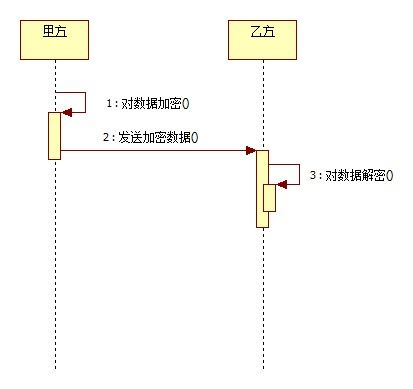
单向加密算法
本篇内容简要介绍BASE64、MD5、SHA、HMAC几种加密算法。
BASE64编码算法不算是真正的加密算法。
MD5、SHA、HMAC这三种加密算法,可谓是非可逆加密,就是不可解密的加密方法,我们称之为单向加密算法。我们通常只把他们作为加密的基础。单纯的以上三种的加密并不可靠。
BASE64
按照RFC2045的定义,Base64被定义为:Base64内容传送编码被设计用来把任意序列的8位字节描述为一种不易被人直接识别的形式。(The Base64 Content-Transfer-Encoding is designed to represent arbitrary sequences of octets in a form that need not be humanly readable.)
常见于邮件、http加密,截取http信息,你就会发现登录操作的用户名、密码字段通过BASE64加密的。
通过java代码实现如下:
1./**
2. * BASE64解密
3. *
4. * @param key
5. * @return
6. * @throws Exception
7. */
8.public static byte[] decryptBASE64(String key) throws Exception {
9. return (new BASE64Decoder()).decodeBuffer(key);
10.}
11.
12./**
13. * BASE64加密
14. *
15. * @param key
16. * @return
17. * @throws Exception
18. */
19.public static String encryptBASE64(byte[] key) throws Exception {
20. return (new BASE64Encoder()).encodeBuffer(key);
21.}
主要就是BASE64Encoder、BASE64Decoder两个类,我们只需要知道使用对应的方法即可。另,BASE加密后产生的字节位数是8的倍数,如果不够位数以=符号填充。
MD5
MD5 -- message-digest algorithm 5 (信息-摘要算法)缩写,广泛用于加密和解密技术,常用于文件校验。校验?不管文件多大,经过MD5后都能生成唯一的MD5值。好比现在的ISO校验,都是MD5校验。怎么用?当然是把ISO经过MD5后产生MD5的值。一般下载linux-ISO的朋友都见过下载链接旁边放着MD5的串。就是用来验证文件是否一致的。 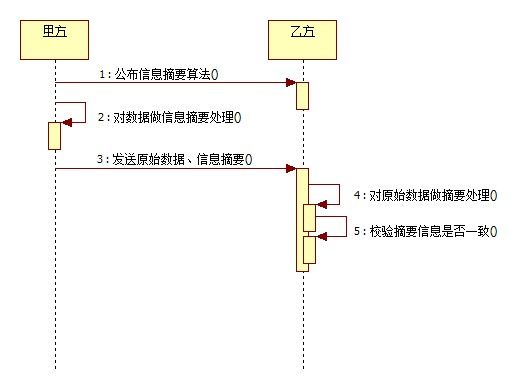
1./**
2. * MD5加密
3. *
4. * @param data
5. * @return
6. * @throws Exception
7. */
8.public static byte[] encryptMD5(byte[] data) throws Exception {
9.
10. MessageDigest md5 = MessageDigest.getInstance(KEY_MD5);
11. md5.update(data);
12.
13. return md5.digest();
14.
15.}
通常我们不直接使用上述MD5加密。通常将MD5产生的字节数组交给BASE64再加密一把,得到相应的字符串。
SHA
SHA(Secure Hash Algorithm,安全散列算法),数字签名等密码学应用中重要的工具,被广泛地应用于电子商务等信息安全领域。虽然,SHA与MD5通过碰撞法都被破解了,![]() 但是SHA仍然是公认的安全加密算法,较之MD5更为安全。
但是SHA仍然是公认的安全加密算法,较之MD5更为安全。![]()

通过java代码实现如下:
/**
2. * SHA加密
3. *
4. * @param data
5. * @return
6. * @throws Exception
7. */
8. public static byte[] encryptSHA(byte[] data) throws Exception {
9.
10. MessageDigest sha = MessageDigest.getInstance(KEY_SHA);
11. sha.update(data);
12.
13. return sha.digest();
14.
15. }
16.}
HMAC
HMAC(Hash Message Authentication Code,散列消息鉴别码,基于密钥的Hash算法的认证协议。消息鉴别码实现鉴别的原理是,用公开函数和密钥产生一个固定长度的值作为认证标识,用这个标识鉴别消息的完整性。使用一个密钥生成一个固定大小的小数据块,即MAC,并将其加入到消息中,然后传输。接收方利用与发送方共享的密钥进行鉴别认证等。 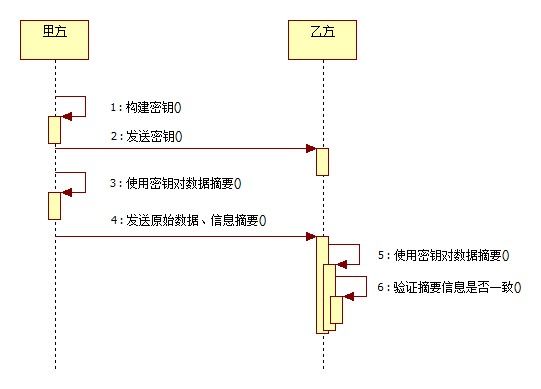
通过java代码实现如下:
1./**
2. * 初始化HMAC密钥
3. *
4. * @return
5. * @throws Exception
6. */
7.public static String initMacKey() throws Exception {
8. KeyGenerator keyGenerator = KeyGenerator.getInstance(KEY_MAC);
9.
10. SecretKey secretKey = keyGenerator.generateKey();
11. return encryptBASE64(secretKey.getEncoded());
12.}
13.
14./**
15. * HMAC加密
16. *
17. * @param data
18. * @param key
19. * @return
20. * @throws Exception
21. */
22.public static byte[] encryptHMAC(byte[] data, String key) throws Exception {
23.
24. SecretKey secretKey = new SecretKeySpec(decryptBASE64(key), KEY_MAC);
25. Mac mac = Mac.getInstance(secretKey.getAlgorithm());
26. mac.init(secretKey);
27.
28. return mac.doFinal(data);
29.
30.}
给出一个完整类,如下:
1.import java.security.MessageDigest;
2.
3.import javax.crypto.KeyGenerator;
4.import javax.crypto.Mac;
5.import javax.crypto.SecretKey;
6.
7.import sun.misc.BASE64Decoder;
8.import sun.misc.BASE64Encoder;
9.
10./**
11. * 基础加密组件
12. *
13. * @author 梁栋
14. * @version 1.0
15. * @since 1.0
16. */
17.public abstract class Coder {
18. public static final String KEY_SHA = "SHA";
19. public static final String KEY_MD5 = "MD5";
20.
21. /**
22. * MAC算法可选以下多种算法
23. *
24. * <pre>
25. * HmacMD5
26. * HmacSHA1
27. * HmacSHA256
28. * HmacSHA384
29. * HmacSHA512
30. * </pre>
31. */
32. public static final String KEY_MAC = "HmacMD5";
33.
34. /**
35. * BASE64解密
36. *
37. * @param key
38. * @return
39. * @throws Exception
40. */
41. public static byte[] decryptBASE64(String key) throws Exception {
42. return (new BASE64Decoder()).decodeBuffer(key);
43. }
44.
45. /**
46. * BASE64加密
47. *
48. * @param key
49. * @return
50. * @throws Exception
51. */
52. public static String encryptBASE64(byte[] key) throws Exception {
53. return (new BASE64Encoder()).encodeBuffer(key);
54. }
55.
56. /**
57. * MD5加密
58. *
59. * @param data
60. * @return
61. * @throws Exception
62. */
63. public static byte[] encryptMD5(byte[] data) throws Exception {
64.
65. MessageDigest md5 = MessageDigest.getInstance(KEY_MD5);
66. md5.update(data);
67.
68. return md5.digest();
69.
70. }
71.
72. /**
73. * SHA加密
74. *
75. * @param data
76. * @return
77. * @throws Exception
78. */
79. public static byte[] encryptSHA(byte[] data) throws Exception {
80.
81. MessageDigest sha = MessageDigest.getInstance(KEY_SHA);
82. sha.update(data);
83.
84. return sha.digest();
85.
86. }
87.
88. /**
89. * 初始化HMAC密钥
90. *
91. * @return
92. * @throws Exception
93. */
94. public static String initMacKey() throws Exception {
95. KeyGenerator keyGenerator = KeyGenerator.getInstance(KEY_MAC);
96.
97. SecretKey secretKey = keyGenerator.generateKey();
98. return encryptBASE64(secretKey.getEncoded());
99. }
100.
101. /**
102. * HMAC加密
103. *
104. * @param data
105. * @param key
106. * @return
107. * @throws Exception
108. */
109. public static byte[] encryptHMAC(byte[] data, String key) throws Exception {
110.
111. SecretKey secretKey = new SecretKeySpec(decryptBASE64(key), KEY_MAC);
112. Mac mac = Mac.getInstance(secretKey.getAlgorithm());
113. mac.init(secretKey);
114.
115. return mac.doFinal(data);
116.
117. }
118.}
再给出一个测试类:
1.import static org.junit.Assert.*;
2.
3.import org.junit.Test;
4.
5./**
6. *
7. * @author 梁栋
8. * @version 1.0
9. * @since 1.0
10. */
11.public class CoderTest {
12.
13. @Test
14. public void test() throws Exception {
15. String inputStr = "简单加密";
16. System.err.println("原文:\n" + inputStr);
17.
18. byte[] inputData = inputStr.getBytes();
19. String code = Coder.encryptBASE64(inputData);
20.
21. System.err.println("BASE64加密后:\n" + code);
22.
23. byte[] output = Coder.decryptBASE64(code);
24.
25. String outputStr = new String(output);
26.
27. System.err.println("BASE64解密后:\n" + outputStr);
28.
29. // 验证BASE64加密解密一致性
30. assertEquals(inputStr, outputStr);
31.
32. // 验证MD5对于同一内容加密是否一致
33. assertArrayEquals(Coder.encryptMD5(inputData), Coder
34. .encryptMD5(inputData));
35.
36. // 验证SHA对于同一内容加密是否一致
37. assertArrayEquals(Coder.encryptSHA(inputData), Coder
38. .encryptSHA(inputData));
39.
40. String key = Coder.initMacKey();
41. System.err.println("Mac密钥:\n" + key);
42.
43. // 验证HMAC对于同一内容,同一密钥加密是否一致
44. assertArrayEquals(Coder.encryptHMAC(inputData, key), Coder.encryptHMAC(
45. inputData, key));
46.
47. BigInteger md5 = new BigInteger(Coder.encryptMD5(inputData));
48. System.err.println("MD5:\n" + md5.toString(16));
49.
50. BigInteger sha = new BigInteger(Coder.encryptSHA(inputData));
51. System.err.println("SHA:\n" + sha.toString(32));
52.
53. BigInteger mac = new BigInteger(Coder.encryptHMAC(inputData, inputStr));
54. System.err.println("HMAC:\n" + mac.toString(16));
55. }
56.}
控制台输出:
1.原文: 2.简单加密 3.BASE64加密后: 4.566A5Y2V5Yqg5a+G 5. 6.BASE64解密后: 7.简单加密 8.Mac密钥: 9.uGxdHC+6ylRDaik++leFtGwiMbuYUJ6mqHWyhSgF4trVkVBBSQvY/a22xU8XT1RUemdCWW155Bke 10.pBIpkd7QHg== 11. 12.MD5: 13.-550b4d90349ad4629462113e7934de56 14.SHA: 15.91k9vo7p400cjkgfhjh0ia9qthsjagfn 16.HMAC: 17.2287d192387e95694bdbba2fa941009a
BASE64的加密解密是双向的,可以求反解。
MD5、SHA以及HMAC是单向加密,任何数据加密后只会产生唯一的一个加密串,通常用来校验数据在传输过程中是否被修改。其中HMAC算法有一个密钥,增强了数据传输过程中的安全性,强化了算法外的不可控因素。![]()
单向加密的用途主要是为了校验数据在传输过程中是否被修改。