XMLBeans处理xml数据的好帮手 - 编译、测试和应用实例
3 编译schema
3.1 定义schema
<xs:schema targetNamespace="http://openuri.org/easypo"
xmlns:po="http://openuri.org/easypo"
xmlns:xs="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema"
elementFormDefault="qualified">
<xs:element name="purchase-order">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="customer" type="po:customer"/>
<xs:element name="date" type="xs:dateTime"/>
<xs:element name="line-item" type="po:line-item" minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded"/>
<xs:element name="shipper" type="po:shipper" minOccurs="0"/>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:complexType name="customer">
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="name" type="xs:string"/>
<xs:element name="address" type="xs:string"/>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
<xs:complexType name="line-item">
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="description" type="xs:string"/>
<xs:element name="per-unit-ounces" type="xs:decimal"/>
<xs:element name="price" type="xs:double"/>
<xs:element name="quantity" type="xs:int"/>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
<xs:complexType name="shipper">
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="name" type="xs:string"/>
<xs:element name="per-ounce-rate" type="xs:decimal"/>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:schema>
3.2 schema解释
1)我们在这里定义了三种复杂类型(complex types)客户,商品列表、以及卖家。他们都是purchase-order的子元素。在schema中复杂元素通常包含子元素和属性。他的子元素被sequence包含,并且嵌套在复杂类型中。同时purchase-order又是global类型因为他们在schema的根元素下。这就意味着它可以在schema中的任何地方引用。
2)在复杂类型中使用了简单类型(simple types)如:姓名、地址、商品描述。它们都是xs:string类型,这种类型schema的内置类型,共有46种内置类型。如:xs:double 、xs:int、xs:decimal等等。
3)全局元素(global element)purchase-order,它是由多个复杂子元素构成的,注意这种复杂元素引用了在schema中定义的复杂元素。
然后你就可以用XMLBean通过这个XSD文件编译出我们所需要的jar文件。这个jar包含了根据schema产生的一系列接口。
3.3 通过这个.xsd文件编译出xmlbeans
Scomp 它是Schema Compiler的缩写,顾名思义就是schema编译器的意思。
进入命令行运行命令:
C:\xmlbeans2.2\schemas>scomp -out biz.jar biz.xsd
很不幸你十有八九会碰到这种情况

不要着这其实是XMLBeans需要制定一个额外的java 编译器。我们加上一个编译器的参数就可以了。
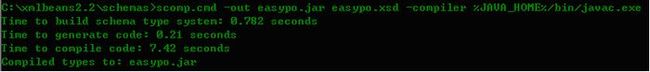
Ok,我们最终编译jar文件成功!
4 测试XMLBeans
4.1 工程结构
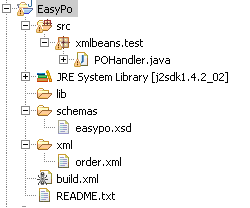
4.2 必要的Jar 包
注意不要忘记把必要的Jar加入你的工程。注意我们这里用的是easypo.jar,而不是biz.jar。这个jar的名字无所谓,只要是你刚才通过scomp编译出来的jar就可以了。你可以自己定义jar的名字。
[img]http://yangyang.iteye.com/upload/picture/pic/6447/1452634c-1e79-48c9-8bca-2d2a8a122e6c.bmp [/img]
4.3 测试代码
我们来写一个类来测试一下easypo.jar:
package xmlbeans.test;
import java.io.File;
import org.openuri.easypo.LineItem;
import org.openuri.easypo.PurchaseOrderDocument;
import org.openuri.easypo.PurchaseOrderDocument.PurchaseOrder;
public class POHandler
{
public static void printItems(File po) throws Exception
{
/*
* All XMLBeans schema types provide a nested Factory class you can
* use to bind XML to the type, or to create new instances of the type.
* Note that a "Document" type such as this one is an XMLBeans
* construct for representing a global element. It provides a way
* for you to get and set the contents of the entire element.
*
* Also, note that the parse method will only succeed if the
* XML you're parsing appears to conform to the schema.
*/
PurchaseOrderDocument poDoc =
PurchaseOrderDocument.Factory.parse(po);
/*
* The PurchaseOrder type represents the purchase-order element's
* complex type.
*/
PurchaseOrder po1 = poDoc.getPurchaseOrder();
/*
* When an element may occur more than once as a child element,
* the schema compiler will generate methods that refer to an
* array of that element. The line-item element is defined with
* a maxOccurs attribute value of "unbounded", meaning that
* it may occur as many times in an instance document as needed.
* So there are methods such as getLineItemArray and setLineItemArray.
*/
LineItem[] lineitems = po1.getLineItemArray();
System.out.println("Purchase order has " + lineitems.length + " line items.");
double totalAmount = 0.0;
int numberOfItems = 0;
/*
* Loop through the line-item elements, using generated accessors to
* get values for child elements such a description, quantity, and
* price.
*/
for (int j = 0; j < lineitems.length; j++)
{
System.out.println(" Line item: " + j);
System.out.println(
" Description: " + lineitems[j].getDescription());
System.out.println(" Quantity: " + lineitems[j].getQuantity());
System.out.println(" Price: " + lineitems[j].getPrice());
//numberOfItems += lineitems[j].getQuantity();
//totalAmount += lineitems[j].getPrice() * lineitems[j].getQuantity();
}
// System.out.println("Total items: " + numberOfItems);
// System.out.println("Total amount: " + totalAmount);
}
public static void main(String args[]){
try {
POHandler.printItems(new File("xml/order.xml"));
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
Order.xml文件内容:
<purchase-order xmlns="http://openuri.org/easypo">
<customer>
<name>Gladys Kravitz</name>
<address>Anytown, PA</address>
</customer>
<date>2003-01-07T14:16:00-05:00</date>
<line-item>
<description>Burnham's Celestial Handbook, Vol 1</description>
<per-unit-ounces>5</per-unit-ounces>
<price>21.79</price>
<quantity>2</quantity>
</line-item>
<line-item>
<description>Burnham's Celestial Handbook, Vol 2</description>
<per-unit-ounces>5</per-unit-ounces>
<price>19.89</price>
<quantity>2</quantity>
</line-item>
<shipper>
<name>ZipShip</name>
<per-ounce-rate>0.74</per-ounce-rate>
</shipper>
</purchase-order>
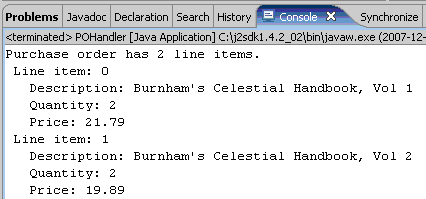
运行后得到结果:
That’s all ! 下面一张我们会进一步讨论XMlBeans的使用。
5 几个XMLBeans 使用的例子
5.1 验证xml 数据
XMLBeans 是根据编译时的schema 来验证xml 数据的。
public static boolean validate( File file){
PurchaseOrderDocument myDoc = null;
try {
myDoc = PurchaseOrderDocument.Factory.parse(file);
} catch (XmlException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
// Set up the validation error listener.
ArrayList validationErrors = new ArrayList();
XmlOptions validationOptions = new XmlOptions();
validationOptions.setErrorListener(validationErrors);
// Do some editing to myDoc.
// During validation, errors are added to the ArrayList for
// retrieval and printing by the printErrors method.
boolean isValid = myDoc.validate(validationOptions);
// Print the errors if the XML is invalid.
if (!isValid)
{
Iterator iter = validationErrors.iterator();
while (iter.hasNext())
{
System.out.println(">> " + iter.next() + "\n");
}
}
return isValid;
}
注:file是一个xml数据文件。
5.2 读取xml数据
使用XMLBeans来将xml 数据包装成对象,并且通过对象读取信息。
public static void printItems(File file) throws Exception
{
PurchaseOrderDocument poDoc =
PurchaseOrderDocument.Factory.parse(file);
PurchaseOrder po1 = poDoc.getPurchaseOrder();
LineItem[] lineitems = po1.getLineItemArray();
Customer c = po1.getCustomer();
c.getAddress();
c.getAge();
System.out.println("Purchase order has " + lineitems.length + " line items.");
for (int j = 0; j < lineitems.length; j++)
{
System.out.println(" Line item: " + j);
System.out.println(
" Description: " + lineitems[j].getDescription());
System.out.println(" Quantity: " + lineitems[j].getQuantity());
System.out.println(" Price: " + lineitems[j].getPrice());
}
}
注:file是一个xml数据文件。
5.3 创建xml 数据
创建新的xml数据并保存到xml文件中。
public static void createPO()
{
PurchaseOrderDocument newPODoc = PurchaseOrderDocument.Factory.newInstance();
PurchaseOrder newPO = newPODoc.addNewPurchaseOrder();
Customer newCustomer = newPO.addNewCustomer();
newCustomer.setName("Doris Kravitz");
newCustomer.setAddress("Bellflower, CA");
newPODoc .save( new File("xml/newOrder.xml") );
}
除了这些基本的功能以外,XMLBeans还提供了xpath查询,指定位置插入删除xml数据元素等强大功能,值得我们深入研究。
3.1 定义schema
<xs:schema targetNamespace="http://openuri.org/easypo"
xmlns:po="http://openuri.org/easypo"
xmlns:xs="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema"
elementFormDefault="qualified">
<xs:element name="purchase-order">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="customer" type="po:customer"/>
<xs:element name="date" type="xs:dateTime"/>
<xs:element name="line-item" type="po:line-item" minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded"/>
<xs:element name="shipper" type="po:shipper" minOccurs="0"/>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:complexType name="customer">
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="name" type="xs:string"/>
<xs:element name="address" type="xs:string"/>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
<xs:complexType name="line-item">
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="description" type="xs:string"/>
<xs:element name="per-unit-ounces" type="xs:decimal"/>
<xs:element name="price" type="xs:double"/>
<xs:element name="quantity" type="xs:int"/>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
<xs:complexType name="shipper">
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="name" type="xs:string"/>
<xs:element name="per-ounce-rate" type="xs:decimal"/>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:schema>
3.2 schema解释
1)我们在这里定义了三种复杂类型(complex types)客户,商品列表、以及卖家。他们都是purchase-order的子元素。在schema中复杂元素通常包含子元素和属性。他的子元素被sequence包含,并且嵌套在复杂类型中。同时purchase-order又是global类型因为他们在schema的根元素下。这就意味着它可以在schema中的任何地方引用。
2)在复杂类型中使用了简单类型(simple types)如:姓名、地址、商品描述。它们都是xs:string类型,这种类型schema的内置类型,共有46种内置类型。如:xs:double 、xs:int、xs:decimal等等。
3)全局元素(global element)purchase-order,它是由多个复杂子元素构成的,注意这种复杂元素引用了在schema中定义的复杂元素。
然后你就可以用XMLBean通过这个XSD文件编译出我们所需要的jar文件。这个jar包含了根据schema产生的一系列接口。
3.3 通过这个.xsd文件编译出xmlbeans
Scomp 它是Schema Compiler的缩写,顾名思义就是schema编译器的意思。
进入命令行运行命令:
C:\xmlbeans2.2\schemas>scomp -out biz.jar biz.xsd
很不幸你十有八九会碰到这种情况

不要着这其实是XMLBeans需要制定一个额外的java 编译器。我们加上一个编译器的参数就可以了。

Ok,我们最终编译jar文件成功!
4 测试XMLBeans
4.1 工程结构

4.2 必要的Jar 包
注意不要忘记把必要的Jar加入你的工程。注意我们这里用的是easypo.jar,而不是biz.jar。这个jar的名字无所谓,只要是你刚才通过scomp编译出来的jar就可以了。你可以自己定义jar的名字。
[img]http://yangyang.iteye.com/upload/picture/pic/6447/1452634c-1e79-48c9-8bca-2d2a8a122e6c.bmp [/img]
4.3 测试代码
我们来写一个类来测试一下easypo.jar:
package xmlbeans.test;
import java.io.File;
import org.openuri.easypo.LineItem;
import org.openuri.easypo.PurchaseOrderDocument;
import org.openuri.easypo.PurchaseOrderDocument.PurchaseOrder;
public class POHandler
{
public static void printItems(File po) throws Exception
{
/*
* All XMLBeans schema types provide a nested Factory class you can
* use to bind XML to the type, or to create new instances of the type.
* Note that a "Document" type such as this one is an XMLBeans
* construct for representing a global element. It provides a way
* for you to get and set the contents of the entire element.
*
* Also, note that the parse method will only succeed if the
* XML you're parsing appears to conform to the schema.
*/
PurchaseOrderDocument poDoc =
PurchaseOrderDocument.Factory.parse(po);
/*
* The PurchaseOrder type represents the purchase-order element's
* complex type.
*/
PurchaseOrder po1 = poDoc.getPurchaseOrder();
/*
* When an element may occur more than once as a child element,
* the schema compiler will generate methods that refer to an
* array of that element. The line-item element is defined with
* a maxOccurs attribute value of "unbounded", meaning that
* it may occur as many times in an instance document as needed.
* So there are methods such as getLineItemArray and setLineItemArray.
*/
LineItem[] lineitems = po1.getLineItemArray();
System.out.println("Purchase order has " + lineitems.length + " line items.");
double totalAmount = 0.0;
int numberOfItems = 0;
/*
* Loop through the line-item elements, using generated accessors to
* get values for child elements such a description, quantity, and
* price.
*/
for (int j = 0; j < lineitems.length; j++)
{
System.out.println(" Line item: " + j);
System.out.println(
" Description: " + lineitems[j].getDescription());
System.out.println(" Quantity: " + lineitems[j].getQuantity());
System.out.println(" Price: " + lineitems[j].getPrice());
//numberOfItems += lineitems[j].getQuantity();
//totalAmount += lineitems[j].getPrice() * lineitems[j].getQuantity();
}
// System.out.println("Total items: " + numberOfItems);
// System.out.println("Total amount: " + totalAmount);
}
public static void main(String args[]){
try {
POHandler.printItems(new File("xml/order.xml"));
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
Order.xml文件内容:
<purchase-order xmlns="http://openuri.org/easypo">
<customer>
<name>Gladys Kravitz</name>
<address>Anytown, PA</address>
</customer>
<date>2003-01-07T14:16:00-05:00</date>
<line-item>
<description>Burnham's Celestial Handbook, Vol 1</description>
<per-unit-ounces>5</per-unit-ounces>
<price>21.79</price>
<quantity>2</quantity>
</line-item>
<line-item>
<description>Burnham's Celestial Handbook, Vol 2</description>
<per-unit-ounces>5</per-unit-ounces>
<price>19.89</price>
<quantity>2</quantity>
</line-item>
<shipper>
<name>ZipShip</name>
<per-ounce-rate>0.74</per-ounce-rate>
</shipper>
</purchase-order>
运行后得到结果:

That’s all ! 下面一张我们会进一步讨论XMlBeans的使用。
5 几个XMLBeans 使用的例子
5.1 验证xml 数据
XMLBeans 是根据编译时的schema 来验证xml 数据的。
public static boolean validate( File file){
PurchaseOrderDocument myDoc = null;
try {
myDoc = PurchaseOrderDocument.Factory.parse(file);
} catch (XmlException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
// Set up the validation error listener.
ArrayList validationErrors = new ArrayList();
XmlOptions validationOptions = new XmlOptions();
validationOptions.setErrorListener(validationErrors);
// Do some editing to myDoc.
// During validation, errors are added to the ArrayList for
// retrieval and printing by the printErrors method.
boolean isValid = myDoc.validate(validationOptions);
// Print the errors if the XML is invalid.
if (!isValid)
{
Iterator iter = validationErrors.iterator();
while (iter.hasNext())
{
System.out.println(">> " + iter.next() + "\n");
}
}
return isValid;
}
注:file是一个xml数据文件。
5.2 读取xml数据
使用XMLBeans来将xml 数据包装成对象,并且通过对象读取信息。
public static void printItems(File file) throws Exception
{
PurchaseOrderDocument poDoc =
PurchaseOrderDocument.Factory.parse(file);
PurchaseOrder po1 = poDoc.getPurchaseOrder();
LineItem[] lineitems = po1.getLineItemArray();
Customer c = po1.getCustomer();
c.getAddress();
c.getAge();
System.out.println("Purchase order has " + lineitems.length + " line items.");
for (int j = 0; j < lineitems.length; j++)
{
System.out.println(" Line item: " + j);
System.out.println(
" Description: " + lineitems[j].getDescription());
System.out.println(" Quantity: " + lineitems[j].getQuantity());
System.out.println(" Price: " + lineitems[j].getPrice());
}
}
注:file是一个xml数据文件。
5.3 创建xml 数据
创建新的xml数据并保存到xml文件中。
public static void createPO()
{
PurchaseOrderDocument newPODoc = PurchaseOrderDocument.Factory.newInstance();
PurchaseOrder newPO = newPODoc.addNewPurchaseOrder();
Customer newCustomer = newPO.addNewCustomer();
newCustomer.setName("Doris Kravitz");
newCustomer.setAddress("Bellflower, CA");
newPODoc .save( new File("xml/newOrder.xml") );
}
除了这些基本的功能以外,XMLBeans还提供了xpath查询,指定位置插入删除xml数据元素等强大功能,值得我们深入研究。