Heartbeat+DRBD+NFS 构建高可用的文件系统
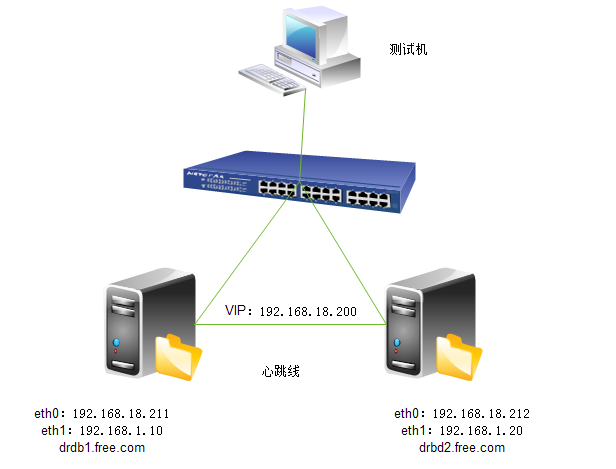
1.实验拓扑图
2.修改主机名
vim /etc/sysconfig/network vim /etc/hosts drbd1.free.com drbd2.free.com
3.同步系统时间
ntp */10 * * * * ntpdate 202.120.2.101
4.修改hosts可互相解析
vim /etc/hosts
5.安装 drbd
rpm -ivh drbd83-8.3.13-2.el5.centos.x86_64.rpm //主文件安装 rpm -ivh kmod-drbd83-8.3.13-1.el5.centos.x86_64.rpm --nodeps //内核文件安装
6.加载内核
modprobe drbd lsmod | grep drdb
7.修改配置文件
vim /etc/drbd.conf //在末行模式下输入如下命令 # # please have a a look at the example configuration file in # /usr/share/doc/drbd83/drbd.conf # # You can find an example in /usr/share/doc/drbd.../drbd.conf.example include "drbd.d/global_common.conf"; include "drbd.d/*.res"; : r /usr/share/doc/drbd83-8.3.13/drbd.conf
8.创建共享空间
fdisk /dev/sdb n --- p 1 --- +10G w partprobe
9.配置全局文件
cd /etc/drbd.d
cp global_common.conf global_common.conf.bak
vim global_common.conf
global {
usage-count no;
# minor-count dialog-refresh disable-ip-verification
}
common {
protocol C;
handlers {
pri-on-incon-degr "/usr/lib/drbd/notify-pri-on-incon-degr.sh; /usr/lib/drbd/notify-emergency-reboot.sh; echo b > /proc/sysrq-trigger ; reboot -f";
pri-lost-after-sb "/usr/lib/drbd/notify-pri-lost-after-sb.sh; /usr/lib/drbd/notify-emergency-reboot.sh; echo b > /proc/sysrq-trigger ; reboot -f";
local-io-error "/usr/lib/drbd/notify-io-error.sh; /usr/lib/drbd/notify-emergency-shutdown.sh; echo o > /proc/sysrq-trigger ; halt -f";
# fence-peer "/usr/lib/drbd/crm-fence-peer.sh";
# split-brain "/usr/lib/drbd/notify-split-brain.sh root";
# out-of-sync "/usr/lib/drbd/notify-out-of-sync.sh root";
# before-resync-target "/usr/lib/drbd/snapshot-resync-target-lvm.sh -p 15 -- -c 16k";
# after-resync-target /usr/lib/drbd/unsnapshot-resync-target-lvm.sh;
}
startup {
# wfc-timeout degr-wfc-timeout outdated-wfc-timeout wait-after-sb
wfc-timeout 120;
degr-wfc-timeout 120;
}
disk {
# on-io-error fencing use-bmbv no-disk-barrier no-disk-flushes
# no-disk-drain no-md-flushes max-bio-bvecs
on-io-error detach;
fencing resource-only;
}
net {
# sndbuf-size rcvbuf-size timeout connect-int ping-int ping-timeout max-buffers
# max-epoch-size ko-count allow-two-primaries cram-hmac-alg shared-secret
# after-sb-0pri after-sb-1pri after-sb-2pri data-integrity-alg no-tcp-cork
cram-hmac-alg "sha1";
shared-secret "mydrbdlab";
}
syncer {
# rate after al-extents use-rle cpu-mask verify-alg csums-alg
rate 100M;
}
}
10.定义资源
cd /etc/drbd.d/
vim web.res
resource web {
on drbd1.free.com {
device /dev/drbd0;
disk /dev/sda6;
address 192.168.18.211:7789;
meta-disk internal;
}
on drbd2.free.com {
device /dev/drbd0;
disk /dev/sda6;
address 192.168.18.212:7789;
meta-disk internal;
}
}
11.drbd1与drbd2上初始化资源Web
drbdadm create-md web
12.启动drbd服务
service drbd start
13.查看节点
drbd-overview
14.将drbd1调整为主节点
drbdadm -- --overwrite-data-of-peer primary web drbd-overview
15.在主节点上创建文件系统
mkfs.ext3 -L drbdweb /dev/drbd0
16.在主节点上创建挂载点,挂载后,写入一个文件
mkdir /mnt/drbd mount /dev/debd0 /mnt/drbd cd /mnt/drbd vim index.html
17.将drbd1.free.com配置成从节点,将drbd2.free.com配置成主节点
节点一
[root@drbd1 drbd]# cd [root@drbd1 ~]# [root@drbd1 ~]# umount /mnt/drbd [root@drbd1 ~]# drbdadm secondary web [root@drbd1 ~]# drbdadm role web Secondary/Primary
节点二
[root@drbd2 ~]# drbdadm primary web [root@drbd2 ~]# drbd-overview 0:web Connected Primary/Secondary UpToDate/UpToDate C r----
在节点二挂载,查看是否有内容
[root@drbd2 ~]# mkdir /mnt/drbd [root@drbd2 ~]# mount /dev/drbd0 /mnt/drbd [root@drbd2 ~]# ll /mnt/drbd/ total 16 -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Jan 20 18:09 index.html //可以看到已经写入成功 drwx------ 2 root root 16384 Jan 20 18:07 lost+found
注: 测试成功
18.安装Heartbeat
yum install heartbeat*
拷贝配置文件到/etc/ha.d/目录中
cd /usr/share/doc/heartbeat-2.1.3/ cp ha.cf haresources authkeys /etc/ha.d/
19.配置结点
1
2
cd /etc/ha.d/
vim ha.cf
#
#There are lots of options in this file. All you have to have is a set
#of nodes listed {"node ...} one of {serial, bcast, mcast, or ucast},
#and a value for "auto_failback".
#
#ATTENTION: As the configuration file is read line by line,
# THE ORDER OF DIRECTIVE MATTERS!
#
#In particular, make sure that the udpport, serial baud rate
#etc. are set before the heartbeat media are defined!
#debug and log file directives go into effect when they
#are encountered.
#
#All will be fine if you keep them ordered as in this example.
#
#
# Note on logging:
# If any of debugfile, logfile and logfacility are defined then they
# will be used. If debugfile and/or logfile are not defined and
# logfacility is defined then the respective logging and debug
# messages will be loged to syslog. If logfacility is not defined
# then debugfile and logfile will be used to log messges. If
# logfacility is not defined and debugfile and/or logfile are not
# defined then defaults will be used for debugfile and logfile as
# required and messages will be sent there.
#
#File to write debug messages to
#debugfile /var/log/ha-debug
#
#
# File to write other messages to
#
#logfile/var/log/ha-log
#
#
#Facility to use for syslog()/logger
#
logfacilitylocal0
#
#
#A note on specifying "how long" times below...
#
#The default time unit is seconds
#10 means ten seconds
#
#You can also specify them in milliseconds
#1500ms means 1.5 seconds
#
#
#keepalive: how long between heartbeats?
#
#keepalive 2
#
#deadtime: how long-to-declare-host-dead?
#
#If you set this too low you will get the problematic
#split-brain (or cluster partition) problem.
#See the FAQ for how to use warntime to tune deadtime.
#
#deadtime 30
#
#warntime: how long before issuing "late heartbeat" warning?
#See the FAQ for how to use warntime to tune deadtime.
#
#warntime 10
#
#
#Very first dead time (initdead)
#
#On some machines/OSes, etc. the network takes a while to come up
#and start working right after you've been rebooted. As a result
#we have a separate dead time for when things first come up.
#It should be at least twice the normal dead time.
#
#initdead 120
#
#
#What UDP port to use for bcast/ucast communication?
#
#udpport694
#
#Baud rate for serial ports...
#
#baud19200
#
#serialserialportname ...
#serial/dev/ttyS0# Linux
#serial/dev/cuaa0# FreeBSD
#serial /dev/cuad0 # FreeBSD 6.x
#serial/dev/cua/a# Solaris
#
#
#What interfaces to broadcast heartbeats over?
#
bcasteth1# Linux
#bcasteth1 eth2# Linux
#bcastle0# Solaris
#bcastle1 le2# Solaris
#
#Set up a multicast heartbeat medium
#mcast [dev] [mcast group] [port] [ttl] [loop]
#
#[dev]device to send/rcv heartbeats on
#[mcast group]multicast group to join (class D multicast address
#224.0.0.0 - 239.255.255.255)
#[port]udp port to sendto/rcvfrom (set this value to the
#same value as "udpport" above)
#[ttl]the ttl value for outbound heartbeats. this effects
#how far the multicast packet will propagate. (0-255)
#Must be greater than zero.
#[loop]toggles loopback for outbound multicast heartbeats.
#if enabled, an outbound packet will be looped back and
#received by the interface it was sent on. (0 or 1)
#Set this value to zero.
#
#
#mcast eth0 225.0.0.1 694 1 0
#
#Set up a unicast / udp heartbeat medium
#ucast [dev] [peer-ip-addr]
#
#[dev]device to send/rcv heartbeats on
#[peer-ip-addr]IP address of peer to send packets to
#
#ucast eth0 192.168.1.2
#
#
#About boolean values...
#
#Any of the following case-insensitive values will work for true:
#true, on, yes, y, 1
#Any of the following case-insensitive values will work for false:
#false, off, no, n, 0
#
#
#
#auto_failback: determines whether a resource will
#automatically fail back to its "primary" node, or remain
#on whatever node is serving it until that node fails, or
#an administrator intervenes.
#
#The possible values for auto_failback are:
#on- enable automatic failbacks
#off- disable automatic failbacks
#legacy- enable automatic failbacks in systems
#where all nodes do not yet support
#the auto_failback option.
#
#auto_failback "on" and "off" are backwards compatible with the old
#"nice_failback on" setting.
#
#See the FAQ for information on how to convert
#from "legacy" to "on" without a flash cut.
#(i.e., using a "rolling upgrade" process)
#
#The default value for auto_failback is "legacy", which
#will issue a warning at startup. So, make sure you put
#an auto_failback directive in your ha.cf file.
#(note: auto_failback can be any boolean or "legacy")
#
auto_failback on
#
#
# Basic STONITH support
# Using this directive assumes that there is one stonith
# device in the cluster. Parameters to this device are
# read from a configuration file. The format of this line is:
#
# stonith <stonith_type> <configfile>
#
# NOTE: it is up to you to maintain this file on each node in the
# cluster!
#
#stonith baytech /etc/ha.d/conf/stonith.baytech
#
# STONITH support
# You can configure multiple stonith devices using this directive.
# The format of the line is:
# stonith_host <hostfrom> <stonith_type> <params...>
# <hostfrom> is the machine the stonith device is attached
# to or * to mean it is accessible from any host.
# <stonith_type> is the type of stonith device (a list of
# supported drives is in /usr/lib/stonith.)
# <params...> are driver specific parameters. To see the
# format for a particular device, run:
# stonith -l -t <stonith_type>
#
#
#Note that if you put your stonith device access information in
#here, and you make this file publically readable, you're asking
#for a denial of service attack ;-)
#
#To get a list of supported stonith devices, run
#stonith -L
#For detailed information on which stonith devices are supported
#and their detailed configuration options, run this command:
#stonith -h
#
#stonith_host * baytech 10.0.0.3 mylogin mysecretpassword
#stonith_host ken3 rps10 /dev/ttyS1 kathy 0
#stonith_host kathy rps10 /dev/ttyS1 ken3 0
#
#Watchdog is the watchdog timer. If our own heart doesn't beat for
#a minute, then our machine will reboot.
#NOTE: If you are using the software watchdog, you very likely
#wish to load the module with the parameter "nowayout=0" or
#compile it without CONFIG_WATCHDOG_NOWAYOUT set. Otherwise even
#an orderly shutdown of heartbeat will trigger a reboot, which is
#very likely NOT what you want.
#
#watchdog /dev/watchdog
#
#Tell what machines are in the cluster
#nodenodename ...-- must match uname -n
#nodeken3
#nodekathy
nodedrbd1.free.com
nodedrbd2.free.com
#
#Less common options...
#
#Treats 10.10.10.254 as a psuedo-cluster-member
#Used together with ipfail below...
#note: don't use a cluster node as ping node
#
#ping 10.10.10.254
#
#Treats 10.10.10.254 and 10.10.10.253 as a psuedo-cluster-member
# called group1. If either 10.10.10.254 or 10.10.10.253 are up
# then group1 is up
#Used together with ipfail below...
#
#ping_group group1 10.10.10.254 10.10.10.253
#
#HBA ping derective for Fiber Channel
#Treats fc-card-name as psudo-cluster-member
#used with ipfail below ...
#
#You can obtain HBAAPI from http://hbaapi.sourceforge.net. You need
#to get the library specific to your HBA directly from the vender
#To install HBAAPI stuff, all You need to do is to compile the common
#part you obtained from the sourceforge. This will produce libHBAAPI.so
#which you need to copy to /usr/lib. You need also copy hbaapi.h to
#/usr/include.
#
#The fc-card-name is the name obtained from the hbaapitest program
#that is part of the hbaapi package. Running hbaapitest will produce
#a verbose output. One of the first line is similar to:
#Apapter number 0 is named: qlogic-qla2200-0
#Here fc-card-name is qlogic-qla2200-0.
#
#hbaping fc-card-name
#
#
#Processes started and stopped with heartbeat. Restarted unless
#they exit with rc=100
#
#respawn userid /path/name/to/run
#respawn hacluster /usr/lib/heartbeat/ipfail
#
#Access control for client api
# default is no access
#
#apiauth client-name gid=gidlist uid=uidlist
#apiauth ipfail gid=haclient uid=hacluster
###########################
#
#Unusual options.
#
###########################
#
#hopfudge maximum hop count minus number of nodes in config
#hopfudge 1
#
#deadping - dead time for ping nodes
#deadping 30
#
#hbgenmethod - Heartbeat generation number creation method
#Normally these are stored on disk and incremented as needed.
#hbgenmethod time
#
#realtime - enable/disable realtime execution (high priority, etc.)
#defaults to on
#realtime off
#
#debug - set debug level
#defaults to zero
#debug 1
#
#API Authentication - replaces the fifo-permissions-based system of the past
#
#
#You can put a uid list and/or a gid list.
#If you put both, then a process is authorized if it qualifies under either
#the uid list, or under the gid list.
#
#The groupname "default" has special meaning. If it is specified, then
#this will be used for authorizing groupless clients, and any client groups
#not otherwise specified.
#
#There is a subtle exception to this. "default" will never be used in the
#following cases (actual default auth directives noted in brackets)
# ipfail (uid=HA_CCMUSER)
# ccm (uid=HA_CCMUSER)
# ping(gid=HA_APIGROUP)
# cl_status(gid=HA_APIGROUP)
#
#This is done to avoid creating a gaping security hole and matches the most
#likely desired configuration.
#
#apiauth ipfail uid=hacluster
#apiauth ccm uid=hacluster
#apiauth cms uid=hacluster
#apiauth ping gid=haclient uid=alanr,root
#apiauth default gid=haclient
# message format in the wire, it can be classic or netstring,
#default: classic
#msgfmt classic/netstring
#Do we use logging daemon?
#If logging daemon is used, logfile/debugfile/logfacility in this file
#are not meaningful any longer. You should check the config file for logging
#daemon (the default is /etc/logd.cf)
#more infomartion can be fould in http://www.linux-ha.org/ha_2ecf_2fUseLogdDirective
#Setting use_logd to "yes" is recommended
#
# use_logd yes/no
#
#the interval we reconnect to logging daemon if the previous connection failed
#default: 60 seconds
#conn_logd_time 60
#
#
#Configure compression module
#It could be zlib or bz2, depending on whether u have the corresponding
#libraryin the system.
#compressionbz2
#
#Confiugre compression threshold
#This value determines the threshold to compress a message,
#e.g. if the threshold is 1, then any message with size greater than 1 KB
#will be compressed, the default is 2 (KB)
#compression_threshold 2
20.配置认证文件authkeys
dd if=/dev/random bs=512 count=1 | openssl md5 vim authkeys //两边节点要一致 drbd1 drbd2 auth 3 3 md5 7eadaabaa7891f4f327918df9af10fc3 chmod 600 authkeys
21.手工创建文件killnfsd
vim resource.d/killnfsd killall -9 nfsd; /etc/init.d/nfs restart; exit 0 chmod 755 resource.d/killnfsd
22.配置加载虚拟IP文件
vim haresources drbd1.free.com IPaddr::192.168.18.200/24/eth0 drbddisk::webFilesystem::/dev/drbd0::/mnt/drbd::ext3 killnfsd
23.配置NFS服务共享
编写共享
vim /etc/exports /mnt/drbd 192.168.18.0/24(ro)
导出共享清单
vim /etc/exports /mnt/drbd 192.168.18.0/24(ro)
修改nfs启动脚本
vim /etc/init.d/nfs 122行 killproc nfsd -9
启动nfs与heartbeat服务
service nfs start service heartbeat start
24.测试
mkdir /mnt/drbd mount 192.168.18.200:/mnt/drbd /mnt/drbd/ mount
主节点破坏掉,再检查情况
service heartbeat stop service drbd status
25.最后将所有服务加入开机自启动
chkconfig nfs on chkconfig drbd on chkconfig heartbeat on