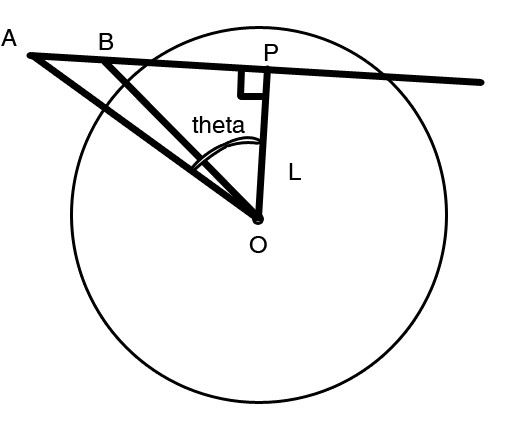
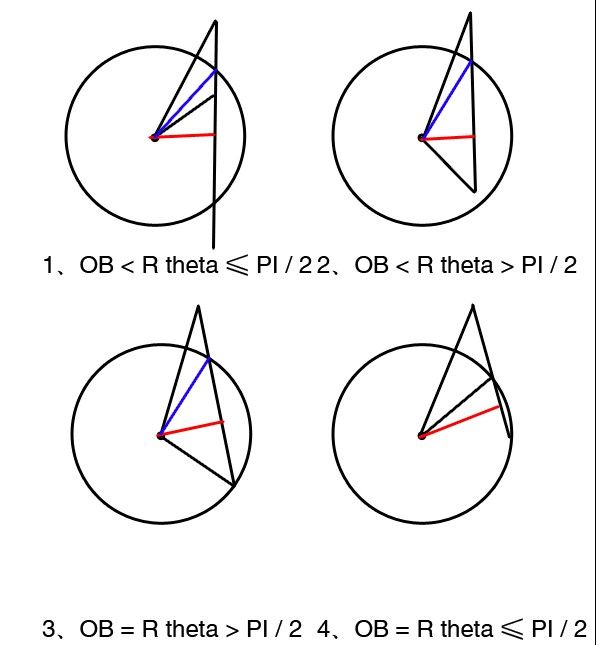
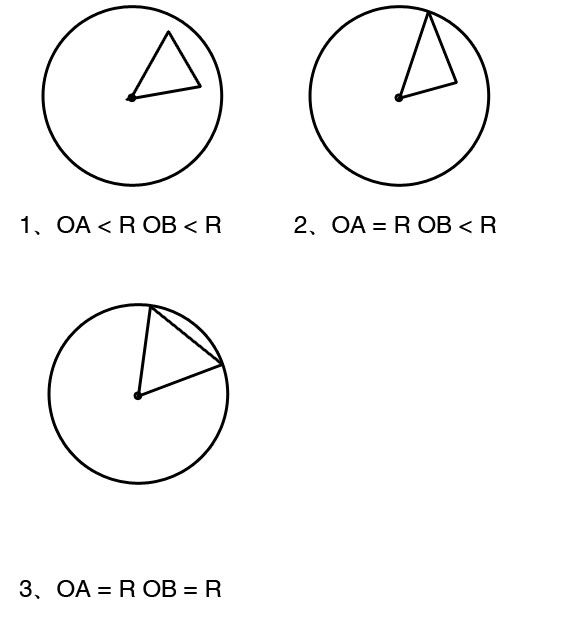
PKU 3675 Telescope .
Telescope
| Time Limit: 1000MS | Memory Limit: 65536K | |
| Total Submissions: 1178 | Accepted: 308 |
Description
Updog is watching a plane object with a telescope. The field of vision in the telescope can be described as a circle. The center is at the origin and the radius is R. The object can be seen as a simple polygon of N vertexes. Updog wants to know the area of the part of the object that can be seen in the telescope.
Input
The input will contain several test cases. For each case:
The first line contains only one real number R.
The second line contains an integer N. The following N lines contain two real numbers xi and yi each, which describe the coordinates of a vertex. Two vertexes in adjacent lines are also adjacent on the polygon.
Constraints: 3 ≤ N ≤50, 0.1 ≤ R ≤1000, -1000 ≤ xi, yi ≤ 1000
Output
For each test case, output one real number on a separate line, which is the area of the part that can be seen. The result should be rounded to two decimal places.
Sample Input
10 3 0 20 10 0 -10 0
Sample Output
144.35
Source
| 8994621 | GZHU1006100106 | 3675 | Accepted | 224K | 0MS | C++ | 2887B | 2011-07-25 15:52:39 |
#include <iostream>
#include <cmath>
using namespace std;
#define MAXI 0x400
#define sq(x) ((x) * (x))
#define sng(x) (x == 0.0? 0.0: (x > 0? 1.0: -1.0))
#define fmax(x, y) (x > y? x: y)
#define fmin(x, y) (x < y? x: y)
struct pt
{
double x, y;
pt(double a = 0, double b = 0)
{
x = a;
y = b;
}
double len() { return sqrt(sq(x) + sq(y)); }
double operator * (pt o) { return x * o.y - o.x * y; }
double operator % (pt o) { return x * o.x + y * o.y; }
} ps[MAXI];
struct sg
{
pt a, b;
double A, B, C;
sg(pt x, pt y)
{
a = x;
b = y;
A = a.y - b.y;
B = b.x - a.x;
C = -(a.y * B + a.x * A);
}
bool ons(pt o)
{
if (fmin(a.x, b.x) <= o.x && o.x <= fmax(a.x, b.x))
if (fmin(a.y, b.y) <= o.y && o.y <= fmax(a.y, b.y))
return 1;
return 0;
}
double len() { return sqrt(sq(a.x - b.x) + sq(a.y - b.y)); }
double ang() { return acos((a % b) / (a.len() * b.len())); }
pt inr(sg o)
{
double d = (A * o.B - o.A * B);
double x = B * o.C - o.B * C;
double y = A * o.C - o.A * C;
return pt(x / d, -y / d);
}
};
double r;
int n;
double TGL(pt a, pt b) //Triangulate
{
#if 0
printf("a = [%.2lf, %.2lf], b = [%.2lf, %.2lf]\n", a.x, a.y, b.x, b.y);
putchar('\n');
#endif
double sn = sng(a * b);
if (a.len() < b.len())
swap(a ,b);
pt lp(a.x - b.x, a.y - b.y), np(-lp.y, lp.x), cp;
sg l(a, b), nl(pt(0, 0), np);
pt tp = l.inr(nl);
double tsu = 0;
double oa = a.len();
double ob = b.len();
double ol = tp.len();;
double ang, d;
if (oa == 0.0 || oa == 0.0 || ol == 0.0)
return 0.0;
if (oa <= r && ob <= r)
{
tsu += fabs(a * b / 2.0);
#if 0
printf("stu 1");
putchar('\n');
#endif
}
else if (oa > r && ob <= r)
{
d = sqrt(sq(r) - sq(tp.len())) / l.len();
tp = pt(tp.x + lp.x * d, tp.y + lp.y * d);
ang = sg(a, tp).ang();
tsu += ang * sq(r) / 2.0;
tsu += fabs(tp * b/ 2.0);
#if 0
printf("stu 2");
printf("tp = [%.2lf, %.2lf]\n", tp.x, tp.y);
printf("part1 : %.2lf part2 %.2lf\n", ang * sq(r) / 2.0, fabs(tp * b/ 2.0));
putchar('\n');
#endif
}
else
{
ang = acos(ol / r);
tsu += l.ang() * sq(r) / 2.0;
if (oa > r && ob > r && ol < r && l.ons(tp))
tsu += ol * r * sin(ang) - ang * sq(r);
#if 0
printf("stu 3\n");
printf("%.2lf\n", acos(ol / r));
printf("part1 : %.2lf part2 %.2lf\n", l.ang() * sq(r) / 2.0, ol * r * sin(ang) - ang * sq(r));
putchar('\n');
#endif
}
#if 0
printf("tsu = %.2lf\n\n", tsu * sn);
#endif
return tsu * sn;
}
int main()
{
int i;
double tsu;
while (scanf("%lf", &r) != EOF)
{
scanf("%d", &n);
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
scanf("%lf%lf", &ps[i].x, &ps[i].y);
tsu = 0.0;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
tsu += TGL(ps[i], ps[(i + 1) % n]);
printf("%.2lf\n", fabs(tsu));
}
return 0;
}