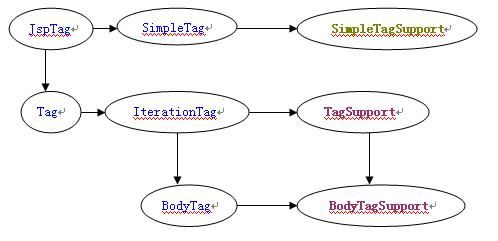
jsp2.0自定义标签Tag
在JSP2.0 中,对于自定义的标签有两种实现方法,实现接口或者继承现有的类
如下图,标注蓝色的是接口,其它是标签类(SimpleTagSupport 只在JSP2.0 中才有)
在以上接口和类中,定义了一些静态常量,如下:
Tag 中定义:
SKIP_BODY = 0; // 不处理标签体,直接调用doEndTag() 方法
EVAL_BODY_INCLUDE = 1; // 解析标签体, 但绕过 doInitBody () 和 setBodyContent () 方法
SKIP_PAGE = 5; // 不解析标签后面的JSP 内容
EVAL_PAGE = 6; // 解析标签后, 继续解析标签后面的JSP 内容
IterationTag 中定义:
EVAL_BODY_AGAIN = 2;
BodyTag 中定义:
EVAL_BODY_TAG = 2; // deprecated
EVAL_BODY_BUFFERED = 2; //
特别的,对于EVAL_BODY_AGAIN 和EVAL_BODY_BUFFERED :
在doAferBody 中返回SKIP_BODY ,表示终止标记正文处理 ;若返回的是 EVAL_BODY_BUFFERED ,将会再一次调用 doAferBody 方法,重新处理标记正文,直到返回SKIP_BODY 为止。 // ①
TagSupport 默认doStartTag()/doAfterBody() 返回SKIP_BODY
BodyTagSupport 默认doStartTag() 返回EVAL_BODY_BUFFERED / doInitBody() 什么也不做 /doAfterBody() 返回SKIP_BODY
下面是自定义tag 的执行过程(由上至下),对于以上各常量的实际运用为:
注意其中的 doInitBody/setBodyContent 方法在自定义标签实现了 BodyTag 接口或继承BodyTagSupport 才可以使用
| Tag 方法 |
可返回的静态常量 |
| doStartTag |
SKIP_BODY 、EVAL_BODY_INCLUDE 、 EVAL_BODY_AGAIN/EVAL_BODY_BUFFERED |
| doInitBody |
做标签一些初始化工作,无返回值 |
| setBodyContent |
在 doInitBody 之后执行,使用setBodyContent 得到JSP 页面中标签体之间内容 |
| doAfterBody |
最终必须返回SKIP_BODY ,否则可能导致OutOfMemoryError ,可参考上面① |
| doEndTag |
SKIP_PAGE/EVAL_PAGE |
附 ① 示例代码如下:
public int doAfterBody() throws JspException {
try {
this.pageContext.getOut().write("<br>");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
if(cou>1){
cou--;
return this.EVAL_BODY_AGAIN;
}else{
return this.SKIP_BODY; // 最终必须返回SKIP_BODY
}
}
自定义标签的开发包括:
1. 开发标签的处理程序(java 类)
2. .tld 文件中指定标签使用的类
3. 在web.xml 中指定JSP 中使.tld( 标签库描述文件) 文件的位置。
在.tld 文件中
<tag>
<name>out</name>
<tag-class>org.apache.taglibs.standard.tag.el.core.OutTag</tag-class>
<body-content >JSP</body-content>
<attribute>
<name>value</name>
<required>true</required>
<rtexprvalue >false</rtexprvalue>
</attribute>
</tag>
body-content :
根据web-jsptaglibrary_2_0.xsd (位于servlet-api.jar 包($TOMCAT_HOME\common\lib )中的\javax\servlet\resources 下,其中web.xml 验证时所需要的xsd 文件都位于此resources 目录下), body-content 的值有下面4 种:
| <xsd:enumeration value="tagdependent "/> <xsd:enumeration value="JSP "/> <xsd:enumeration value="empty "/> <xsd:enumeration value="scriptless "/> |
tagdependent : 标签体内容 直接被写入BodyContent ,由自定义标签类来进行处理,而不被JSP 容器解释 ,
如下:
<test:myList>
select name,age from users
</test:myList>
JSP : 接受所有JSP 语法,如定制的或内部的tag 、scripts 、静态HTML 、脚本元素、JSP 指令和动作。如:
<my:test>
<%=request.getProtocol()%> // ②
</my:test>
具体可参考后面附源码。
empty : 空标记,即起始标记和结束标记之间没有内容。
下面几种写法都是有效的,
<test:mytag />
<test:mytag uname="Tom" />
<test:mytag></test:mytag>
scriptless : 接受文本、EL 和JSP 动作。如上述② 使用<body-content> scriptless </body-content> 则报错 ,具体可参考后面附源码。
rtexprvalue:
由请求时表达式来指定属性的值,默认为false ,如下必须设置为true :
<test:welcome uname="<%=request.getParameter("username") %>" />
附body-content 为 JSP/scriptless 时标签体可以接受的代码(jasper-compiler.jar 包 ($TOMCAT_HOME\common\lib )中 的\org\apache\jasper\compiler\Parser.java 中):
JSP:
private void parseElements(Node parent)
throws JasperException
{
if( scriptlessCount > 0 ) {
// vc: ScriptlessBody
// We must follow the ScriptlessBody production if one of
// our parents is ScriptlessBody.
parseElementsScriptless( parent );
return;
}
start = reader.mark();
if (reader.matches("<%--")) {
parseComment(parent);
} else if (reader.matches("<%@")) {
parseDirective(parent);
} else if (reader.matches("<jsp:directive.")) {
parseXMLDirective(parent);
} else if (reader.matches("<%!")) {
parseDeclaration(parent);
} else if (reader.matches("<jsp:declaration")) {
parseXMLDeclaration(parent);
} else if (reader.matches("<%=")) {
parseExpression(parent);
} else if (reader.matches("<jsp:expression")) {
parseXMLExpression(parent);
} else if (reader.matches("<%")) {
parseScriptlet(parent);
} else if (reader.matches("<jsp:scriptlet")) {
parseXMLScriptlet(parent);
} else if (reader.matches("<jsp:text")) {
parseXMLTemplateText(parent);
} else if (reader.matches("${")) {
parseELExpression(parent);
} else if (reader.matches("<jsp:")) {
parseStandardAction(parent);
} else if (!parseCustomTag(parent)) {
checkUnbalancedEndTag();
parseTemplateText(parent);
}
}
Scriptless:
private void parseElementsScriptless(Node parent)
throws JasperException
{
// Keep track of how many scriptless nodes we've encountered
// so we know whether our child nodes are forced scriptless
scriptlessCount++;
start = reader.mark();
if (reader.matches("<%-- ")) {
parseComment(parent);
} else if (reader.matches("<%@ ")) {
parseDirective(parent);
} else if (reader.matches("<jsp:directive. ")) {
parseXMLDirective(parent);
} else if (reader.matches("<%!")) {
err.jspError( reader.mark(), "jsp.error.no.scriptlets" );
} else if (reader.matches("<jsp:declaration")) {
err.jspError( reader.mark(), "jsp.error.no.scriptlets" );
} else if (reader.matches("<%=")) {
err.jspError( reader.mark(), "jsp.error.no.scriptlets" );
} else if (reader.matches("<jsp:expression")) {
err.jspError( reader.mark(), "jsp.error.no.scriptlets" );
} else if (reader.matches("<%")) {
err.jspError( reader.mark(), "jsp.error.no.scriptlets" );
} else if (reader.matches("<jsp:scriptlet")) {
err.jspError( reader.mark(), "jsp.error.no.scriptlets" );
} else if (reader.matches("<jsp:text ")) {
parseXMLTemplateText(parent);
} else if (reader.matches("${ ")) {
parseELExpression(parent);
} else if (reader.matches("<jsp: ")) {
parseStandardAction(parent);
} else if (!parseCustomTag(parent)) {
checkUnbalancedEndTag();
parseTemplateText(parent);
}
scriptlessCount--;
}
由上面可以看出,局限性比较小,在body-content 可以使用 Scriptless 的地方都可以用 JSP 代替,反之则不可。
(转自: http://www.blogjava.net/xiaodaoxiaodao/archive/2007/01/05/103438.html)