等待队列的原理与源码分析
一、等待队列相关数据结构
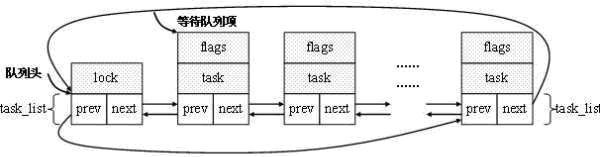
每一个等待队列都由两部分组成:等待队列头(struct wait_queue_head_t)和等待队列成员(struct wait_queue)。
- struct __wait_queue_head {
- spinlock_t lock; /*因为等待队列可以在中断时随时修改,因此设置一个自旋锁保证一致性*/
- struct list_head task_list;
- };
- typedef struct __wait_queue_head wait_queue_head_t
- struct __wait_queue {
- unsigned int flags; /*指明等待的进程是互斥进程还是非互斥进程*/
- #define WQ_FLAG_EXCLUSIVE0x01
- void *private; /*指向任务的task_struct*/
- wait_queue_func_t func;
- struct list_head task_list;
- };
- typedef struct __wait_queue_head wait_queue_head_t
最后形成的结果就是一个等待队列头串起多个等待队列成员,如图1所示:
等待队列的使用分为以下两部分:
(1)为使当前进程在一个等待队列中睡眠,需要调用wait_event(或某个等价函数),此后,进程进入睡眠,将控制权交给调度器。以块设备为例,当内核向块设备发出请求后,因为数据传输不会立即发生,因此进程睡眠
(2)相对应的,是当数据到达后,必须调用wake_up函数(或某个等价函数)来唤醒等待队列中睡眠的进程
二、等待队列相关的接口函数
1. 声明和初始化相关的接口
(1)静态初始化一个等待队列实例: DEFINE_WAIT(&wq)
- #define DEFINE_WAIT_FUNC(name, function)/
- wait_queue_t name = {/
- .private= current,/
- .func= function,/
- .task_list= LIST_HEAD_INIT((name).task_list),/
- }
- #define DEFINE_WAIT(name) DEFINE_WAIT_FUNC(name, autoremove_wake_function)
autoremove_wake_function是默认的唤醒函数:
- int autoremove_wake_function(wait_queue_t *wait, unsigned mode, int sync, void *key)
- {
- int ret = default_wake_function(wait, mode, sync, key);
- if (ret)
- list_del_init(&wait->task_list);
- return ret;
- }
其主要功能是唤醒睡眠进程,并从等待队列链表上将这个等待队列成员删除。
(2)动态声明和初始化一个等待队列
- struct wait_queue_t myqueue;
- init_waitqueue_entry(&myqueue, tsk);
- static inline void init_waitqueue_entry(wait_queue_t *q, struct task_struct *p)
- {
- q->flags = 0;
- q->private = p;
- q->func = default_wake_function;
- }
2. 使进程在等待队列上睡眠相关接口
(1)将进程加入某个等待队列链表
- void prepare_to_wait(wait_queue_head_t *q, wait_queue_t *wait, int state)
- {
- unsigned long flags;
- wait->flags &= ~WQ_FLAG_EXCLUSIVE;
- spin_lock_irqsave(&q->lock, flags);
- if (list_empty(&wait->task_list)) /*判断当前等待队列是否已经被加入过某个链表,如果没有将wait加入q*/
- __add_wait_queue(q, wait);
- set_current_state(state); /*加入等待队列后,进程的状态需要按要求改变*/
- spin_unlock_irqrestore(&q->lock, flags);
- }
另外还有一个添加函数,不过这个函数同常不会直接使用:
- void add_wait_queue(wait_queue_head_t *q, wait_queue_t *wait)
- {
- unsigned long flags;
- wait->flags &= ~WQ_FLAG_EXCLUSIVE;
- spin_lock_irqsave(&q->lock, flags);
- __add_wait_queue(q, wait);
- spin_unlock_irqrestore(&q->lock, flags);
- }
比较常用的几个宏:
(1)wait_event:将当前进程加入指定的等待队列列表wq,因为在smp的环境下,condition在任何地方都有可能改变,因此,在检查前首先检查 等待条件有没有改变,如果没有改变才会真正加入,如果改变了就可以直接退出。当prepare_to_wait加入等待队列后,再去检查等待状态有没有改变,如果没有改变,那么当前进程就应该放弃CPU了,调用schedule()。
- #define wait_event(wq, condition) /
- do {/
- if (condition) /
- break;/
- __wait_event(wq, condition);/
- } while (0)
- #define __wait_event(wq, condition) /
- do {/
- DEFINE_WAIT(__wait);/
- /
- for (;;) {/
- prepare_to_wait(&wq, &__wait, TASK_UNINTERRUPTIBLE);/
- if (condition)/
- break;/
- schedule();/
- }/
- finish_wait(&wq, &__wait);/
- } while (0)
(2)wait_event_interruptible(wq, conditon):设置进程的状态为TASK_INTERRUPTIBLE,因此,进程除了当喊醒条件变化时被唤醒外,还可以通过接收信号而被唤醒。
(3)wait_event_timeout():等待满足的条件为指定的时间后就可以被唤醒,防止了永久等待
(4)wait_evnt_interruptible_timeout():是(2)和(3)的结合体。
3. 等待队列上进程唤醒相关的接口
有睡眠就必须要唤醒,但是不要求是一种一对一的配对行为,下面列举了比较常用的唤醒相关的宏:
(1)wake_up(x)
- #define wake_up(x)__wake_up(x, TASK_NORMAL, 1, NULL)
- void __wake_up(wait_queue_head_t *q, unsigned int mode,
- int nr_exclusive, void *key) /*mode表示要唤醒的进程的状态*/
- {
- unsigned long flags;
- spin_lock_irqsave(&q->lock, flags);
- __wake_up_common(q, mode, nr_exclusive, 0, key);
- spin_unlock_irqrestore(&q->lock, flags);
- }
- static void __wake_up_common(wait_queue_head_t *q, unsigned int mode,
- int nr_exclusive, int wake_flags, void *key)
- {
- wait_queue_t *curr, *next;
- list_for_each_entry_safe(curr, next, &q->task_list, task_list) {
- unsigned flags = curr->flags;
- /*执行工作队列处理函数,并选择执行多少个独占的进程,需要注意的是独占进程被添加到了工作队列的尾端,因此,会首先处理普通的进程,最后才去处理独占进程,nr_exclusive就是用来解决“惊群”问题的*/
- if (curr->func(curr, mode, wake_flags, key) &&
- (flags & WQ_FLAG_EXCLUSIVE) && !--nr_exclusive)
- break;
- }
- }
(2)其他唤醒宏:
- #define wake_up_nr(x, nr)__wake_up(x, TASK_NORMAL, nr, NULL)
- #define wake_up_all(x)__wake_up(x, TASK_NORMAL, 0, NULL)
- #define wake_up_locked(x)__wake_up_locked((x), TASK_NORMAL)
- #define wake_up_interruptible(x)__wake_up(x, TASK_INTERRUPTIBLE, 1, NULL)
- #define wake_up_interruptible_nr(x, nr)__wake_up(x, TASK_INTERRUPTIBLE, nr, NULL)
- #define wake_up_interruptible_all(x)__wake_up(x, TASK_INTERRUPTIBLE, 0, NULL)
- #define wake_up_interruptible_sync(x)__wake_up_sync((x), TASK_INTERRUPTIBLE, 1)