E100.C简析(~/drivers/net/ethernet/intel/e100.c)
支持网络协议栈的底层网卡驱动是一个怎么也绕不过去的话题,以Intel PRO/100网卡驱动为例,分析一下Linux下网卡驱动的实现。同时也兼谈一些pci总线的问题。PCI总线的框架系统只提供对PCI总线系统的框架性管理,对于具体的PCI设备提供何种功能,不做任何的管理。
PCI总线
PCI总线规定了以下设计目标:
- 支持高传输带宽
- 简单且易于自动化配置附接的外设
- 平台独立性,不绑定到特定的处理器类型或系统平台
设备标识
- 总线编号,是该设备所在的总线编号,从0开始,PCI规范最多允许255个总线(由于255条总线对于大型系统不够,Linux目前支持PCI域)
- 插槽编号,是总线内部的一个唯一标识编号,一个总线最多能够附接32个设备,不同总线上的设备插槽标号可能相同
- 功能编号,用于在一个扩展卡上, 包括实现多个扩展设备的设备。
每个设备都通过一个16(8:5:3)位编号唯一标识,Linux中定义为pci_dev的数据结构
地址空间
- I/O空间通过32个比特位描述,因而,对用于与设备通信的端口地址,提供最大4GB的空间
- 数据空间(内存空间),取决于处理器类型,数据空间由32或64个比特位描述。系统中的设备分配到上述两个地址空间,因而有唯一的地址
- 配置空间包含了各个设备的类型和特征的详细信息,以省去危险的自动探测工作。PCI接口标准在ISA之上的主要创新在于配置地址空间。因此,除了通常的驱动代码之外,PCI驱动程序还需要访问配置空间的能力,以便免去冒险探测的工作。
配置信息
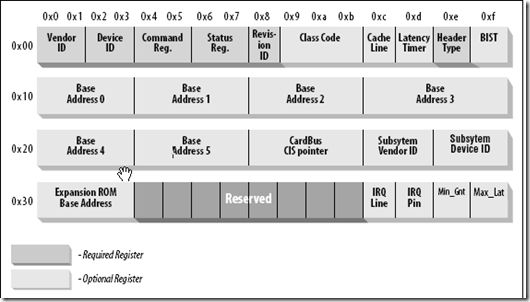 尽管该结构长度必须是256字节,但只有前64字节是标准化的。VendorID和DeviceID唯一地标志了厂商和设备类型。这两个ID合起来通常称之为设备的签名。两个具有相似名称的附加字段:Subsystem Vendor ID和Subsystem Device ID,也可以同时使用,以更精确的描述设备的通用接口。Rev ID用于区分不同的设备修订级别。Class Code字段用于将设备分配到不同的功能组,该字段分为两部分。前8个比特位表示基类,而剩余的16个比特位表示基类的一个子类。
尽管该结构长度必须是256字节,但只有前64字节是标准化的。VendorID和DeviceID唯一地标志了厂商和设备类型。这两个ID合起来通常称之为设备的签名。两个具有相似名称的附加字段:Subsystem Vendor ID和Subsystem Device ID,也可以同时使用,以更精确的描述设备的通用接口。Rev ID用于区分不同的设备修订级别。Class Code字段用于将设备分配到不同的功能组,该字段分为两部分。前8个比特位表示基类,而剩余的16个比特位表示基类的一个子类。
- 大容量存储器(PCI_BASE_CLASS_STORAGE)
- scsi控制器(PCI_CLASS_STORAGE_SCSI)
- ide控制器(PCI_CLASS_STORAGE_IDE)
- RAID控制器(PCI_CLASS_STORAGE_RAID)
- 网络(PCI_BASE_CLASS_NETWORK)
- 以太网(PCI_BASE_NETWORK_ETHERNET)
- FDDI(PCI_BASE_NETWORK_FDDI)
- 系统组件(PCI_BASE_CLASS_SYSTEM)
- DMA控制器(PCI_CLASS_SYSTEM_DMA)
- 实时时钟(PCI_CLASS_SYSTEM_RTC)
当PCI设备上电时,硬件保持未激活状态。换句话说,该设备只会对配置事务做出响应。上电时,设备上不会有内存和I/O端口映射到计算机的地址空间,其他设备相关功能,例如中断报告,也被禁止。幸运的是,每个PCI主板均配备有能够处理PCI的固件,固件通过读写PCI控制器中的寄存器,提供了对设备配置地址空间的访问。系统引导时,固件(或Linux内核)在每个PCI外设上执行配置事务,以便为它提供的每个地址区域分配一个安全的位置。当驱动程序访问设备的时候,它的内存和I/O区域已经被映射到了处理器的地址空间。驱动程序可以修改这个默认配置,不过从来不需要这样做。
内核中PCI设备的实现
系统为PCI驱动程序提供的框架,可以粗略的分为两个类别:
- PCI系统的初始化(和资源的分配),以及预备对应的数据结构以反映各个总线和设备的容量和能力,使得能够较为容易地操作总线/设备
- 支持访问所有PCI选项的标准化函数接口
PCI总线:
1: struct pci_bus {
2: struct list_head node; /* node in list of buses */
3: struct pci_bus *parent; /* parent bus this bridge is on */
4: struct list_head children; /* list of child buses */
5: struct list_head devices; /* list of devices on this bus */
6: struct pci_dev *self; /* bridge device as seen by parent */
7: struct list_head slots; /* list of slots on this bus */
8: struct resource *resource[PCI_BRIDGE_RESOURCE_NUM];
9: struct list_head resources; /* address space routed to this bus */
10:
11: struct pci_ops *ops; /* configuration access functions */
12: void *sysdata; /* hook for sys-specific extension */
13: struct proc_dir_entry *procdir; /* directory entry in /proc/bus/pci */
14:
15: unsigned char number; /* bus number */
16: unsigned char primary; /* number of primary bridge */
17: unsigned char secondary; /* number of secondary bridge */
18: unsigned char subordinate; /* max number of subordinate buses */
19: unsigned char max_bus_speed; /* enum pci_bus_speed */
20: unsigned char cur_bus_speed; /* enum pci_bus_speed */
21:
22: char name[48];
23:
24: unsigned short bridge_ctl; /* manage NO_ISA/FBB/et al behaviors */
25: pci_bus_flags_t bus_flags; /* Inherited by child busses */
26: struct device *bridge;
27: struct device dev;
28: struct bin_attribute *legacy_io; /* legacy I/O for this bus */
29: struct bin_attribute *legacy_mem; /* legacy mem */
30: unsigned int is_added:1;
31: };
1: extern struct list_head pci_root_buses; /* list of all known PCI buses */
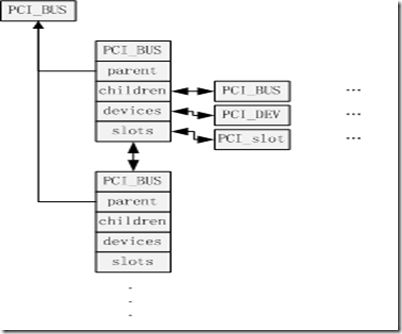
所有已知的PCI总线都通过pci_root_buses连接起来。
struct pci_bus结构分为不同的功能部分。第一部分包括与其他PCI数据结构建立关联所需的所有成员。node是一个链表元素,用于将所有总线连接到全局链表中。parent是一个指针,指向更高层次总线的数据结构。每个总线只可能有一个父总线。某个总线的下级总线或子总线都必须通过children作为表头的链表管理。所有总线上附接的设备头通过devices为表头的链表管理。除总线0以外,所有系统总线都可以通过一个PCI桥接器寻址,桥接器类似一个普通的PCI设备。每个总线的self指向桥接器的pci_dev实例。resource数组只是用于保存该总线在虚拟内存中占用的地址区域。
1: struct resource {
2: resource_size_t start;
3: resource_size_t end;
4: const char *name;
5: unsigned long flags;
6: struct resource *parent, *sibling, *child;
7: };
ops成员,其中包含大量函数指针。这些是一组用于访问配置空间的函数。sysdata成员使得总线结构可以关联到特定于硬件的函数。proc提供了一个到proc文件系统的接口,以便使用/proc/bus/pci向用户空间导出有关各个总线的信息。number是一个连续号码,在系统中唯一地标志了该总线。subordinate是该特定总线可以拥有的下级总线的最大数目。name字段包含该总线的一个文本名称。
在PCI子系统初始化时,会建立所有系统总线的列表。这些总线以两种不同的方式彼此连接。第一种方法使用一个线性链表,表头是上文所述的pci_root_buses全局变量,包括系统中的所有总线。parent和children结构成员,方便了以树的形式表示PCI总线的二维拓扑结构。
PCI设备
1: /*
2: * The pci_dev structure is used to describe PCI devices.
3: */
4: struct pci_dev {
5: struct list_head bus_list; /* node in per-bus list */
6: struct pci_bus *bus; /* bus this device is on */
7: struct pci_bus *subordinate; /* bus this device bridges to */
8:
9: void *sysdata; /* hook for sys-specific extension */
10: struct proc_dir_entry *procent; /* device entry in /proc/bus/pci */
11: struct pci_slot *slot; /* Physical slot this device is in */
12:
13: unsigned int devfn; /* encoded device & function index */
14: unsigned short vendor;
15: unsigned short device;
16: unsigned short subsystem_vendor;
17: unsigned short subsystem_device;
18: unsigned int class; /* 3 bytes: (base,sub,prog-if) */
19: u8 revision; /* PCI revision, low byte of class word */
20: u8 hdr_type; /* PCI header type (`multi' flag masked out) */
21: u8 pcie_cap; /* PCI-E capability offset */
22: u8 pcie_type:4; /* PCI-E device/port type */
23: u8 pcie_mpss:3; /* PCI-E Max Payload Size Supported */
24: u8 rom_base_reg; /* which config register controls the ROM */
25: u8 pin; /* which interrupt pin this device uses */
26:
27: struct pci_driver *driver; /* which driver has allocated this device */
28: u64 dma_mask; /* Mask of the bits of bus address this
29: device implements. Normally this is
30: 0xffffffff. You only need to change
31: this if your device has broken DMA
32: or supports 64-bit transfers. */
33:
34: struct device_dma_parameters dma_parms;
35:
36: pci_power_t current_state; /* Current operating state. In ACPI-speak,
37: this is D0-D3, D0 being fully functional,
38: and D3 being off. */
39: int pm_cap; /* PM capability offset in the
40: configuration space */
41: unsigned int pme_support:5; /* Bitmask of states from which PME#
42: can be generated */
43: unsigned int pme_interrupt:1;
44: unsigned int pme_poll:1; /* Poll device's PME status bit */
45: unsigned int d1_support:1; /* Low power state D1 is supported */
46: unsigned int d2_support:1; /* Low power state D2 is supported */
47: unsigned int no_d1d2:1; /* Only allow D0 and D3 */
48: unsigned int mmio_always_on:1; /* disallow turning off io/mem
49: decoding during bar sizing */
50: unsigned int wakeup_prepared:1;
51: unsigned int d3_delay; /* D3->D0 transition time in ms */
52:
53: #ifdef CONFIG_PCIEASPM
54: struct pcie_link_state *link_state; /* ASPM link state. */
55: #endif
56:
57: pci_channel_state_t error_state; /* current connectivity state */
58: struct device dev; /* Generic device interface */
59:
60: int cfg_size; /* Size of configuration space */
61:
62: /*
63: * Instead of touching interrupt line and base address registers
64: * directly, use the values stored here. They might be different!
65: */
66: unsigned int irq;
67: struct resource resource[DEVICE_COUNT_RESOURCE]; /* I/O and memory regions + expansion ROMs */
68: resource_size_t fw_addr[DEVICE_COUNT_RESOURCE]; /* FW-assigned addr */
69:
70: /* These fields are used by common fixups */
71: unsigned int transparent:1; /* Transparent PCI bridge */
72: unsigned int multifunction:1;/* Part of multi-function device */
73: /* keep track of device state */
74: unsigned int is_added:1;
75: unsigned int is_busmaster:1; /* device is busmaster */
76: unsigned int no_msi:1; /* device may not use msi */
77: unsigned int block_cfg_access:1; /* config space access is blocked */
78: unsigned int broken_parity_status:1; /* Device generates false positive parity */
79: unsigned int irq_reroute_variant:2; /* device needs IRQ rerouting variant */
80: unsigned int msi_enabled:1;
81: unsigned int msix_enabled:1;
82: unsigned int ari_enabled:1; /* ARI forwarding */
83: unsigned int is_managed:1;
84: unsigned int is_pcie:1; /* Obsolete. Will be removed.
85: Use pci_is_pcie() instead */
86: unsigned int needs_freset:1; /* Dev requires fundamental reset */
87: unsigned int state_saved:1;
88: unsigned int is_physfn:1;
89: unsigned int is_virtfn:1;
90: unsigned int reset_fn:1;
91: unsigned int is_hotplug_bridge:1;
92: unsigned int __aer_firmware_first_valid:1;
93: unsigned int __aer_firmware_first:1;
94: pci_dev_flags_t dev_flags;
95: atomic_t enable_cnt; /* pci_enable_device has been called */
96:
97: u32 saved_config_space[16]; /* config space saved at suspend time */
98: struct hlist_head saved_cap_space;
99: struct bin_attribute *rom_attr; /* attribute descriptor for sysfs ROM entry */
100: int rom_attr_enabled; /* has display of the rom attribute been enabled? */
101: struct bin_attribute *res_attr[DEVICE_COUNT_RESOURCE]; /* sysfs file for resources */
102: struct bin_attribute *res_attr_wc[DEVICE_COUNT_RESOURCE]; /* sysfs file for WC mapping of resources */
103: #ifdef CONFIG_PCI_MSI
104: struct list_head msi_list;
105: struct kset *msi_kset;
106: #endif
107: struct pci_vpd *vpd;
108: #ifdef CONFIG_PCI_ATS
109: union {
110: struct pci_sriov *sriov; /* SR-IOV capability related */
111: struct pci_dev *physfn; /* the PF this VF is associated with */
112: };
113: struct pci_ats *ats; /* Address Translation Service */
114: #endif
115: };
bus_list用于将设备放置到特定于总线的设备链表上。bus成员用于建立设备和总线之间的逆向关联。它指向设备所在总线的pci_bus实例。另一个到总线的关联保存在subordinate成员中,仅当设备表示连接两个PCI总线的PCI连接器时,该成员才包含有效值(否则为NULL指针)。如果确实如此(桥接器),则subordinate指向“下级”PCI总线的数据结构。其他数据结构的内容包括对PCI设备的配置空间内容的存储,其中填充的是系统初始化时从硬件读取的数据。driver指向用于控制该设备的驱动程序。每个PCI驱动程序都通过该结构的一个实例唯一的标识。dev用于将PCI设备关联到通用设备模型。irq指定了该设备的中断数目,resource数组保存了驱动程序为I/O内存分配的资源。
PCI驱动程序
1: struct pci_driver {
2: struct list_head node;
3: const char *name;
4: const struct pci_device_id *id_table; /* must be non-NULL for probe to be called */
5: int (*probe) (struct pci_dev *dev, const struct pci_device_id *id); /* New device inserted */
6: void (*remove) (struct pci_dev *dev); /* Device removed (NULL if not a hot-plug capable driver) */
7: int (*suspend) (struct pci_dev *dev, pm_message_t state); /* Device suspended */
8: int (*suspend_late) (struct pci_dev *dev, pm_message_t state);
9: int (*resume_early) (struct pci_dev *dev);
10: int (*resume) (struct pci_dev *dev); /* Device woken up */
11: void (*shutdown) (struct pci_dev *dev);
12: struct pci_error_handlers *err_handler;
13: struct device_driver driver;
14: struct pci_dynids dynids;
15: };
用于实现PCI驱动程序,表示了通用内核代码和设备的底层硬件驱动程序之间的接口。每个PCI驱动程序都必须将其函数填到该接口中,使得内核可以一致的控制可用的驱动程序。PCI驱动程序最重要的方面是对检测、安装、移除设备的支持。为此提供了两个函数指针,probe检测该驱动程序是否支持某个PCI设备,remove用于移除设备。只用系统支持热插拔时,移除PCI设备才有意义。驱动程序必须知道它负责管理的设备。pci_dev_id唯一的标识所支持的设备,与pci_dev是对同一事物的不同层面的刻画。id_table数组中保存了该设备支持的设备。
1: struct pci_device_id {
2: __u32 vendor, device; /* Vendor and device ID or PCI_ANY_ID*/
3: __u32 subvendor, subdevice; /* Subsystem ID's or PCI_ANY_ID */
4: __u32 class, class_mask; /* (class,subclass,prog-if) triplet */
5: kernel_ulong_t driver_data; /* Data private to the driver */
6: };
1: static DEFINE_PCI_DEVICE_TABLE(e100_id_table) = {
2: INTEL_8255X_ETHERNET_DEVICE(0x1029, 0),
3: INTEL_8255X_ETHERNET_DEVICE(0x1030, 0),
4: INTEL_8255X_ETHERNET_DEVICE(0x1031, 3),
5: INTEL_8255X_ETHERNET_DEVICE(0x1032, 3),
6: INTEL_8255X_ETHERNET_DEVICE(0x1033, 3),
7: INTEL_8255X_ETHERNET_DEVICE(0x1034, 3),
8: INTEL_8255X_ETHERNET_DEVICE(0x1038, 3),
9: INTEL_8255X_ETHERNET_DEVICE(0x1039, 4),
10: INTEL_8255X_ETHERNET_DEVICE(0x103A, 4),
11: INTEL_8255X_ETHERNET_DEVICE(0x103B, 4),
12: INTEL_8255X_ETHERNET_DEVICE(0x103C, 4),
13: INTEL_8255X_ETHERNET_DEVICE(0x103D, 4),
14: INTEL_8255X_ETHERNET_DEVICE(0x103E, 4),
15: INTEL_8255X_ETHERNET_DEVICE(0x1050, 5),
16: INTEL_8255X_ETHERNET_DEVICE(0x1051, 5),
17: INTEL_8255X_ETHERNET_DEVICE(0x1052, 5),
18: INTEL_8255X_ETHERNET_DEVICE(0x1053, 5),
19: INTEL_8255X_ETHERNET_DEVICE(0x1054, 5),
20: INTEL_8255X_ETHERNET_DEVICE(0x1055, 5),
21: INTEL_8255X_ETHERNET_DEVICE(0x1056, 5),
22: INTEL_8255X_ETHERNET_DEVICE(0x1057, 5),
23: INTEL_8255X_ETHERNET_DEVICE(0x1059, 0),
24: INTEL_8255X_ETHERNET_DEVICE(0x1064, 6),
25: INTEL_8255X_ETHERNET_DEVICE(0x1065, 6),
26: INTEL_8255X_ETHERNET_DEVICE(0x1066, 6),
27: INTEL_8255X_ETHERNET_DEVICE(0x1067, 6),
28: INTEL_8255X_ETHERNET_DEVICE(0x1068, 6),
29: INTEL_8255X_ETHERNET_DEVICE(0x1069, 6),
30: INTEL_8255X_ETHERNET_DEVICE(0x106A, 6),
31: INTEL_8255X_ETHERNET_DEVICE(0x106B, 6),
32: INTEL_8255X_ETHERNET_DEVICE(0x1091, 7),
33: INTEL_8255X_ETHERNET_DEVICE(0x1092, 7),
34: INTEL_8255X_ETHERNET_DEVICE(0x1093, 7),
35: INTEL_8255X_ETHERNET_DEVICE(0x1094, 7),
36: INTEL_8255X_ETHERNET_DEVICE(0x1095, 7),
37: INTEL_8255X_ETHERNET_DEVICE(0x10fe, 7),
38: INTEL_8255X_ETHERNET_DEVICE(0x1209, 0),
39: INTEL_8255X_ETHERNET_DEVICE(0x1229, 0),
40: INTEL_8255X_ETHERNET_DEVICE(0x2449, 2),
41: INTEL_8255X_ETHERNET_DEVICE(0x2459, 2),
42: INTEL_8255X_ETHERNET_DEVICE(0x245D, 2),
43: INTEL_8255X_ETHERNET_DEVICE(0x27DC, 7),
44: { 0, }
45: };
内核提供了pci_match_id函数,将PCI设备数据与ID表中的数据进行比较。
1: const struct pci_device_id *pci_match_id(const struct pci_device_id *ids,
2: struct pci_dev *dev)
注册驱动程序
1: int __must_check __pci_register_driver(struct pci_driver *, struct module *,
2: const char *mod_name)
1: static int __init e100_init_module(void)
2: {
3: if (((1 << debug) - 1) & NETIF_MSG_DRV) {
4: pr_info("%s, %s\n", DRV_DESCRIPTION, DRV_VERSION);
5: pr_info("%s\n", DRV_COPYRIGHT);
6: }
7: return pci_register_driver(&e100_driver);
8: }
驱动程序与设备的关联
1: /**
2: * driver_attach - try to bind driver to devices.
3: * @drv: driver.
4: *
5: * Walk the list of devices that the bus has on it and try to
6: * match the driver with each one. If driver_probe_device()
7: * returns 0 and the @dev->driver is set, we've found a
8: * compatible pair.
9: */
10: int driver_attach(struct device_driver *drv)
11: {
12: return bus_for_each_dev(drv->bus, NULL, drv, __driver_attach);
13: }
14: EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(driver_attach);
1: static int __driver_attach(struct device *dev, void *data)
2: {
3: struct device_driver *drv = data;
4:
5: /*
6: * Lock device and try to bind to it. We drop the error
7: * here and always return 0, because we need to keep trying
8: * to bind to devices and some drivers will return an error
9: * simply if it didn't support the device.
10: *
11: * driver_probe_device() will spit a warning if there
12: * is an error.
13: */
14:
15: if (!driver_match_device(drv, dev))
16: return 0;
17:
18: if (dev->parent) /* Needed for USB */
19: device_lock(dev->parent);
20: device_lock(dev);
21: if (!dev->driver)
22: driver_probe_device(drv, dev);
23: device_unlock(dev);
24: if (dev->parent)
25: device_unlock(dev->parent);
26:
27: return 0;
28: }
e100.c分析
1: static int __devinit e100_probe(struct pci_dev *pdev,
2: const struct pci_device_id *ent)
3: {
4: struct net_device *netdev;
5: struct nic *nic;
6: int err;
7:
8: if (!(netdev = alloc_etherdev(sizeof(struct nic)))) {
9: if (((1 << debug) - 1) & NETIF_MSG_PROBE)
10: pr_err("Etherdev alloc failed, aborting\n");
11: return -ENOMEM;
12: }
13:
14: netdev->netdev_ops = &e100_netdev_ops;
15: SET_ETHTOOL_OPS(netdev, &e100_ethtool_ops);
16: netdev->watchdog_timeo = E100_WATCHDOG_PERIOD;
17: strncpy(netdev->name, pci_name(pdev), sizeof(netdev->name) - 1);
18:
19: nic = netdev_priv(netdev);
20: netif_napi_add(netdev, &nic->napi, e100_poll, E100_NAPI_WEIGHT);
21: nic->netdev = netdev;
22: nic->pdev = pdev;
23: nic->msg_enable = (1 << debug) - 1;
24: nic->mdio_ctrl = mdio_ctrl_hw;
25: pci_set_drvdata(pdev, netdev);
26:
27: if ((err = pci_enable_device(pdev))) {
28: netif_err(nic, probe, nic->netdev, "Cannot enable PCI device, aborting\n");
29: goto err_out_free_dev;
30: }
31:
32: if (!(pci_resource_flags(pdev, 0) & IORESOURCE_MEM)) {
33: netif_err(nic, probe, nic->netdev, "Cannot find proper PCI device base address, aborting\n");
34: err = -ENODEV;
35: goto err_out_disable_pdev;
36: }
37:
38: if ((err = pci_request_regions(pdev, DRV_NAME))) {
39: netif_err(nic, probe, nic->netdev, "Cannot obtain PCI resources, aborting\n");
40: goto err_out_disable_pdev;
41: }
42:
43: if ((err = pci_set_dma_mask(pdev, DMA_BIT_MASK(32)))) {
44: netif_err(nic, probe, nic->netdev, "No usable DMA configuration, aborting\n");
45: goto err_out_free_res;
46: }
47:
48: SET_NETDEV_DEV(netdev, &pdev->dev);
49:
50: if (use_io)
51: netif_info(nic, probe, nic->netdev, "using i/o access mode\n");
52:
53: nic->csr = pci_iomap(pdev, (use_io ? 1 : 0), sizeof(struct csr));
54: if (!nic->csr) {
55: netif_err(nic, probe, nic->netdev, "Cannot map device registers, aborting\n");
56: err = -ENOMEM;
57: goto err_out_free_res;
58: }
59:
60: if (ent->driver_data)
61: nic->flags |= ich;
62: else
63: nic->flags &= ~ich;
64:
65: e100_get_defaults(nic);
66:
67: /* D100 MAC doesn't allow rx of vlan packets with normal MTU */
68: if (nic->mac < mac_82558_D101_A4)
69: netdev->features |= NETIF_F_VLAN_CHALLENGED;
70:
71: /* locks must be initialized before calling hw_reset */
72: spin_lock_init(&nic->cb_lock);
73: spin_lock_init(&nic->cmd_lock);
74: spin_lock_init(&nic->mdio_lock);
75:
76: /* Reset the device before pci_set_master() in case device is in some
77: * funky state and has an interrupt pending - hint: we don't have the
78: * interrupt handler registered yet. */
79: e100_hw_reset(nic);
80:
81: pci_set_master(pdev);
82:
83: init_timer(&nic->watchdog);
84: nic->watchdog.function = e100_watchdog;
85: nic->watchdog.data = (unsigned long)nic;
86:
87: INIT_WORK(&nic->tx_timeout_task, e100_tx_timeout_task);
88:
89: if ((err = e100_alloc(nic))) {
90: netif_err(nic, probe, nic->netdev, "Cannot alloc driver memory, aborting\n");
91: goto err_out_iounmap;
92: }
93:
94: if ((err = e100_eeprom_load(nic)))
95: goto err_out_free;
96:
97: e100_phy_init(nic);
98:
99: memcpy(netdev->dev_addr, nic->eeprom, ETH_ALEN);
100: memcpy(netdev->perm_addr, nic->eeprom, ETH_ALEN);
101: if (!is_valid_ether_addr(netdev->perm_addr)) {
102: if (!eeprom_bad_csum_allow) {
103: netif_err(nic, probe, nic->netdev, "Invalid MAC address from EEPROM, aborting\n");
104: err = -EAGAIN;
105: goto err_out_free;
106: } else {
107: netif_err(nic, probe, nic->netdev, "Invalid MAC address from EEPROM, you MUST configure one.\n");
108: }
109: }
110:
111: /* Wol magic packet can be enabled from eeprom */
112: if ((nic->mac >= mac_82558_D101_A4) &&
113: (nic->eeprom[eeprom_id] & eeprom_id_wol)) {
114: nic->flags |= wol_magic;
115: device_set_wakeup_enable(&pdev->dev, true);
116: }
117:
118: /* ack any pending wake events, disable PME */
119: pci_pme_active(pdev, false);
120:
121: strcpy(netdev->name, "eth%d");
122: if ((err = register_netdev(netdev))) {
123: netif_err(nic, probe, nic->netdev, "Cannot register net device, aborting\n");
124: goto err_out_free;
125: }
126: nic->cbs_pool = pci_pool_create(netdev->name,
127: nic->pdev,
128: nic->params.cbs.max * sizeof(struct cb),
129: sizeof(u32),
130: 0);
131: netif_info(nic, probe, nic->netdev,
132: "addr 0x%llx, irq %d, MAC addr %pM\n",
133: (unsigned long long)pci_resource_start(pdev, use_io ? 1 : 0),
134: pdev->irq, netdev->dev_addr);
135:
136: return 0;
137:
138: err_out_free:
139: e100_free(nic);
140: err_out_iounmap:
141: pci_iounmap(pdev, nic->csr);
142: err_out_free_res:
143: pci_release_regions(pdev);
144: err_out_disable_pdev:
145: pci_disable_device(pdev);
146: err_out_free_dev:
147: pci_set_drvdata(pdev, NULL);
148: free_netdev(netdev);
149: return err;
150: }
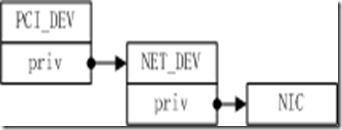
__driver_attach函数会调用此函数。该函数调用完成后,构建完成如下的数据结构。
首先分配网卡设备结构,填充netdev_ops和ethtool_ops函数指针,然后分配struct nic结构,填充相应的结构,最后将个数据结构组装在一起,形成上图的数据结构。然后正式进行pci设备的启动工作。最后会向系统注册netdev设备。当PCI层发现它正在搜索驱动程序的设备ID与前面提到的id_table匹配,就会调用此函数。此函数应该开启硬件、分配net_device结构、初始化并注册新设备。此函数中,驱动程序也会分配正确工作所需的所有数据结构。
1: static inline void e100_write_flush(struct nic *nic)
2: {
3: /* Flush previous PCI writes through intermediate bridges
4: * by doing a benign read */
5: (void)ioread8(&nic->csr->scb.status);
6: }
把PCI总线读一下,强迫写操作完成。
1: static void e100_enable_irq(struct nic *nic)
2: {
3: unsigned long flags;
4: //自旋锁,关中断
5: spin_lock_irqsave(&nic->cmd_lock, flags);
6: iowrite8(irq_mask_none, &nic->csr->scb.cmd_hi);//开网卡中断
7: e100_write_flush(nic);//刷新,命令生效
8: spin_unlock_irqrestore(&nic->cmd_lock, flags);
9: }
设置多播地址
1: static void e100_multi(struct nic *nic, struct cb *cb, struct sk_buff *skb)
2: {
3: struct net_device *netdev = nic->netdev;
4: struct netdev_hw_addr *ha;
5: u16 i, count = min(netdev_mc_count(netdev), E100_MAX_MULTICAST_ADDRS);
6:
7: cb->command = cpu_to_le16(cb_multi);
8: cb->u.multi.count = cpu_to_le16(count * ETH_ALEN);
9: i = 0;
10: netdev_for_each_mc_addr(ha, netdev) {
11: if (i == count)
12: break;
13: memcpy(&cb->u.multi.addr[i++ * ETH_ALEN], &ha->addr,
14: ETH_ALEN);
15: }
16: }
17:
18: static void e100_set_multicast_list(struct net_device *netdev)
19: {
20: struct nic *nic = netdev_priv(netdev);
21:
22: netif_printk(nic, hw, KERN_DEBUG, nic->netdev,
23: "mc_count=%d, flags=0x%04X\n",
24: netdev_mc_count(netdev), netdev->flags);
25:
26: if (netdev->flags & IFF_PROMISC)
27: nic->flags |= promiscuous;
28: else
29: nic->flags &= ~promiscuous;
30:
31: if (netdev->flags & IFF_ALLMULTI ||
32: netdev_mc_count(netdev) > E100_MAX_MULTICAST_ADDRS)
33: nic->flags |= multicast_all;
34: else
35: nic->flags &= ~multicast_all;
36:
37: e100_exec_cb(nic, NULL, e100_configure);
38: e100_exec_cb(nic, NULL, e100_multi);
39: }
更新网卡统计信息
1: static void e100_update_stats(struct nic *nic)
2: {
3: struct net_device *dev = nic->netdev;
4: struct net_device_stats *ns = &dev->stats;
5: struct stats *s = &nic->mem->stats;
6: __le32 *complete = (nic->mac < mac_82558_D101_A4) ? &s->fc_xmt_pause :
7: (nic->mac < mac_82559_D101M) ? (__le32 *)&s->xmt_tco_frames :
8: &s->complete;
9:
10: /* Device's stats reporting may take several microseconds to
11: * complete, so we're always waiting for results of the
12: * previous command. */
13:
14: if (*complete == cpu_to_le32(cuc_dump_reset_complete)) {
15: *complete = 0;
16: nic->tx_frames = le32_to_cpu(s->tx_good_frames);
17: nic->tx_collisions = le32_to_cpu(s->tx_total_collisions);
18: ns->tx_aborted_errors += le32_to_cpu(s->tx_max_collisions);
19: ns->tx_window_errors += le32_to_cpu(s->tx_late_collisions);
20: ns->tx_carrier_errors += le32_to_cpu(s->tx_lost_crs);
21: ns->tx_fifo_errors += le32_to_cpu(s->tx_underruns);
22: ns->collisions += nic->tx_collisions;
23: ns->tx_errors += le32_to_cpu(s->tx_max_collisions) +
24: le32_to_cpu(s->tx_lost_crs);
25: ns->rx_length_errors += le32_to_cpu(s->rx_short_frame_errors) +
26: nic->rx_over_length_errors;
27: ns->rx_crc_errors += le32_to_cpu(s->rx_crc_errors);
28: ns->rx_frame_errors += le32_to_cpu(s->rx_alignment_errors);
29: ns->rx_over_errors += le32_to_cpu(s->rx_overrun_errors);
30: ns->rx_fifo_errors += le32_to_cpu(s->rx_overrun_errors);
31: ns->rx_missed_errors += le32_to_cpu(s->rx_resource_errors);
32: ns->rx_errors += le32_to_cpu(s->rx_crc_errors) +
33: le32_to_cpu(s->rx_alignment_errors) +
34: le32_to_cpu(s->rx_short_frame_errors) +
35: le32_to_cpu(s->rx_cdt_errors);
36: nic->tx_deferred += le32_to_cpu(s->tx_deferred);
37: nic->tx_single_collisions +=
38: le32_to_cpu(s->tx_single_collisions);
39: nic->tx_multiple_collisions +=
40: le32_to_cpu(s->tx_multiple_collisions);
41: if (nic->mac >= mac_82558_D101_A4) {
42: nic->tx_fc_pause += le32_to_cpu(s->fc_xmt_pause);
43: nic->rx_fc_pause += le32_to_cpu(s->fc_rcv_pause);
44: nic->rx_fc_unsupported +=
45: le32_to_cpu(s->fc_rcv_unsupported);
46: if (nic->mac >= mac_82559_D101M) {
47: nic->tx_tco_frames +=
48: le16_to_cpu(s->xmt_tco_frames);
49: nic->rx_tco_frames +=
50: le16_to_cpu(s->rcv_tco_frames);
51: }
52: }
53: }
54:
55:
56: if (e100_exec_cmd(nic, cuc_dump_reset, 0))
57: netif_printk(nic, tx_err, KERN_DEBUG, nic->netdev,
58: "exec cuc_dump_reset failed\n");
59: }
网卡信息监测,根据MII的监测工具进行监测,如果发现有网卡动作,则调整统计信息,把网卡设置成UP/DOWN状态
1: static void e100_watchdog(unsigned long data)
2: {
3: struct nic *nic = (struct nic *)data;
4: struct ethtool_cmd cmd = { .cmd = ETHTOOL_GSET };
5: u32 speed;
6:
7: netif_printk(nic, timer, KERN_DEBUG, nic->netdev,
8: "right now = %ld\n", jiffies);
9:
10: /* mii library handles link maintenance tasks */
11:
12: mii_ethtool_gset(&nic->mii, &cmd);
13: speed = ethtool_cmd_speed(&cmd);
14:
15: if (mii_link_ok(&nic->mii) && !netif_carrier_ok(nic->netdev)) {
16: netdev_info(nic->netdev, "NIC Link is Up %u Mbps %s Duplex\n",
17: speed == SPEED_100 ? 100 : 10,
18: cmd.duplex == DUPLEX_FULL ? "Full" : "Half");
19: } else if (!mii_link_ok(&nic->mii) && netif_carrier_ok(nic->netdev)) {
20: netdev_info(nic->netdev, "NIC Link is Down\n");
21: }
22:
23: mii_check_link(&nic->mii);
24:
25: /* Software generated interrupt to recover from (rare) Rx
26: * allocation failure.
27: * Unfortunately have to use a spinlock to not re-enable interrupts
28: * accidentally, due to hardware that shares a register between the
29: * interrupt mask bit and the SW Interrupt generation bit */
30: spin_lock_irq(&nic->cmd_lock);
31: iowrite8(ioread8(&nic->csr->scb.cmd_hi) | irq_sw_gen,&nic->csr->scb.cmd_hi);
32: e100_write_flush(nic);
33: spin_unlock_irq(&nic->cmd_lock);
34:
35: e100_update_stats(nic);
36: e100_adjust_adaptive_ifs(nic, speed, cmd.duplex);
37:
38: if (nic->mac <= mac_82557_D100_C)
39: /* Issue a multicast command to workaround a 557 lock up */
40: e100_set_multicast_list(nic->netdev);
41:
42: if (nic->flags & ich && speed == SPEED_10 && cmd.duplex == DUPLEX_HALF)
43: /* Need SW workaround for ICH[x] 10Mbps/half duplex Tx hang. */
44: nic->flags |= ich_10h_workaround;
45: else
46: nic->flags &= ~ich_10h_workaround;
47:
48: mod_timer(&nic->watchdog,
49: round_jiffies(jiffies + E100_WATCHDOG_PERIOD));//启动下一次监测
50: }
1: static int e100_up(struct nic *nic)
2: {
3: int err;
4:
5: if ((err = e100_rx_alloc_list(nic)))//分配收包队列
6: return err;
7: if ((err = e100_alloc_cbs(nic)))//分配控制队列
8: goto err_rx_clean_list;
9: if ((err = e100_hw_init(nic)))//硬件初始化
10: goto err_clean_cbs;
11: e100_set_multicast_list(nic->netdev);//设置多播地址
12: e100_start_receiver(nic, NULL);//准备工作
13: mod_timer(&nic->watchdog, jiffies);//时间狗,自动检查网卡状态
14: if ((err = request_irq(nic->pdev->irq, e100_intr, IRQF_SHARED,
15: nic->netdev->name, nic->netdev)))//请求IRQ分配
16: goto err_no_irq;
17: netif_wake_queue(nic->netdev);//唤醒网络队列,通知核心,这个网卡启动了
18: napi_enable(&nic->napi);//NAPI方式,把pool使能
19: /* enable ints _after_ enabling poll, preventing a race between
20: * disable ints+schedule */
21: e100_enable_irq(nic);//使能中断
22: return 0;
23:
24: err_no_irq:
25: del_timer_sync(&nic->watchdog);
26: err_clean_cbs:
27: e100_clean_cbs(nic);
28: err_rx_clean_list:
29: e100_rx_clean_list(nic);
30: return err;
31: }
网卡启动函数
1: static const struct net_device_ops e100_netdev_ops = {
2: .ndo_open = e100_open,
3: .ndo_stop = e100_close,
4: .ndo_start_xmit = e100_xmit_frame,
5: .ndo_validate_addr = eth_validate_addr,
6: .ndo_set_rx_mode = e100_set_multicast_list,
7: .ndo_set_mac_address = e100_set_mac_address,
8: .ndo_change_mtu = e100_change_mtu,
9: .ndo_do_ioctl = e100_do_ioctl,
10: .ndo_tx_timeout = e100_tx_timeout,
11: #ifdef CONFIG_NET_POLL_CONTROLLER
12: .ndo_poll_controller = e100_netpoll,
13: #endif
14: };
e100.c实现的网络设备方法。其基本作用如下:
open,打开接口。在ifconfig激活接口时,接口将被打开。open函数应该注册所有的系统资源(I/O端口,IRQ,DMA等等),打开硬件,并对设备执行所有其他所需的设置。
stop,停止接口。当接口终止时应该被停止。在该函数中执行的操作与打开时执行的操作相反。包括停止出口队列、释放硬件资源以及停止设备驱动程序使用的任何定时器。
hard_start_xmit,该方法初始化数据包的传输。完整的数据包(协议头和数据)包含在一个套接字缓冲区(sk_buffer)结构中。
tx_timeout,如果数据包的传输在合理的时间段内失败,则假定丢失了中断或接口被锁住,这是网络代码将调用该方法。它负责解决问题并重新开始数据包的传输。
do_ioctl,执行接口特有的ioctl命令。如果接口不需要实现任何接口特有的命令,则设置为NULL
1: static int e100_open(struct net_device *netdev)
2: {
3: struct nic *nic = netdev_priv(netdev);
4: int err = 0;
5:
6: netif_carrier_off(netdev);
7: if ((err = e100_up(nic)))
8: netif_err(nic, ifup, nic->netdev, "Cannot open interface, aborting\n");
9: return err;
10: }
1: static int e100_close(struct net_device *netdev)
2: {
3: e100_down(netdev_priv(netdev));
4: return 0;
5: }
1: static void e100_down(struct nic *nic)
2: {
3: /* wait here for poll to complete */
4: napi_disable(&nic->napi);
5: netif_stop_queue(nic->netdev);
6: e100_hw_reset(nic);
7: free_irq(nic->pdev->irq, nic->netdev);
8: del_timer_sync(&nic->watchdog);
9: netif_carrier_off(nic->netdev);
10: e100_clean_cbs(nic);
11: e100_rx_clean_list(nic);
12: }
基本上就是e100_open的逆操作。
1: static int e100_tx_clean(struct nic *nic) //对发包队列进行清理
2: {
3: struct net_device *dev = nic->netdev;
4: struct cb *cb;
5: int tx_cleaned = 0;
6:
7: spin_lock(&nic->cb_lock);
8:
9: /* Clean CBs marked complete */
10: for (cb = nic->cb_to_clean;
11: cb->status & cpu_to_le16(cb_complete);
12: cb = nic->cb_to_clean = cb->next) {
13: rmb(); /* read skb after status */
14: netif_printk(nic, tx_done, KERN_DEBUG, nic->netdev,
15: "cb[%d]->status = 0x%04X\n",
16: (int)(((void*)cb - (void*)nic->cbs)/sizeof(struct cb)),
17: cb->status);
18:
19: if (likely(cb->skb != NULL)) {
20: dev->stats.tx_packets++;
21: dev->stats.tx_bytes += cb->skb->len;
22:
23: pci_unmap_single(nic->pdev,
24: le32_to_cpu(cb->u.tcb.tbd.buf_addr),
25: le16_to_cpu(cb->u.tcb.tbd.size),
26: PCI_DMA_TODEVICE);//解除PCI通道的DMA映射
27: dev_kfree_skb_any(cb->skb);//释放skb
28: cb->skb = NULL;
29: tx_cleaned = 1;
30: }
31: cb->status = 0;
32: nic->cbs_avail++;
33: }
34:
35: spin_unlock(&nic->cb_lock);
36:
37: /* Recover from running out of Tx resources in xmit_frame */
38: if (unlikely(tx_cleaned && netif_queue_stopped(nic->netdev)))
39: netif_wake_queue(nic->netdev);//唤醒网卡的等待队列
40:
41: return tx_cleaned;
42: }
1: static int e100_rx_alloc_skb(struct nic *nic, struct rx *rx)
2: {
3: if (!(rx->skb = netdev_alloc_skb_ip_align(nic->netdev, RFD_BUF_LEN)))
4: return -ENOMEM;
5:
6: /* Init, and map the RFD. */
7: skb_copy_to_linear_data(rx->skb, &nic->blank_rfd, sizeof(struct rfd));
8: rx->dma_addr = pci_map_single(nic->pdev, rx->skb->data,
9: RFD_BUF_LEN, PCI_DMA_BIDIRECTIONAL);
10:
11: if (pci_dma_mapping_error(nic->pdev, rx->dma_addr)) {
12: dev_kfree_skb_any(rx->skb);
13: rx->skb = NULL;
14: rx->dma_addr = 0;
15: return -ENOMEM;
16: }
17:
18: /* Link the RFD to end of RFA by linking previous RFD to
19: * this one. We are safe to touch the previous RFD because
20: * it is protected by the before last buffer's el bit being set */
21: if (rx->prev->skb) {
22: struct rfd *prev_rfd = (struct rfd *)rx->prev->skb->data;
23: put_unaligned_le32(rx->dma_addr, &prev_rfd->link);
24: pci_dma_sync_single_for_device(nic->pdev, rx->prev->dma_addr,
25: sizeof(struct rfd), PCI_DMA_BIDIRECTIONAL);
26: }
27:
28: return 0;
29: }
给收包过程分配skb,这个过程主要完成skb的分配工作,如果rx队列没有skb,则新分配一个,否则吧状态同步一下,然后直接使用就的skb,用于提高效率。分配好的skb要做pci_map动作,就是把内存挂在网卡的DMA通道,等有中断发生,内存就是网络数据包了,校验的动作在后面会做。
1: static int e100_rx_indicate(struct nic *nic, struct rx *rx,
2: unsigned int *work_done, unsigned int work_to_do)
3: {
4: struct net_device *dev = nic->netdev;
5: struct sk_buff *skb = rx->skb;
6: struct rfd *rfd = (struct rfd *)skb->data;
7: u16 rfd_status, actual_size;
8:
9: if (unlikely(work_done && *work_done >= work_to_do))
10: return -EAGAIN;
11:
12: /* Need to sync before taking a peek at cb_complete bit */
13: pci_dma_sync_single_for_cpu(nic->pdev, rx->dma_addr,
14: sizeof(struct rfd), PCI_DMA_BIDIRECTIONAL);//同步一下状态,也就是skb的前16字节的内存,后面根据rdf_status判断包是否收全了。
15: rfd_status = le16_to_cpu(rfd->status);
16:
17: netif_printk(nic, rx_status, KERN_DEBUG, nic->netdev,
18: "status=0x%04X\n", rfd_status);
19: rmb(); /* read size after status bit */
20:
21: /* If data isn't ready, nothing to indicate */
22: if (unlikely(!(rfd_status & cb_complete))) {
23: /* If the next buffer has the el bit, but we think the receiver
24: * is still running, check to see if it really stopped while
25: * we had interrupts off.
26: * This allows for a fast restart without re-enabling
27: * interrupts */
28: if ((le16_to_cpu(rfd->command) & cb_el) &&
29: (RU_RUNNING == nic->ru_running))
30:
31: if (ioread8(&nic->csr->scb.status) & rus_no_res)
32: nic->ru_running = RU_SUSPENDED;
33: pci_dma_sync_single_for_device(nic->pdev, rx->dma_addr,
34: sizeof(struct rfd),
35: PCI_DMA_FROMDEVICE);
36: return -ENODATA;
37: }
38:
39: /* Get actual data size */
40: actual_size = le16_to_cpu(rfd->actual_size) & 0x3FFF;
41: if (unlikely(actual_size > RFD_BUF_LEN - sizeof(struct rfd)))
42: actual_size = RFD_BUF_LEN - sizeof(struct rfd);
43:
44: /* Get data */
45: pci_unmap_single(nic->pdev, rx->dma_addr,
46: RFD_BUF_LEN, PCI_DMA_BIDIRECTIONAL);//解除DMA映射,这样skb->data可以自由使用了
47:
48: /* If this buffer has the el bit, but we think the receiver
49: * is still running, check to see if it really stopped while
50: * we had interrupts off.
51: * This allows for a fast restart without re-enabling interrupts.
52: * This can happen when the RU sees the size change but also sees
53: * the el bit set. */
54: if ((le16_to_cpu(rfd->command) & cb_el) &&
55: (RU_RUNNING == nic->ru_running)) {
56:
57: if (ioread8(&nic->csr->scb.status) & rus_no_res)
58: nic->ru_running = RU_SUSPENDED;
59: }
60:
61: /* Pull off the RFD and put the actual data (minus eth hdr) */
62: skb_reserve(skb, sizeof(struct rfd));
63: skb_put(skb, actual_size);
64: skb->protocol = eth_type_trans(skb, nic->netdev);
65:
66: if (unlikely(!(rfd_status & cb_ok))) {
67: /* Don't indicate if hardware indicates errors */
68: dev_kfree_skb_any(skb);
69: } else if (actual_size > ETH_DATA_LEN + VLAN_ETH_HLEN) {
70: /* Don't indicate oversized frames */
71: nic->rx_over_length_errors++;
72: dev_kfree_skb_any(skb);
73: } else {
74: dev->stats.rx_packets++;
75: dev->stats.rx_bytes += actual_size;
76: netif_receive_skb(skb);
77: if (work_done)
78: (*work_done)++;
79: }
80:
81: rx->skb = NULL;
82:
83: return 0;
84: }
主要的收包过程,有中断发生后,这个函数把接收的包首先接触PCI_DMA映射,然后纠错,最后要把包送到协议栈。
1: static int e100_poll(struct napi_struct *napi, int budget)
2: {
3: struct nic *nic = container_of(napi, struct nic, napi);
4: unsigned int work_done = 0;
5:
6: e100_rx_clean(nic, &work_done, budget);
7: e100_tx_clean(nic);
8:
9: /* If budget not fully consumed, exit the polling mode */
10: if (work_done < budget) {
11: napi_complete(napi);
12: e100_enable_irq(nic);
13: }
14:
15: return work_done;
16: }