qooxdoo's events handle and dispatch
qooxdoo的事件处理机制相当简洁且不失灵活,qx.core.Target定义了如下3个常用的事件处理方法:
1. addEventListener
最简单的写法是
当然你也可以用inline function
比如,偶们有一个button,希望在点击它的时候能够隐藏,那么用事件处理机制就可以这样来写:
代码简单、好用、而且还充满亲切感。
如果你需要传递不同的context object,还可以这样调用:
2. removeEventListener
//TODO...
3. createDispatchEvent
//TODO..
举一个实际的Wizard Window来看一下qooxdoo的事件处理机制在构建复杂Widget时候的优势,先上图片:
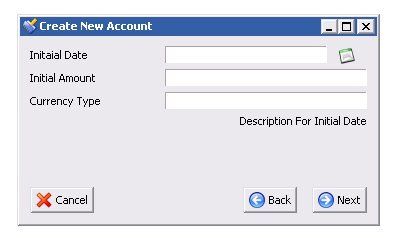
这个Wizard Window继承了qx.ui.window.Window,然后加入了几个button,并且在用户点击next button的时候,分发了一个DataEvent:
任何注册了qx.constant.Event.DIALOGNEXT事件的Listener Function就可以拿到这个事件用来做校验或者其他的工作,在下面代码里面,就是用来校验3个栏位是否都已经填写了值:
1. addEventListener
最简单的写法是
classInstance.addEventListener("eventName", functionPointer);
function functionPointer() {...};
当然你也可以用inline function
classInstance.addEventListener("eventName", functionPointer() {});
比如,偶们有一个button,希望在点击它的时候能够隐藏,那么用事件处理机制就可以这样来写:
var btnHideMe = new qx.ui.form.Button("Hide Me", "icon/16/ok.png");
btnFinish.addEventListener(qx.constant.Event.EXECUTE, function(){
this.hide();
});
代码简单、好用、而且还充满亲切感。
如果你需要传递不同的context object,还可以这样调用:
classInstance.addEventListener("eventName", functionPointer() {}, contextObject);
2. removeEventListener
//TODO...
3. createDispatchEvent
//TODO..
举一个实际的Wizard Window来看一下qooxdoo的事件处理机制在构建复杂Widget时候的优势,先上图片:

这个Wizard Window继承了qx.ui.window.Window,然后加入了几个button,并且在用户点击next button的时候,分发了一个DataEvent:
qx.OO.defineClass("com.javaeye.qooxdoo.WizardWindow", qx.ui.window.Window,
function(vCaption, vIcon, vWindowManager)
{
qx.ui.window.Window.call(this, vCaption, vIcon, vWindowManager);
var btnNext = this._btnNext = new qx.ui.form.Button("Next", "icon/16/forward.png");
btnNext.addEventListener(qx.constant.Event.EXECUTE, function() {
this.createDispatchDataEvent(qx.constant.Event.DIALOGNEXT, this.getSelectedIndex());
if(this.getCheckNext()){
this.next();
}
}, this);
var btnBack = this._btnBack = new qx.ui.form.Button("Back", "icon/16/back.png");
//...
});
任何注册了qx.constant.Event.DIALOGNEXT事件的Listener Function就可以拿到这个事件用来做校验或者其他的工作,在下面代码里面,就是用来校验3个栏位是否都已经填写了值:
var w = new com.javaeye.qooxdoo.WizardWindow("Create New Account", "icon/16/editor.png");
w.addEventListener(qx.constant.Event.DIALOGNEXT, function(e) {
switch(e.getData()){
case 0:
this.setCheckNext(true);
if(!txtAccountName.getValue()) {
txtAccountName.focus();
this.setCheckNext(false);
}
break;
case 1:
this.setCheckNext(true);
if(!txtInitialDate.getValue()) {
txtInitialDate.focus();
this.setCheckNext(false);
break;
}
if(!txtInitialAmount.getValue()) {
txtInitialAmount.focus();
this.setCheckNext(false);
break;
}
if(!txtCurrency.getValue()) {
txtCurrency.focus();
this.setCheckNext(false);
break;
}
break;
}
});