刨根问底-struts-返回结果result详解
刨根问底-strtus-详解加载struts.xml文件
分析了加载action标签的具体方法,刨根问底-struts-怎么预加载配置的相应的信息
分析了加载action标签的具体过程。刨根问底-struts-serviceAction()创建并执行action
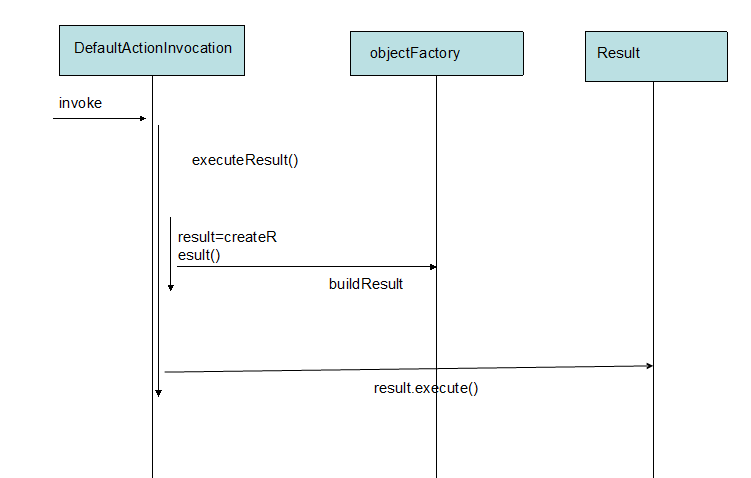
具体分析了创建action,并且执行action,返回结果result,现在在详细的分析 result是怎么执行的?请看流程图:
1、DefaultActionInvocation的invoke()执行了action,并且返回来resultCode,后面调用executeResult()执行结果
回来再看看DefaultActionInvocation中executeResult()方法:
private void executeResult() throws Exception {
result = createResult();
String timerKey = "executeResult: " + getResultCode();
try {
UtilTimerStack.push(timerKey);
if (result != null) {
result.execute(this);
} else if (resultCode != null && !Action.NONE.equals(resultCode)) {
throw new ConfigurationException("No result defined for action " + getAction().getClass().getName()
+ " and result " + getResultCode(), proxy.getConfig());
} else {
if (LOG.isDebugEnabled()) {
LOG.debug("No result returned for action " + getAction().getClass().getName() + " at " + proxy.getConfig().getLocation());
}
}
} finally {
UtilTimerStack.pop(timerKey);
}
} 注释:(1)result = createResult()创建result对象
(2)result.execute(this)执行这个方法
2、createResult()方法:
public Result createResult() throws Exception {
if (explicitResult != null) {
Result ret = explicitResult;
explicitResult = null;
return ret;
}
ActionConfig config = proxy.getConfig();
Map<String, ResultConfig> results = config.getResults();
ResultConfig resultConfig = null;
synchronized (config) {
try {
resultConfig = results.get(resultCode);
} catch (NullPointerException e) {
// swallow
}
if (resultConfig == null) {
// If no result is found for the given resultCode, try to get a wildcard '*' match.
resultConfig = results.get("*");
}
}
if (resultConfig != null) {
try {
return objectFactory.buildResult(resultConfig, invocationContext.getContextMap());
} catch (Exception e) {
LOG.error("There was an exception while instantiating the result of type " + resultConfig.getClassName(), e);
throw new XWorkException(e, resultConfig);
}
} else if (resultCode != null && !Action.NONE.equals(resultCode) && unknownHandlerManager.hasUnknownHandlers()) {
return unknownHandlerManager.handleUnknownResult(invocationContext, proxy.getActionName(), proxy.getConfig(), resultCode);
}
return null;
} 注释:(1)判断explicitResult是否为空,不为空直接返回,前面也解释了
explicitResult值是什么
(2) proxy.getConfig()获取前面相应action的配置对象
(3) config.getResults()获取action标签下面的result标签的配置信息,请看
gaokao-struts2-init_Traditio...加载struts.xml文件
(4)results.get(resultCode)根据action的执行结果resultCode查找相应result的配置
(5)objectFactory.buildResult()根据上面获得result的配置,创建Result对象
3、buildResult代码:
public Result buildResult(ResultConfig resultConfig, Map<String, Object> extraContext) throws Exception {
String resultClassName = resultConfig.getClassName();
Result result = null;
if (resultClassName != null) {
result = (Result) buildBean(resultClassName, extraContext);
Map<String, String> params = resultConfig.getParams();
if (params != null) {
for (Map.Entry<String, String> paramEntry : params.entrySet()) {
try {
reflectionProvider.setProperty(paramEntry.getKey(), paramEntry.getValue(), result, extraContext, true);
} catch (ReflectionException ex) {
if (LOG.isErrorEnabled())
LOG.error("Unable to set parameter [#0] in result of type [#1]", ex,
paramEntry.getKey(), resultConfig.getClassName());
if (result instanceof ReflectionExceptionHandler) {
((ReflectionExceptionHandler) result).handle(ex);
}
}
}
}
}
return result;
} 注释:(1)resultConfig.getClassName()就是result标签属性type对应的实现类。例如:type=
dispatcher实现类就是class="org.apache.struts2.dispatcher.ServletDispatcherResult"
(2)result = (Result) buildBean(resultClassName, extraContext)通过反射机制创建result对象。
4、result 对象已经创建好了,现在就调用result.execute(this)执行方法,现在看看org.apache.struts2.dispatcher.ServletDispatcherResult:
public class ServletDispatcherResult extends StrutsResultSupport {
public ServletDispatcherResult() {
super();
}
public ServletDispatcherResult(String location) {
super(location);
}
public void doExecute(String finalLocation, ActionInvocation invocation) throws Exception {
。。。
}
} 怎么没有
execute方法,有什么猫腻呢?看看他的父类StrutsResultSupport
public abstract class StrutsResultSupport implements Result, StrutsStatics {
public void execute(ActionInvocation invocation) throws Exception {
lastFinalLocation = conditionalParse(location, invocation);
doExecute(lastFinalLocation, invocation);
}
protected abstract void doExecute(String finalLocation, ActionInvocation invocation) throws Exception;
} 原来是这样啊!父类
StrutsResultSupport中实现了
execute()方法,并且在其中调用了抽象方法doExecute(),而自雷子类ServletDispatcherResult就可以实现doExecute()方法,这样利于扩展。