【java开发系列】—— java输入输出流
前言
任何语言输入输出流都是很重要的部分,比如从一个文件读入内容,进行分析,或者输出到另一个文件等等,都需要文件流的操作。这里简单介绍下reader,wirter,inputstream,outputstream的使用方法。其实Apache commons里面有个方法IOUtils可是实现方便快捷的流拷贝,感兴趣的可以参考官方文档。
JAVA的输入输出流有两种,一种是字节流(InPutStream,OutPutStream),一种是字符流(Reader,Writer)。
字节流是普遍适用的,比如我们读取一个视频,音乐,或者文本都可以用这种方式。
字符流只能读取类似文本这种文件。那么它们之间是什么关系呢?看下面这张图吧!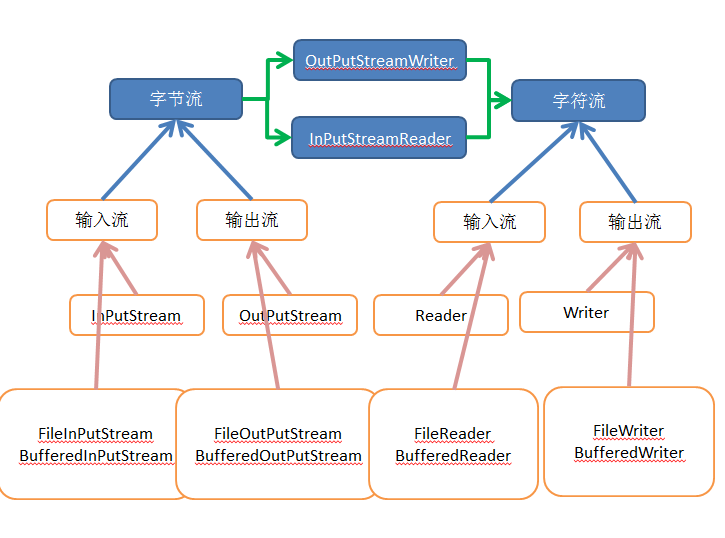
大致可以看到它们之间的关系,我们可以使用InPutStreamReader来实现字节流到字符流的转换。比如
Reader reader = new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream(fileName));
也可以使用OutPutStreamWriter来实现字节流到字符流的转换,如
Writer writer = new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream(filePathName));
下面简单介绍下,文件读取和文件写入的样例!
按行读取文件!
1 /** 2 * 以行为单位读取文件,常用于读面向行的格式化文件 3 * 4 * @paramfileName:文件名 5 */ 6 public static List<String> readFileByLines(String fileName) { 7 List<String> list = new ArrayList<String>(); 8 if (fileName != null && !"".equals(fileName)) { 9 File file = new File(fileName); 10 BufferedReader reader = null; 11 try { 12 System.out.println("以行为单位读取文件内容,一次读一整行:"); 13 reader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(file)); 14 String tempString = null; 15 /* 一次读入一行,直到读入null为文件结束 */ 16 while ((tempString = reader.readLine()) != null) { 17 System.out.println(tempString); 18 list.add(tempString); 19 } 20 } catch (IOException e) { 21 System.out.println("读取文本文件异常" + e); 22 } finally { 23 if (reader != null) { 24 try { 25 reader.close(); 26 } catch (IOException e1) { 27 System.out.println("读取文本文件异常" + e1); 28 } 29 } 30 } 31 } 32 return list; 33 }
向文件中写入内容,直接覆盖掉原来的内容。
1 /** 2 * 把内容写到文件 3 * 4 * @paramfilePathName文件名 5 * @paramList<String>文件内容 6 */ 7 public static boolean writerFile(String filePathName, String content) { 8 boolean flag = false; 9 OutputStreamWriter osw = null; 10 try { 11 if (filePathName != null && !"".equals(filePathName)) { 12 osw = new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream(filePathName)); 13 } 14 } catch (FileNotFoundException e1) { 15 flag = false; 16 e1.printStackTrace(); 17 } 18 if (osw != null) { 19 BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(osw); 20 try { 21 if (content != null && !"".equals(content)) { 22 bw.write(content); 23 flag = true; 24 } 25 } catch (IOException e) { 26 flag = false; 27 e.printStackTrace(); 28 } finally { 29 try { 30 bw.close(); 31 osw.close(); 32 } catch (IOException e) { 33 flag = false; 34 e.printStackTrace(); 35 } 36 } 37 } 38 return flag; 39 }
向文件中追加内容,追加到末尾。
1 /** 2 * 把内容写到文件或追加到文件中 3 * 4 * @paramfilePathName文件名 5 * @paramList<String>文件内容 6 */ 7 public static boolean writerFileIsAppend(String filePathName, String content) { 8 boolean flag = false; 9 OutputStreamWriter osw = null; 10 try { 11 if (filePathName != null && !"".equals(filePathName)) { 12 osw = new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream(filePathName, 13 true)); 14 } 15 } catch (Exception e1) { 16 flag = false; 17 e1.printStackTrace(); 18 } 19 if (osw != null) { 20 BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(osw); 21 try { 22 if (content != null && !"".equals(content)) { 23 bw.write(content); 24 flag = true; 25 } 26 } catch (IOException e) { 27 flag = false; 28 e.printStackTrace(); 29 } finally { 30 try { 31 bw.close(); 32 osw.close(); 33 } catch (IOException e) { 34 flag = false; 35 e.printStackTrace(); 36 } 37 } 38 } 39 return flag; 40 }
全部代码
1 package testIO; 2 3 import java.io.BufferedReader; 4 import java.io.BufferedWriter; 5 import java.io.File; 6 import java.io.FileInputStream; 7 import java.io.FileNotFoundException; 8 import java.io.FileOutputStream; 9 import java.io.FileReader; 10 import java.io.IOException; 11 import java.io.InputStream; 12 import java.io.InputStreamReader; 13 import java.io.OutputStreamWriter; 14 import java.io.Reader; 15 import java.util.ArrayList; 16 import java.util.List; 17 18 public class testIO { 19 public static void main(String[] args) { 20 readFileByBytes("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\新建文本文档.txt"); 21 readFileByChars("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\新建文本文档.txt"); 22 readFileByLines("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\新建文本文档.txt"); 23 writerFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\新建文本文档.txt", 24 "BufferedWriter"); 25 writerFileIsAppend("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\新建文本文档.txt", 26 "Append"); 27 } 28 29 /** 30 * 以字节为单位读取文件,常用于读二进制文件,如图片、声音、影像等文件。 31 * 32 * @paramfileName:文件的名 33 */ 34 public static void readFileByBytes(String fileName) { 35 File file = new File(fileName); 36 InputStream in = null; 37 try { 38 System.out.println("以字节为单位读取文件内容,一次读多个字节:"); 39 /* 一次读多个字节 */ 40 byte[] tempbytes = new byte[100]; 41 int byteread = 0; 42 in = new FileInputStream(file); 43 /* 读入多个字节到字节数组中,byteread为一次读入的字节数 */ 44 while ((byteread = in.read(tempbytes)) != -1) { 45 for (byte b : tempbytes) { 46 System.out.println((char) b); 47 } 48 System.out.println(byteread); 49 } 50 } catch (Exception e1) { 51 System.out.println("读取文本文件异常" + e1); 52 } finally { 53 if (in != null) { 54 try { 55 in.close(); 56 } catch (IOException e1) { 57 System.out.println("读取文本文件异常" + e1); 58 } 59 } 60 } 61 } 62 63 /** 64 * 以字符为单位读取文件,常用于读文本,数字等类型的文件 65 * 66 * @paramfileName:文件名 67 */ 68 public static void readFileByChars(String fileName) { 69 Reader reader = null; 70 try { 71 System.out.println("以字符为单位读取文件内容,一次读多个字节:"); 72 /* 一次读多个字符 */ 73 char[] tempchars = new char[100]; 74 int charread = 0; 75 if (fileName != null && !"".equals(fileName)) { 76 reader = new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream(fileName)); 77 /* 读入多个字符到字符数组中,charread为一次读取字符数 */ 78 while ((charread = reader.read(tempchars)) != -1) { 79 for (char c : tempchars) { 80 System.out.println(c); 81 } 82 } 83 } 84 } catch (Exception e1) { 85 System.out.println("读取文本文件异常" + e1); 86 } finally { 87 if (reader != null) { 88 try { 89 reader.close(); 90 } catch (IOException e1) { 91 System.out.println("读取文本文件异常" + e1); 92 } 93 } 94 } 95 } 96 97 /** 98 * 以行为单位读取文件,常用于读面向行的格式化文件 99 * 100 * @paramfileName:文件名 101 */ 102 public static List<String> readFileByLines(String fileName) { 103 List<String> list = new ArrayList<String>(); 104 if (fileName != null && !"".equals(fileName)) { 105 File file = new File(fileName); 106 BufferedReader reader = null; 107 try { 108 System.out.println("以行为单位读取文件内容,一次读一整行:"); 109 reader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(file)); 110 String tempString = null; 111 /* 一次读入一行,直到读入null为文件结束 */ 112 while ((tempString = reader.readLine()) != null) { 113 System.out.println(tempString); 114 list.add(tempString); 115 } 116 } catch (IOException e) { 117 System.out.println("读取文本文件异常" + e); 118 } finally { 119 if (reader != null) { 120 try { 121 reader.close(); 122 } catch (IOException e1) { 123 System.out.println("读取文本文件异常" + e1); 124 } 125 } 126 } 127 } 128 return list; 129 } 130 131 /** 132 * 把内容写到文件 133 * 134 * @paramfilePathName文件名 135 * @paramList<String>文件内容 136 */ 137 public static boolean writerFile(String filePathName, String content) { 138 boolean flag = false; 139 OutputStreamWriter osw = null; 140 try { 141 if (filePathName != null && !"".equals(filePathName)) { 142 osw = new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream(filePathName)); 143 } 144 } catch (FileNotFoundException e1) { 145 flag = false; 146 e1.printStackTrace(); 147 } 148 if (osw != null) { 149 BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(osw); 150 try { 151 if (content != null && !"".equals(content)) { 152 bw.write(content); 153 flag = true; 154 } 155 } catch (IOException e) { 156 flag = false; 157 e.printStackTrace(); 158 } finally { 159 try { 160 bw.close(); 161 osw.close(); 162 } catch (IOException e) { 163 flag = false; 164 e.printStackTrace(); 165 } 166 } 167 } 168 return flag; 169 } 170 171 /** 172 * 把内容写到文件或追加到文件中 173 * 174 * @paramfilePathName文件名 175 * @paramList<String>文件内容 176 */ 177 public static boolean writerFileIsAppend(String filePathName, String content) { 178 boolean flag = false; 179 OutputStreamWriter osw = null; 180 try { 181 if (filePathName != null && !"".equals(filePathName)) { 182 osw = new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream(filePathName, 183 true)); 184 } 185 } catch (Exception e1) { 186 flag = false; 187 e1.printStackTrace(); 188 } 189 if (osw != null) { 190 BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(osw); 191 try { 192 if (content != null && !"".equals(content)) { 193 bw.write(content); 194 flag = true; 195 } 196 } catch (IOException e) { 197 flag = false; 198 e.printStackTrace(); 199 } finally { 200 try { 201 bw.close(); 202 osw.close(); 203 } catch (IOException e) { 204 flag = false; 205 e.printStackTrace(); 206 } 207 } 208 } 209 return flag; 210 } 211 }
内容参考
http://www.2cto.com/kf/201206/136072.html
http://blog.csdn.net/liuhenghui5201/article/details/8292552