图论算法-求(有向)图中任意两点间所有路径
求(有向)图中任意两点间所有路径
1建图:
图类中包括如下信息:顶点集合,邻接矩阵。
节点类中包括如下信息:是否被访问过,节点的名称,从这个节点访问到下一个节点的集合
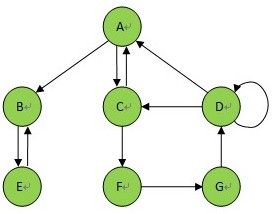
图1
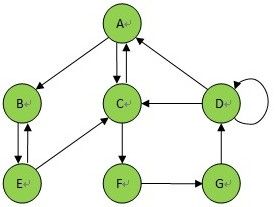
图2
2 算法思路
A 将始点设置为已访问,将其入栈
B 查看栈顶节点V在图中,有没有可以到达、且没有入栈、且没有从这个节点V出发访问过的节点
C 如果有,则将找到的这个节点入栈
D 如果没有,则将节点V访问到下一个节点的集合中每个元素赋值为零,V出栈
E 当栈顶元素为终点时,设置终点没有被访问过,打印栈中元素,弹出栈顶节点
F 重复执行B – E,直到栈中元素为空
package util;
public class Graph {
private Vertex vertexList[]; // list of vertices
private int adjMat[][]; // adjacency matrix
private int nVerts;
private static int MAX_VERTS = 7; // n个点
int i = 0;
int j = 0;
public Vertex[] getVertexList() {
return vertexList;
}
public int[][] getAdjMat() {
return adjMat;
}
public int getN() {
return MAX_VERTS;
}
public Graph(int index) {
adjMat = new int[MAX_VERTS][MAX_VERTS]; // 邻接矩阵
vertexList = new Vertex[MAX_VERTS]; // 顶点数组
nVerts = 0;
for (i = 0; i < MAX_VERTS; i++) {
for (j = 0; j < MAX_VERTS; j++) {
adjMat[i][j] = 0;
}
}
addVertex('A');
addVertex('B');
addVertex('C');
addVertex('D');
addVertex('E');
addVertex('F');
addVertex('G');
addEdge(0, 1);
addEdge(0, 2);
addEdge(1, 4);
addEdge(2, 0);
addEdge(2, 5);
addEdge(3, 0);
addEdge(3, 2);
addEdge(3, 3);
addEdge(4, 1);
addEdge(4, 2);
addEdge(5, 6);
addEdge(6, 3);
switch (index) {
case 0:
break;
case 1:
delEdge(4, 2);
break;
default:
break;
}
}
private void delEdge(int start, int end) {
adjMat[start][end] = 0;
}
private void addEdge(int start, int end) {// 有向图,添加边
adjMat[start][end] = 1;
// adjMat[end][start] = 1;
}
public void addVertex(char lab) {
vertexList[nVerts++] = new Vertex(lab);// 添加点
}
public char displayVertex(int i) {
return vertexList[i].getLabel();
}
public boolean displayVertexVisited(int i) {
return vertexList[i].WasVisited();
}
public void printGraph() {
for (i = 0; i < MAX_VERTS; i++) {
System.out.print("第" + displayVertex(i) + "个节点:" + " ");
for (j = 0; j < MAX_VERTS; j++) {
System.out.print(displayVertex(i) + "-" + displayVertex(j)
+ ":" + adjMat[i][j] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
package util;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class Vertex {
boolean wasVisited; // 是否遍历过
public char label; // 节点名称
ArrayList<Integer> allVisitedList;// 节点已访问过的顶点
public void setAllVisitedList(ArrayList<Integer> allVisitedList) {
this.allVisitedList = allVisitedList;
}
public ArrayList<Integer> getAllVisitedList() {
return allVisitedList;
}
public boolean WasVisited() {
return wasVisited;
}
public void setWasVisited(boolean wasVisited) {
this.wasVisited = wasVisited;
}
public char getLabel() {
return label;
}
public void setLabel(char label) {
this.label = label;
}
public Vertex(char lab) // constructor
{
label = lab;
wasVisited = false;
}
public void setVisited(int j) {
allVisitedList.set(j, 1);
}
}
package util;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Stack;
public class AF {
boolean isAF = true;
Graph graph;
int n;
int start, end;
Stack<Integer> theStack;
private ArrayList<Integer> tempList;
private String counterexample;
public AF(Graph graph, int start, int end) {
this.graph = graph;
this.start = start;
this.end = end;
}
public boolean getResult() {
graph.printGraph();
n = graph.getN();
theStack = new Stack<Integer>();
if (!isConnectable(start, end)) {
isAF = false;
counterexample = "节点之间没有通路";
} else {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
tempList = new ArrayList<Integer>();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
tempList.add(0);
}
graph.getVertexList()[j].setAllVisitedList(tempList);
}
isAF = af(start, end);
}
return isAF;
}
private boolean af(int start, int end) {
graph.getVertexList()[start].setWasVisited(true); // mark it
theStack.push(start); // push it
while (!theStack.isEmpty()) {
int v = getAdjUnvisitedVertex(theStack.peek());
if (v == -1) // if no such vertex,
{
tempList = new ArrayList<Integer>();
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
tempList.add(0);
}
graph.getVertexList()[theStack.peek()]
.setAllVisitedList(tempList);// 把栈顶节点访问过的节点链表清空
theStack.pop();
} else // if it exists,
{
theStack.push(v); // push it
}
if (!theStack.isEmpty() && end == theStack.peek()) {
graph.getVertexList()[end].setWasVisited(false); // mark it
printTheStack(theStack);
System.out.println();
theStack.pop();
}
}
return isAF;
}
// 判断连个节点是否能连通
private boolean isConnectable(int start, int end) {
ArrayList<Integer> queue = new ArrayList<Integer>();
ArrayList<Integer> visited = new ArrayList<Integer>();
queue.add(start);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (graph.getAdjMat()[start][j] == 1 && !visited.contains(j)) {
queue.add(j);
}
}
if (queue.contains(end)) {
return true;
} else {
visited.add(queue.get(0));
queue.remove(0);
if (!queue.isEmpty()) {
start = queue.get(0);
}
}
}
return false;
}
public String counterexample() {
for (Integer integer : theStack) {
counterexample += graph.displayVertex(integer);
if (integer != theStack.peek()) {
counterexample += "-->";
}
}
return counterexample;
}
// 与节点v相邻,并且这个节点没有被访问到,并且这个节点不在栈中
public int getAdjUnvisitedVertex(int v) {
ArrayList<Integer> arrayList = graph.getVertexList()[v]
.getAllVisitedList();
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (graph.getAdjMat()[v][j] == 1 && arrayList.get(j) == 0
&& !theStack.contains(j)) {
graph.getVertexList()[v].setVisited(j);
return j;
}
}
return -1;
} // end getAdjUnvisitedVertex()
public void printTheStack(Stack<Integer> theStack2) {
for (Integer integer : theStack2) {
System.out.print(graph.displayVertex(integer));
if (integer != theStack2.peek()) {
System.out.print("-->");
}
}
}
}
import util.AF;
import util.Graph;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//第几张图,有两张(0,1),起点序号(0-6),终点序号(0-6)
AF operation = new AF(new Graph(0), 3, 6);
operation.getResult();
}
}