheSize=", ((getCurrentTotalCacheSize() / 1024f)) + "KB");
// 以cache size为key,以chunks map为value,如果比这个cache size大得slab不存在,则创建一个
// 否则,在大约cache size的slab中找一个最小的slab
if((entry = slabs.tailMap(theSize).firstEntry()) == null) {
Float floorKey = slabs.floorKey(theSize);
float needSize = floorKey == null ? theSize : floorKey * scale;
while(needSize < theSize) {
needSize = needSize * scale;
}
LocalMCSlab<K, byte[]> slab = new LocalMCSlab<K, byte[]>((int) needSize);
slab.put(key, value, false);
slabs.put(needSize, slab);
return true;
}
else {
// 当当前全部cache size + 这个缓存的size > 分配给整个cache的initSize时,则需使用LRU策略
boolean isLRU = getCurrentTotalCacheSize() + theSize > initSize;
entry.getValue().put(key, value, isLRU);
return true;
}
}
每一个slab基于一个Map<K, V>实现。同时为实现LRU,实现了一个链表从头插入从尾部取出,这样链表尾部对象为last recent used,代码如下,
private static class LinkedListNode {
public LinkedListNode previous;
public LinkedListNode next;
public Object object;
/**
* Constructs a new linked list node.
* @param object the Object that the node represents.
* @param next a reference to the next LinkedListNode in the list.
* @param previous a reference to the previous LinkedListNode in the list.
*/
public LinkedListNode(Object object, LinkedListNode next,
LinkedListNode previous) {
this.object = object;
this.next = next;
this.previous = previous;
}
...
}
public static class LinkedList {
/**
* The root of the list keeps a reference to both the first and last
* elements of the list.
*/
private LinkedListNode head = new LinkedListNode("head", null, null);
/**
* Creates a new linked list.
*/
public LinkedList() {
head.next = head.previous = head;
}
/**
* Returns the first linked list node in the list.
*
* @return the first element of the list.
*/
public LinkedListNode getFirst() {
LinkedListNode node = head.next;
if (node == head) {
return null;
}
return node;
}
/**
* Returns the last linked list node in the list.
*
* @return the last element of the list.
*/
public LinkedListNode getLast() {
LinkedListNode node = head.previous;
if (node == head) {
return null;
}
return node;
}
public LinkedListNode removeLast() {
LinkedListNode node = head.previous;
if (node == head) {
return null;
}
head.previous = node.previous;
return node;
}
/**
* Adds a node to the beginning of the list.
*
* @param node the node to add to the beginning of the list.
*/
public LinkedListNode addFirst(LinkedListNode node) {
node.next = head.next;
head.next = node;
node.previous = head;
node.next.previous = node;
return node;
}
...
}
当LRU策略发生时,不再创建新的byte[],而是重写最老的一个byte[],并把这个cache移动到链表头部
if(removeLRU) {
LinkedListNode lastNode = ageList.removeLast();
Object lasthashKey = hashKeyMap.remove(lastNode.object);
if(lasthashKey == null) {
return false;
}
Stat.inc("eviction[" + this.chunkSize + "]");
CacheObject<byte[]> data = map.get(lasthashKey);
System.arraycopy(value, 0, data.object, 0, value.length);
data.length = value.length;
// update key / hashkey mapping
hashKeyMap.put(key, lasthashKey);
lastNode.object = key;
ageList.addFirst(lastNode);
}
注意使用了一个hashKeyMap,它的key是这次put的cache对象的key,value作为byte[]的key,在第一次创建byte[]时创建。这样做也是为了不重新创建对象。
全部代码及测试类见附件。
测试
测试参数
java -Xms2g -Xmx2g -Xmn128m -XX:+UseConcMarkSweepGC -server -XX:SurvivorRatio=5 -XX:CMSInitiatingOccupancyFraction=80 -XX:+PrintTenuringDistribution -XX:+PrintGCDetails -XX:+PrintGCTimeStamps -XX:+PrintGCApplicationStoppedTime -XX:+PrintGCApplicationConcurrentTime -Xloggc:./gc.log test.TestMain
测试表现稳定,内存全部在Minor GC阶段回收。
分配cache=1G,实际CacheSize==1048625.2KB;
各个slab chunk个数:
Chunk[100.0] count==5
Chunk[209758.16] count==1231
Chunk[165163.9] count==4938
总结
本来想写一个伪代码的,后来觉得Java中还是有不少比较好的数据结构,比如ConcurrentSkipListMap和LRUMap还是想介绍给大家。因此就写了这个比较粗糙的版本,基本可以反映出类似Memcached slab/chunk管理内存的方式。实际测试中表现也有一定收益。可以基于这个版本开发线上服务。但是这个实现里面还没有很好的处理并发问题,对内存的使用也有一些坑。使用中如果遇到问题,欢迎大家一起讨论。