什么是RPC?Remote Procedure Call,远程过程调用。也就是说,调用过程代码并不是在调用者本地运行,而是要实现调用者与被调用者二地之间的连接与通信。比较严格的定义是:
Remote procedure call (RPC) is a protocol that allows a computer program running on one computer to cause a subroutine on another computer to be executed without the programmer explicitly coding the details for this interaction. When the software in question is written using object-oriented principles, RPC may be referred to asremote invocation or remote method invocation.
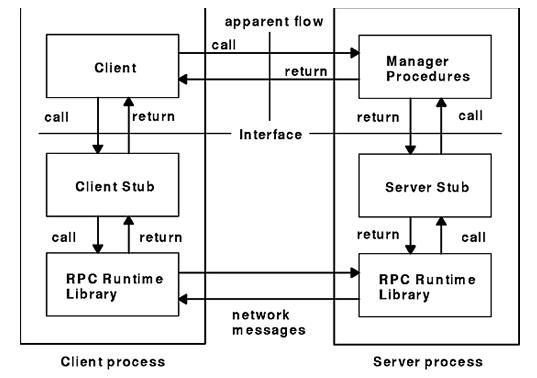
这样一讲, 容易联想到C/S模式的程序设计,我想是对的。RPC的基本通信模型是基于Client/Server进程间相互通信模型的一种同步通信形式;它对 Client提供了远程服务的过程抽象,其底层消息传递操作对Client是透明的。在RPC中,Client即是请求服务的调用者(Caller),而 Server则是执行Client的请求而被调用的程序 (Callee)。下图是RPC调用协议图:
首先是建立RPC服务,约定底层的RPC传输通道(UDP或是TCP)。客户端的调用参数根据传输前所提供的目的地址及RPC 上层应用程序号,通过底层的RPC传输通道转至相应的服务器,即RPC Application Porgramme Server。客户端随即处于等待状态,以服务器等待应答或Time Out超时信号。当服务器端获得了请求消息,会根据注册RPC时告诉RPC系统的程序入口地址执行相应的操作,并将结果返回至客户端。当一次RPC调用结束后,相应线程发送相应的信号,客户端程序便继续运行。
下载xml-rpc jar包 http://ws.apache.org/xmlrpc/download.html 当前版本:3.1.3
1、业务处理接口
public interface ServicesHandler {
public String execute(String str);
}
2、业务接口实现
public class HelloHandler implements ServicesHandler {
public String execute(String str) {
return "hello "+str+"!";
}
}
3、客户端
import java.net.MalformedURLException;
import java.net.URL;
import java.util.Vector;
import org.apache.xmlrpc.XmlRpcException;
import org.apache.xmlrpc.client.XmlRpcClient;
import org.apache.xmlrpc.client.XmlRpcClientConfigImpl;
public class TestClient {
/**
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
//配置客户端
XmlRpcClientConfigImpl config = new XmlRpcClientConfigImpl();
//设置服务器端地址
config.setServerURL(new URL("http://localhost:8080/Rpc/HelloHandler"));
//创建XmlRpc客户端
XmlRpcClient client = new XmlRpcClient();
//绑定以上设置
client.setConfig(config);
//创建参数列表
Vector<String> params = new Vector<String>();
params.addElement("flyoung");
//执行XML-RPC 请求
String result =(String) client.execute("HelloHandler.execute", params);
System.out.println("result:"+result);
} catch (MalformedURLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (XmlRpcException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
4、服务器端
import java.io.IOException;
import javax.servlet.ServletConfig;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import org.apache.xmlrpc.XmlRpcException;
import org.apache.xmlrpc.server.PropertyHandlerMapping;
import org.apache.xmlrpc.server.XmlRpcServerConfigImpl;
import org.apache.xmlrpc.webserver.XmlRpcServletServer;
import com.flyoung.xmlrpc.HelloHandler;
public class XmlRpcServicesServlet extends HttpServlet {
private XmlRpcServletServer server;
@Override
public void init(ServletConfig config) throws ServletException {
super.init(config);
try {
//创建XmlRpcServletServer对象
server = new XmlRpcServletServer();
//set up handler mapping of XmlRpcServletServer object
PropertyHandlerMapping pmp = new PropertyHandlerMapping();
pmp.addHandler("HelloHandler", HelloHandler.class);
server.setHandlerMapping(pmp);
//more config of XmlRpcServletServer object
XmlRpcServerConfigImpl serverConfig = (XmlRpcServerConfigImpl)server.getConfig();
serverConfig.setEnabledForExtensions(true);
serverConfig.setContentLengthOptional(false);
} catch (XmlRpcException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp)
throws ServletException, IOException {
server.execute(req, resp);
}
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp)
throws ServletException, IOException {
server.execute(req, resp);
}
}
5、xml配置
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<web-app version="2.5"
xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee
http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_2_5.xsd">
<display-name></display-name>
<welcome-file-list>
<welcome-file>index.jsp</welcome-file>
</welcome-file-list>
<servlet>
<servlet-name>XmlRpcServer</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>com.flyoung.xmlrpc.XmlRpcServicesServlet</servlet-class>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>XmlRpcServer</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/HelloHandler</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
</web-app>
6、测试结果
result:hello flyoung!
在RPC中,当一个请求到达RPC服务器时,这个请求就包含了一个参数集和一个文本值,通常形成“classname.methodname”的形 式。这就向RPC服务器表明,被请求的方法在为“classname”的类中,名叫“methodname”。然后RPC服务器就去搜索与之相匹配的类和 方法,并把它作为那种方法参数类型的输入。这里的参数类型是与RPC请求中的类型是匹配的。一旦匹配成功,这个方法就被调用了,其结果被编码后返回客户 方。
缺点:
1)XML-RPC的消息系统过于简单,没有完整意义上的消息模型;
2)XML-RPC调用服务的方式要求直接指定对象和方法,称不上完整的面向服务的体系;
3)XML-RPC服务器端提供的服务实际上是特定对象的某个方法,限制了服务器端的开发。