Android应用程序启动过程源代码分析
http://blog.csdn.net/luoshengyang/article/details/6689748
Android应用程序启动过程源代码分析
前文简要介绍了Android应用程序的Activity的启动过程。在Android系统中,应用程序是由Activity组成的,因此,应用程序的启动过程实际上就是应用程序中的默认Activity的启动过程,本文将详细分析应用程序框架层的源代码,了解Android应用程序的启动过程。
在上一篇文章Android应用程序的Activity启动过程简要介绍和学习计划中,我们举例子说明了启动Android应用程序中的Activity的两种情景,其中,在手机屏幕中点击应用程序图标的情景就会引发Android应用程序中的默认Activity的启动,从而把应用程序启动起来。这种启动方式的特点是会启动一个新的进程来加载相应的Activity。这里,我们继续以这个例子为例来说明Android应用程序的启动过程,即MainActivity的启动过程。
MainActivity的启动过程如下图所示:
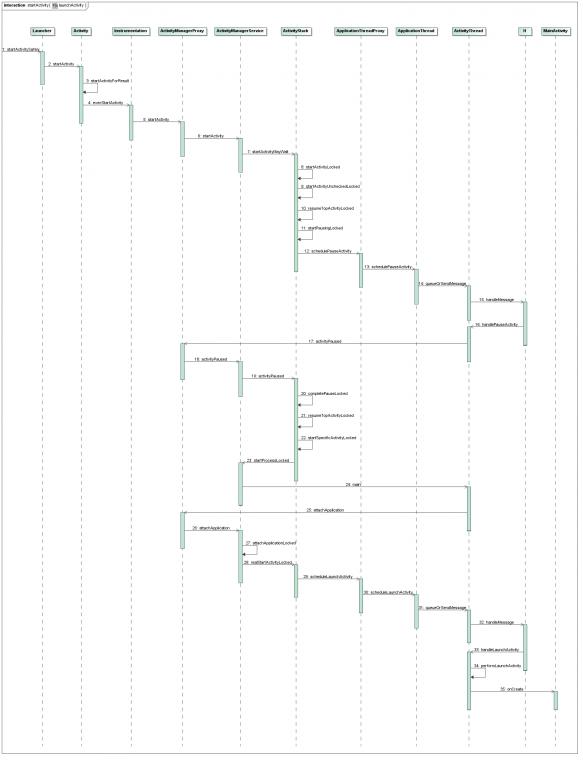
点击查看大图
下面详细分析每一步是如何实现的。
Step 1. Launcher.startActivitySafely
在Android系统中,应用程序是由Launcher启动起来的,其实,Launcher本身也是一个应用程序,其它的应用程序安装后,就会Launcher的界面上出现一个相应的图标,点击这个图标时,Launcher就会对应的应用程序启动起来。
Launcher的源代码工程在packages/apps/Launcher2目录下,负责启动其它应用程序的源代码实现在src/com/android/launcher2/Launcher.java文件中:
/**
* Default launcher application.
*/
publicfinalclass Launcher extends Activity
implements View.OnClickListener, OnLongClickListener, LauncherModel.Callbacks, AllAppsView.Watcher {
......
/**
* Launches the intent referred by the clicked shortcut.
*
* @param v The view representing the clicked shortcut.
*/
publicvoid onClick(View v) {
Object tag = v.getTag();
if (tag instanceof ShortcutInfo) {
// Open shortcut
final Intent intent = ((ShortcutInfo) tag).intent;
int[] pos = newint[2];
v.getLocationOnScreen(pos);
intent.setSourceBounds(new Rect(pos[0], pos[1],
pos[0] + v.getWidth(), pos[1] + v.getHeight()));
startActivitySafely(intent, tag);
} elseif (tag instanceof FolderInfo) {
......
} elseif (v == mHandleView) {
......
}
}
void startActivitySafely(Intent intent, Object tag) {
intent.addFlags(Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_TASK);
try {
startActivity(intent);
} catch (ActivityNotFoundException e) {
......
} catch (SecurityException e) {
......
}
}
......
}
/**
* Default launcher application.
*/
public final class Launcher extends Activity
implements View.OnClickListener, OnLongClickListener, LauncherModel.Callbacks, AllAppsView.Watcher {
......
/**
* Launches the intent referred by the clicked shortcut.
*
* @param v The view representing the clicked shortcut.
*/
public void onClick(View v) {
Object tag = v.getTag();
if (tag instanceof ShortcutInfo) {
// Open shortcut
final Intent intent = ((ShortcutInfo) tag).intent;
int[] pos = new int[2];
v.getLocationOnScreen(pos);
intent.setSourceBounds(new Rect(pos[0], pos[1],
pos[0] + v.getWidth(), pos[1] + v.getHeight()));
startActivitySafely(intent, tag);
} else if (tag instanceof FolderInfo) {
......
} else if (v == mHandleView) {
......
}
}
void startActivitySafely(Intent intent, Object tag) {
intent.addFlags(Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_TASK);
try {
startActivity(intent);
} catch (ActivityNotFoundException e) {
......
} catch (SecurityException e) {
......
}
}
......
} 回忆一下前面一篇文章 Android应用程序的Activity启动过程简要介绍和学习计划说到的应用程序Activity,它的默认Activity是MainActivity,这里是AndroidManifest.xml文件中配置的:
<activityandroid:name=".MainActivity"
android:label="@string/app_name">
<intent-filter>
<actionandroid:name="android.intent.action.MAIN"/>
<categoryandroid:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER"/>
</intent-filter>
</activity>
<activity android:name=".MainActivity"
android:label="@string/app_name">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" />
</intent-filter>
</activity> 因此,这里的intent包含的信息为:action = "android.intent.action.Main",category="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER", cmp="shy.luo.activity/.MainActivity",表示它要启动的Activity为shy.luo.activity.MainActivity。Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_TASK表示要在一个新的Task中启动这个Activity,注意,Task是Android系统中的概念,它不同于进程Process的概念。简单地说,一个Task是一系列Activity的集合,这个集合是以堆栈的形式来组织的,遵循后进先出的原则。事实上,Task是一个非常复杂的概念,有兴趣的读者可以到官网 http://developer.android.com/guide/topics/manifest/activity-element.html查看相关的资料。这里,我们只要知道,这个MainActivity要在一个新的Task中启动就可以了。
Step 2. Activity.startActivity
在Step 1中,我们看到,Launcher继承于Activity类,而Activity类实现了startActivity函数,因此,这里就调用了Activity.startActivity函数,它实现在frameworks/base/core/java/android/app/Activity.java文件中:
publicclass Activity extends ContextThemeWrapper
implements LayoutInflater.Factory,
Window.Callback, KeyEvent.Callback,
OnCreateContextMenuListener, ComponentCallbacks {
......
@Override
publicvoid startActivity(Intent intent) {
startActivityForResult(intent, -1);
}
......
}
public class Activity extends ContextThemeWrapper
implements LayoutInflater.Factory,
Window.Callback, KeyEvent.Callback,
OnCreateContextMenuListener, ComponentCallbacks {
......
@Override
public void startActivity(Intent intent) {
startActivityForResult(intent, -1);
}
......
} 这个函数实现很简单,它调用startActivityForResult来进一步处理,第二个参数传入-1表示不需要这个Actvity结束后的返回结果。
Step 3. Activity.startActivityForResult
这个函数也是实现在frameworks/base/core/java/android/app/Activity.java文件中:
publicclass Activity extends ContextThemeWrapper
implements LayoutInflater.Factory,
Window.Callback, KeyEvent.Callback,
OnCreateContextMenuListener, ComponentCallbacks {
......
publicvoid startActivityForResult(Intent intent, int requestCode) {
if (mParent == null) {
Instrumentation.ActivityResult ar =
mInstrumentation.execStartActivity(
this, mMainThread.getApplicationThread(), mToken, this,
intent, requestCode);
......
} else {
......
}
......
}
public class Activity extends ContextThemeWrapper
implements LayoutInflater.Factory,
Window.Callback, KeyEvent.Callback,
OnCreateContextMenuListener, ComponentCallbacks {
......
public void startActivityForResult(Intent intent, int requestCode) {
if (mParent == null) {
Instrumentation.ActivityResult ar =
mInstrumentation.execStartActivity(
this, mMainThread.getApplicationThread(), mToken, this,
intent, requestCode);
......
} else {
......
}
......
} 这里的mInstrumentation是Activity类的成员变量,它的类型是Intrumentation,定义在frameworks/base/core/java/android/app/Instrumentation.java文件中,它用来监控应用程序和系统的交互。
这里的mMainThread也是Activity类的成员变量,它的类型是ActivityThread,它代表的是应用程序的主线程,我们在Android系统在新进程中启动自定义服务过程(startService)的原理分析一文中已经介绍过了。这里通过mMainThread.getApplicationThread获得它里面的ApplicationThread成员变量,它是一个Binder对象,后面我们会看到,ActivityManagerService会使用它来和ActivityThread来进行进程间通信。这里我们需注意的是,这里的mMainThread代表的是Launcher应用程序运行的进程。
这里的mToken也是Activity类的成员变量,它是一个Binder对象的远程接口。
Step 4. Instrumentation.execStartActivity
这个函数定义在frameworks/base/core/java/android/app/Instrumentation.java文件中:
publicclass Instrumentation {
......
public ActivityResult execStartActivity(
Context who, IBinder contextThread, IBinder token, Activity target,
Intent intent, int requestCode) {
IApplicationThread whoThread = (IApplicationThread) contextThread;
if (mActivityMonitors != null) {
......
}
try {
int result = ActivityManagerNative.getDefault()
.startActivity(whoThread, intent,
intent.resolveTypeIfNeeded(who.getContentResolver()),
null, 0, token, target != null ? target.mEmbeddedID : null,
requestCode, false, false);
......
} catch (RemoteException e) {
}
returnnull;
}
......
}
public class Instrumentation {
......
public ActivityResult execStartActivity(
Context who, IBinder contextThread, IBinder token, Activity target,
Intent intent, int requestCode) {
IApplicationThread whoThread = (IApplicationThread) contextThread;
if (mActivityMonitors != null) {
......
}
try {
int result = ActivityManagerNative.getDefault()
.startActivity(whoThread, intent,
intent.resolveTypeIfNeeded(who.getContentResolver()),
null, 0, token, target != null ? target.mEmbeddedID : null,
requestCode, false, false);
......
} catch (RemoteException e) {
}
return null;
}
......
} 这里的ActivityManagerNative.getDefault返回ActivityManagerService的远程接口,即ActivityManagerProxy接口,具体可以参考 Android系统在新进程中启动自定义服务过程(startService)的原理分析一文。
这里的intent.resolveTypeIfNeeded返回这个intent的MIME类型,在这个例子中,没有AndroidManifest.xml设置MainActivity的MIME类型,因此,这里返回null。
这里的target不为null,但是target.mEmbddedID为null,我们不用关注。
Step 5. ActivityManagerProxy.startActivity
这个函数定义在frameworks/base/core/java/android/app/ActivityManagerNative.java文件中:
class ActivityManagerProxy implements IActivityManager
{
......
publicint startActivity(IApplicationThread caller, Intent intent,
String resolvedType, Uri[] grantedUriPermissions, int grantedMode,
IBinder resultTo, String resultWho,
int requestCode, boolean onlyIfNeeded,
boolean debug) throws RemoteException {
Parcel data = Parcel.obtain();
Parcel reply = Parcel.obtain();
data.writeInterfaceToken(IActivityManager.descriptor);
data.writeStrongBinder(caller != null ? caller.asBinder() : null);
intent.writeToParcel(data, 0);
data.writeString(resolvedType);
data.writeTypedArray(grantedUriPermissions, 0);
data.writeInt(grantedMode);
data.writeStrongBinder(resultTo);
data.writeString(resultWho);
data.writeInt(requestCode);
data.writeInt(onlyIfNeeded ? 1 : 0);
data.writeInt(debug ? 1 : 0);
mRemote.transact(START_ACTIVITY_TRANSACTION, data, reply, 0);
reply.readException();
int result = reply.readInt();
reply.recycle();
data.recycle();
return result;
}
......
}
class ActivityManagerProxy implements IActivityManager
{
......
public int startActivity(IApplicationThread caller, Intent intent,
String resolvedType, Uri[] grantedUriPermissions, int grantedMode,
IBinder resultTo, String resultWho,
int requestCode, boolean onlyIfNeeded,
boolean debug) throws RemoteException {
Parcel data = Parcel.obtain();
Parcel reply = Parcel.obtain();
data.writeInterfaceToken(IActivityManager.descriptor);
data.writeStrongBinder(caller != null ? caller.asBinder() : null);
intent.writeToParcel(data, 0);
data.writeString(resolvedType);
data.writeTypedArray(grantedUriPermissions, 0);
data.writeInt(grantedMode);
data.writeStrongBinder(resultTo);
data.writeString(resultWho);
data.writeInt(requestCode);
data.writeInt(onlyIfNeeded ? 1 : 0);
data.writeInt(debug ? 1 : 0);
mRemote.transact(START_ACTIVITY_TRANSACTION, data, reply, 0);
reply.readException();
int result = reply.readInt();
reply.recycle();
data.recycle();
return result;
}
......
} 这里的参数比较多,我们先整理一下。从上面的调用可以知道,这里的参数resolvedType、grantedUriPermissions和resultWho均为null;参数caller为ApplicationThread类型的Binder实体;参数resultTo为一个Binder实体的远程接口,我们先不关注它;参数grantedMode为0,我们也先不关注它;参数requestCode为-1;参数onlyIfNeeded和debug均空false。
Step 6. ActivityManagerService.startActivity
上一步Step 5通过Binder驱动程序就进入到ActivityManagerService的startActivity函数来了,它定义在frameworks/base/services/java/com/android/server/am/ActivityManagerService.java文件中:
publicfinalclass ActivityManagerService extends ActivityManagerNative
implements Watchdog.Monitor, BatteryStatsImpl.BatteryCallback {
......
publicfinalint startActivity(IApplicationThread caller,
Intent intent, String resolvedType, Uri[] grantedUriPermissions,
int grantedMode, IBinder resultTo,
String resultWho, int requestCode, boolean onlyIfNeeded,
boolean debug) {
return mMainStack.startActivityMayWait(caller, intent, resolvedType,
grantedUriPermissions, grantedMode, resultTo, resultWho,
requestCode, onlyIfNeeded, debug, null, null);
}
......
}
public final class ActivityManagerService extends ActivityManagerNative
implements Watchdog.Monitor, BatteryStatsImpl.BatteryCallback {
......
public final int startActivity(IApplicationThread caller,
Intent intent, String resolvedType, Uri[] grantedUriPermissions,
int grantedMode, IBinder resultTo,
String resultWho, int requestCode, boolean onlyIfNeeded,
boolean debug) {
return mMainStack.startActivityMayWait(caller, intent, resolvedType,
grantedUriPermissions, grantedMode, resultTo, resultWho,
requestCode, onlyIfNeeded, debug, null, null);
}
......
}