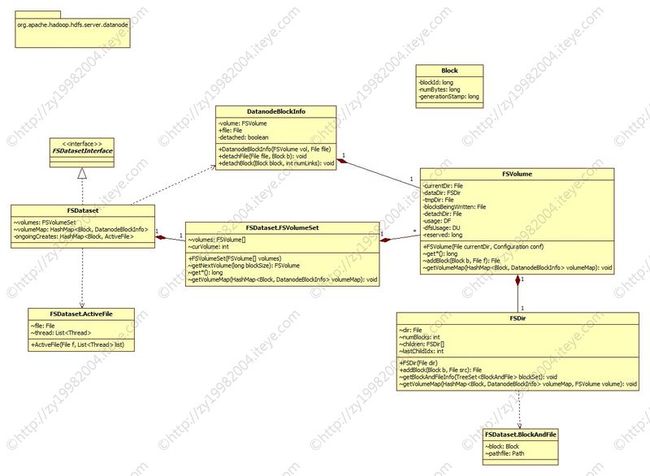
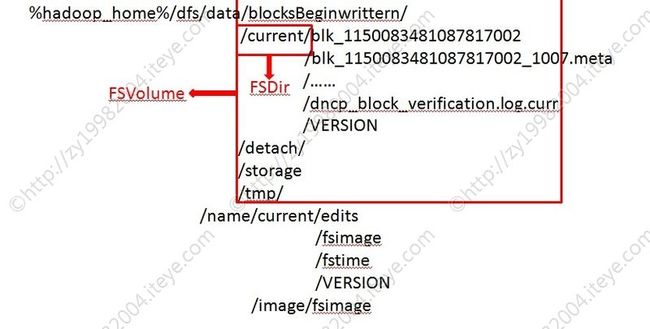
一.FSDataset类图
二.FSVolume FSDir物理概念
三.Block
- Block类只代表一个block的标识,看Block类的属性便知;Block类不代表block文件。
- blk_1150083481087817002是block;%hadoop_home%/dfs/data/current/blk_115008348108781700是block文件。
- block包含block blk_1150083481087817002和block元数据 blk_1150083481087817002_1007.meta。本系列博客中没有特别说明时,block只表示block blk_1150083481087817002。
//blk_1150083481087817002
//blk_1150083481087817002_1007.meta
public class Block implements Writable, Comparable<Block> {
//change fileName to id
static long filename2id(String name) {
return Long.parseLong(name.substring("blk_".length()));
}
//change id to fileName
public String getBlockName() {
return "blk_" + String.valueOf(blockId);
}
private long blockId; //block id:1150083481087817002
private long numBytes; //block大小
private long generationStamp; //从1000L开始:1007 当两个块进行比较的时候,当它们的hashcode相同时,便用generationStamp进行比较
public Block() {
this(0, 0, 0);
}
//blockId相同
//generationStamp时间相同两个条件
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (!(o instanceof Block)) {
return false;
}
final Block that = (Block) o;
return this.blockId == that.blockId
&& GenerationStamp.equalsWithWildcard(this.generationStamp,
that.generationStamp);
}
//根据blockId计算hashcode
public int hashCode() {
return 37 * 17 + (int) (blockId ^ (blockId >>> 32));
}
}
四.BlockAndFile
BlockAndFile类代表了block与block文件的对应关系。
// block与block文件的对应关系
static class BlockAndFile implements Comparable<BlockAndFile> {
final Block block;
// absolute path eg:%hadoop_home%/dfs/data/current/blk_1150083481087817002
final File pathfile;
BlockAndFile(File fullpathname, Block block) {
this.pathfile = fullpathname;
this.block = block;
}
public int compareTo(BlockAndFile o) {
return this.block.compareTo(o.block);
}
}
五.DatanodeBlockInfo
- DatanodeBlockInfo保存了block在文件系统上的信息,包含block存放的卷(FSVolume),文件名和detach状态。
- detach状态:系统在升级时会创建一个snapshot,snapshot的文件和current里的数据块文件和数据块元文件是通过硬链接,指向了相同的内容。当我们需要改变current里的文件时,如果不进行detach操作,那么,修改的内容就会影响snapshot里的文件,这时,我们需要将对应的硬链接解除掉。方法很简单,就是在临时文件夹里,复制文件,然后将临时文件改名成为current里的对应文件,这样的话,current里的文件和snapshot里的文件就detach了。这样的技术,也叫copy-on-write,是一种有效提高系统性能的方法。DatanodeBlockInfo中的detachBlock,能够对Block对应的数据文件和元数据文件进行detach操作。
//Block----->DatanodeBlockInfo class DatanodeBlockInfo { private FSVolume volume; // block所在的FSVolume private File file; // block文件 private boolean detached; // copy-on-write done for block DatanodeBlockInfo(FSVolume vol, File file) { this.volume = vol; this.file = file; detached = false; } /** * 1. Copy specified file into a temporary file. * 2. Then rename the temporary file to the original name. * This will cause any hardlinks to the original file to be removed. * The temporary files are created in the detachDir. * The temporary files will be recovered (especially on Windows) on datanode restart. */ private void detachFile(File file, Block b) throws IOException { ... } } /** * Returns true if this block was copied, otherwise returns false. */ boolean detachBlock(Block block, int numLinks) throws IOException { 。。。 } }
六.FSDir
- FSDir是保存block的文件夹。
- FSDir是一个树状结构,最外层是%hadoop_home%/dfs/data/current。
- 初始化FSDir时,迭代初始化%hadoop_home%/dfs/data/current下的所有children FSDir,构成FSDir树。
- FSDir的重要方法
- addBlock:向此FSDir中添加block,返回这个block对应的block文件。
- getBlockAndFileInfo:获得此FSDir下所有BlockAndFile。
- getVolumeMap:获得此FSDir下所有block到DatanodeBlockInfo的映射关系。
// 保存block的文件夹 class FSDir { File dir; // FSDir会有一个根目录,最外面的当然是/current int numBlocks = 0; // FSDir下的block数量 FSDir children[]; // FSDir下可以继续包含FSDir int lastChildIdx = 0; // 存储上一个数据块的子目录序号 // 初始化时,构建FSDir树 public FSDir(File dir) throws IOException { this.dir = dir; this.children = null; File[] files = FileUtil.listFiles(dir); int numChildren = 0; for (int idx = 0; idx < files.length; idx++) { if (files[idx].isDirectory()) { numChildren++; } else if (Block.isBlockFilename(files[idx])) { numBlocks++; } } if (numChildren > 0) { children = new FSDir[numChildren]; int curdir = 0; for (int idx = 0; idx < files.length; idx++) { if (files[idx].isDirectory()) { // 迭代初始化children FSDir children[curdir] = new FSDir(files[idx]); curdir++; } } } } public File addBlock(Block b, File src) throws IOException { // First try without creating subdirectories File file = addBlock(b, src, false, false); return (file != null) ? file : addBlock(b, src, true, true); } private File addBlock(Block b, File src, boolean createOk, boolean resetIdx) throws IOException { // DataNode节点会首先把文件的数据块存储到存储路径的子目录current/下 if (numBlocks < maxBlocksPerDir) { // src:tmp下 // dest:current下 File dest = new File(dir, b.getBlockName()); // metaData:tmp下 // newmeta:current下 File metaData = getMetaFile(src, b); File newmeta = getMetaFile(dest, b); // tmp下metaData移到current下,tmp下block移到current下 if (!metaData.renameTo(newmeta) || !src.renameTo(dest)) { throw new IOException("could not move files for " + b + " from tmp to " + dest.getAbsolutePath()); } numBlocks += 1; return dest; } // 当子目录current/中已经存储了maxBlocksPerDir个数据块之后 // 就会在目录current/下创建maxBlocksPerDir个子目录,然后从中选择一个子目录,把数据块存储到这个子目录中; // 如果选择的子目录也已经存储了maxBlocksPerDir个数据块,则又在这个子目录下创建maxBlocksPerDir个子目录,从这些子目录中选一个来存储数据块 // 就这样一次递归下去,直到存储路径的剩余存储空间不够存储一个数据块为止。 // maxBlocksPerDir的默认值是64,但也可以通过DataNode的配置文件来设置,它对应的配置选项是dsf.datanode.numblocks。 if (lastChildIdx < 0 && resetIdx) { // reset so that all children will be checked lastChildIdx = random.nextInt(children.length); } if (lastChildIdx >= 0 && children != null) { // Check if any child-tree has room for a block. for (int i = 0; i < children.length; i++) { int idx = (lastChildIdx + i) % children.length; File file = children[idx].addBlock(b, src, false, resetIdx); if (file != null) { lastChildIdx = idx; return file; } } lastChildIdx = -1; } if (!createOk) { return null; } if (children == null || children.length == 0) { children = new FSDir[maxBlocksPerDir]; for (int idx = 0; idx < maxBlocksPerDir; idx++) { children[idx] = new FSDir(new File(dir, DataStorage.BLOCK_SUBDIR_PREFIX + idx)); } } // now pick a child randomly for creating a new set of subdirs. lastChildIdx = random.nextInt(children.length); return children[lastChildIdx].addBlock(b, src, true, false); } // 获得此FSDir下所有BlockAndFile void getBlockAndFileInfo(TreeSet<BlockAndFile> blockSet) { // 迭代children FSDir if (children != null) { for (int i = 0; i < children.length; i++) { children[i].getBlockAndFileInfo(blockSet); } } File blockFiles[] = dir.listFiles(); for (int i = 0; i < blockFiles.length; i++) { if (Block.isBlockFilename(blockFiles[i])) { long genStamp = FSDataset.getGenerationStampFromFile( blockFiles, blockFiles[i]); Block block = new Block(blockFiles[i], blockFiles[i].length(), genStamp); blockSet.add(new BlockAndFile(blockFiles[i] .getAbsoluteFile(), block)); } } } // 建立Block到DatanodeBlockInfo的映射关系 void getVolumeMap(HashMap<Block, DatanodeBlockInfo> volumeMap, FSVolume volume) { // 迭代children FSDir if (children != null) { for (int i = 0; i < children.length; i++) { children[i].getVolumeMap(volumeMap, volume); } } File blockFiles[] = dir.listFiles(); if (blockFiles != null) { for (int i = 0; i < blockFiles.length; i++) { if (Block.isBlockFilename(blockFiles[i])) { long genStamp = FSDataset.getGenerationStampFromFile( blockFiles, blockFiles[i]); volumeMap.put( new Block(blockFiles[i], blockFiles[i].length(), genStamp), new DatanodeBlockInfo(volume, blockFiles[i])); } } } } }
七.FSVolume
- FSVolume对应着DataNode上的一个Storage。一个DataNode可以配置多个Storage,一个DataNode包含多个FSVolume。
- FSVolume的重要方法
- getDfsUsed磁盘使用量 getCapacity磁盘大小 getAvailable磁盘可用量
- addBlock:向FSVolume中添加block,调用FSDir.addBlock完成。
- getVolumeMap:获得此FSVolume下所有block到DatanodeBlockInfo的映射关系,调用FSDir.getVolumeMap完成。
// FSVolume对应一个Storage // 一个DataNode可以配置多个Storage,一个DataNode包含多个FSVolume class FSVolume { private File currentDir; private FSDir dataDir; private File tmpDir; private File blocksBeingWritten; // clients write here private File detachDir; // copy on write for blocks in snapshot private DF usage; private DU dfsUsage; //<property> // <name>dfs.datanode.du.reserved</name> // <value>1024</value> //</property> //每个磁盘写入点能预留1K的空间来 private long reserved; // 初始化一个FSVolume FSVolume(File currentDir, Configuration conf) throws IOException { this.reserved = conf.getLong("dfs.datanode.du.reserved", 0); this.dataDir = new FSDir(currentDir); this.currentDir = currentDir; //根据parent初始化下面各属性,parent is %hadoop_home%/dfs/data File parent = currentDir.getParentFile(); this.detachDir = new File(parent, "detach"); // remove all blocks from "tmp" directory. These were either created // by pre-append clients (0.18.x) or are part of replication // request. // They can be safely removed. this.tmpDir = new File(parent, "tmp"); if (tmpDir.exists()) { FileUtil.fullyDelete(tmpDir); } // Files that were being written when the datanode was last shutdown // should not be deleted. blocksBeingWritten = new File(parent, "blocksBeingWritten"); ... this.usage = new DF(parent, conf); this.dfsUsage = new DU(parent, conf); this.dfsUsage.start(); } //getDfsUsed getCapacity getAvailable long get*() throws IOException { return dfsUsage.get*(); } File addBlock(Block b, File f) throws IOException { //调用FSDir的addBlock File blockFile = dataDir.addBlock(b, f); File metaFile = getMetaFile(blockFile, b); // add 后,磁盘使用量增加 dfsUsage.incDfsUsed(b.getNumBytes() + metaFile.length()); return blockFile; } //当前FSVolume下的volumeMap void getVolumeMap(HashMap<Block, DatanodeBlockInfo> volumeMap) { dataDir.getVolumeMap(volumeMap, this); } }
八.DF DU
- DF被设计用来获取dirPath路径所在的磁盘的空间状态信息,对应的unix的shell脚本命令格式是:df -k path。
- DU类实现了unix的du命令,显示文件或目录dirPath占用磁盘空间的大小信息。
public class DF extends Shell { /** Default DF refresh interval. */ public static final long DF_INTERVAL_DEFAULT = 3 * 1000; private final String dirPath; //执行df命令所在工作目录 private final File dirFile; //执行df命令所在工作目录文件夹 private String filesystem; //磁盘设备名 private String mount; //磁盘挂载位置 //初始化dirPath and dirFile public DF(File path, long dfInterval) throws IOException { super(dfInterval); this.dirPath = path.getCanonicalPath(); this.dirFile = path.getCanonicalFile(); } //getCapacity getUsed getAvailable public long get*() { return dirFile.get*(); } } public class DU extends Shell { private String dirPath; //执行du命令所在工作目录 }
九.FSVolumeSet
- 管理一个DataNode下所有的FSVolume。
- FSVolume的重要方法
- getVolumeMap:获得FSVolume[]下所有block到DatanodeBlockInfo的映射关系,叠加FSVolume.getVolumeMap实现。
- getDfsUsed磁盘使用量 getCapacity磁盘大小 getRemaining磁盘可用量,叠加FSVolume.x实现。
//管理一个DataNode下所有的FSVolume static class FSVolumeSet { FSVolume[] volumes = null; int curVolume = 0; FSVolumeSet(FSVolume[] volumes) { this.volumes = volumes; } //向DataNode添加block时,根据blockSize,获取第一个大于blockSize的FSVolume synchronized FSVolume getNextVolume(long blockSize) throws IOException { // make sure we are not out of bounds if (curVolume >= volumes.length) { curVolume = 0; } int startVolume = curVolume; while (true) { FSVolume volume = volumes[curVolume]; curVolume = (curVolume + 1) % volumes.length; if (volume.getAvailable() > blockSize) { return volume; } //空间不足 if (curVolume == startVolume) { throw new DiskOutOfSpaceException("Insufficient space for an additional block"); } } } long get*() throws IOException { 叠加每个FSVolume } //所有FSVolume下的volumeMap synchronized void getVolumeMap(HashMap<Block, DatanodeBlockInfo> volumeMap) { for (int idx = 0; idx < volumes.length; idx++) { volumes[idx].getVolumeMap(volumeMap); } } }
十.ActiveFile
ActiveFile对象保存了一个文件,和操作这个文件的线程,线程有可能有多个。
static class ActiveFile {
final File file;
final List<Thread> threads = new ArrayList<Thread>(2);
//初始化ActiveFile时会自动地把当前线程加入其中
ActiveFile(File f, List<Thread> list) {
this(f, false);
if (list != null) {
threads.addAll(list);
}
threads.add(Thread.currentThread());
}
}
十一.FSDataset
- FSDataset manages a set of data blocks.通过FSVolumeSet 管理。
- FSDataset实现了FSDatasetInterface接口,FSDatasetInterface接口是DataNode对底层存储的抽象。
public class FSDataset implements FSConstants, FSDatasetInterface { //所有FSVolume FSVolumeSet volumes; //所有Block到DatanodeBlockInfo的映射 HashMap<Block, DatanodeBlockInfo> volumeMap = new HashMap<Block, DatanodeBlockInfo>();; //所有Block到ActiveFile的映射,也就是说,说有正在创建的Block,都会记录在ongoingCreates里。 private HashMap<Block, ActiveFile> ongoingCreates = new HashMap<Block, ActiveFile>(); //初始化FSDataset时初始化volumes and volumeMap public FSDataset(DataStorage storage, Configuration conf)throws IOException { FSVolume[] volArray = new FSVolume[storage.getNumStorageDirs()]; for (int idx = 0; idx < storage.getNumStorageDirs(); idx++) { volArray[idx] = new FSVolume(storage.getStorageDir(idx) .getCurrentDir(), conf); } volumes = new FSVolumeSet(volArray); volumes.getVolumeMap(volumeMap); } //=================================== 根据block 的几个方法 开始=================================== //得到block文件 public synchronized File getBlockFile(Block b) throws IOException ; //得到block元文件 protected File getMetaFile(Block b) throws IOException ; //得到block的元数据长度。 public long getMetaDataLength(Block b) throws IOException ; //得到InputStream MetaDataInputStream包含block长度 public MetaDataInputStream getMetaDataInputStream(Block b) throws IOException; //得到block对应元数据文件的inputstream public InputStream getBlockInputStream(Block b) throws IOException //获得block对应元数据文件的inputstream, 从指定位置开始读 public InputStream getBlockInputStream(Block b, long seekOffset) throws IOException; //得到Block的临时输入流。注意,临时输入流是指对应的文件处于tmp目录中。 //新创建块时,块数据应该写在tmp目录中,直到写操作成功,文件才会被移动到current目录中,如果失败,就不会影响current目录了。简单方法。 public BlockInputStreams getTmpInputStreams(Block b, long blkoff, long ckoff) throws IOException; //得到一个block的输出流。BlockWriteStreams既包含了数据输出流,也包含了元数据(校验文件)输出流。 //参数isRecovery说明这次写是不是对以前失败的写的一次恢复操作。 //正常的写操作流程:首先,如果输入的block是个正常的数据块,或当前的block已经有线程在写,writeToBlock会抛出一个异常。 //否则,将创建相应的临时数据文件和临时元数据文件,并把相关信息,创建一个ActiveFile对象,记录到ongoingCreates中,并创建返回的BlockWriteStreams。 //前面我们已经提过,建立新的ActiveFile时,当前线程会自动保存在ActiveFile的threads中。 //以blk_3148782637964391313为例, //当DataNode需要为Block ID为3148782637964391313创建写流时,DataNode创建文件tmp/blk_3148782637964391313做为临时数据文件, //对应的meta文件是tmp/blk_3148782637964391313_XXXXXX.meta。其中XXXXXX是版本号。 //isRecovery为true时,表明我们需要从某一次不成功的写中恢复,流程相对于正常流程复杂。 //如果不成功的写是由于提交(参考finalizeBlock方法)后的确认信息没有收到,先创建一个detached文件(备份)。 //接着,writeToBlock检查是否有还有对文件写的线程,如果有,则通过线程的interrupt方法,强制结束线程。这就是说,如果有线程还在写对应的文件块,该线程将被终止。 //同时,从ongoingCreates中移除对应的信息。接下来将根据临时文件是否存在,创建/复用临时数据文件和临时数据元文件。 //后续操作就和正常流程一样,根据相关信息,创建一个ActiveFile对象,记录到ongoingCreates中 public BlockWriteStreams writeToBlock(Block b, boolean isRecovery, boolean isReplicationRequest) throws IOException; //提交(或叫:结束finalize)通过writeToBlock打开的block,这意味着写过程没有出错,可以正式把Block从tmp文件夹放到current文件夹。 //将从ongoingCreates中删除对应的block,同时将block对应的DatanodeBlockInfo,放入volumeMap中。 //以blk_3148782637964391313为例,当DataNode提交Block ID为3148782637964391313数据块文件时,DataNode将把tmp/blk_3148782637964391313移到current下某一个目录, //以subdir12为例,这是tmp/blk_3148782637964391313将会挪到current/subdir12/blk_3148782637964391313。对应的meta文件也在目录current/subdir12下。 public void finalizeBlock(Block b) throws IOException; //更新一个block。 //updateBlock的最外层是一个死循环,循环的结束条件,是没有任何和这个数据块相关的写线程。 //每次循环,updateBlock都会去调用一个叫tryUpdateBlock的内部方法。 //tryUpdateBlock发现已经没有线程在写这个块,就会跟新和这个数据块相关的信息,包括元文件和内存中的映射表volumeMap。 //如果tryUpdateBlock发现还有活跃的线程和该块关联,那么,updateBlock会试图结束该线程,并等在join上等待。 public void updateBlock(Block oldblock, Block newblock) throws IOException; //取消通过writeToBlock打开的block,与finalizeBlock方法作用相反。 public void unfinalizeBlock(Block b) throws IOException; //=================================== 根据block 的几个方法 结束=================================== //getDfsUsed getCapacity getRemaining public long get*() throws IOException { return volumes.get*(); } }