Linux运维常用知识(3)
Apache日志统计举例
参考:http://loveyan.blog.51cto.com/829079/745164
http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_79bc8e830101m84w.html
http://www.ttlsa.com/linux/site-troubleshooting-common-commands/
http://www.haiyun.me/archives/nginx-log.html
(1)查看IP($1代表IP)
#cat access_log | awk '{print $1}'
(2)对IP排序
#cat access_log | awk '{print $1}'| sort
(3)打印每一重复行出现的次数,“uniq -c”表示标记出重复数量。
#cat access_log | awk '{print $1}'|sort| uniq -c
(4)排序并统计行数
#cat access_log | awk '{print $1}'|sort|uniq -c|sort -rn | wc -l
(5)显示访问前10位的IP地址,便于查找攻击源
#cat access_log|awk '{print $1}'|sort|uniq-c|sort -nr| head -10
注意awk '{print$1',它表示取日志的第一段,如果换成别的日志,其IP地址在第3段那么就要改变相应数值。
(6)显示指定时间以后的日志($4代表时间)
#cat access_log |awk'$4>="[23/Jul/2012:01:00:01"' access_log
(7)找出访问量最大的IP,并封掉(对排错很有帮助)
#cat access_log |awk '{print $1}'|sort|uniq -c|sort -nr | more
9999192.168.150.179
11 192.168.150.1
#iptables -I INPUT -s 192.168.150.179 -j DROP
#iptables -I INPUT -s 192.168.150.0/24 -j DROP
如果将上面的Shell做以下变形就可以得出访问量TOP 10
#cat access_log |awk '{print $1}'|sort|uniq -c|sort -nr | head -10
(8)找出Apache日志中,下载最多的几个exe文件(下载类网站常用,这里以.exe扩展名举例)
# cat access_log |awk '($7 ~/.exe/){print "$10 "" $1 ""$4""$7}' |sort -n |uniq -c |sort -nr |head -10
2 - 192.168.150.1[25/Jul/2012:05:46:05/test.exe
1 -192.168.150.152[25/Jul/2012:05:46:47/test.exe
使用如下命令:
#cat access_log |awk `($10 >10000000&& $7 ~/.exe/) {print $7}` |sort �Cn|uniq �Cc|sort �Cnr|head -10
这条命令经过增加一个>10000000的条件判断内容就可以显示出大于10MB的exe文件,并统计对应文件发生次数,这条命令对于网站日常分析是非常有帮助的,大家可以灵活使用。
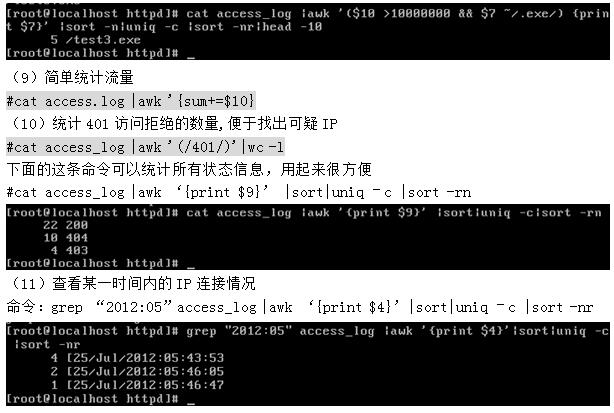
(12)把IP数量输出到文本显示:cat access_log_2011_06_26.log |awk '{print $1}'|uniq -c|wc -l > ip.txt
(13)查看 access.Log 文件ip统计(从高到低)
cat access.log |awk '{print $3}'|sort|uniq -c|sort -rn| wc -l
(14)查看Apache的并发请求数及其TCP连接状态
netstat -n | awk '/^tcp/ {++S[$NF]} END {for(a in S) print a, S[a]}'
返回结果示例:
LAST_ACK 5
SYN_RECV 30
ESTABLISHED 1597
FIN_WAIT1 51
FIN_WAIT2 504
TIME_WAIT 1057
其中的SYN_RECV表示正在等待处理的请求数;ESTABLISHED表示正常数据传输状态;TIME_WAIT表示处理完毕,等待超时结束的请求数。
linux下创建镜像文件
如果没有mkisofs命令,需要安装yum install -y mkisofs
[root@localhost ~]# mkdir test [root@localhost ~]# mkisofs -o test.iso test //创建镜像文件 I: -input-charset not specified, using utf-8 (detected in locale settings) Total translation table size: 0 Total rockridge attributes bytes: 0 Total directory bytes: 0 Path table size(bytes): 10 Max brk space used 0 174 extents written (0 MB) [root@localhost ~]# ls anaconda-ks.cfg install.log install.log.syslog test test.iso [root@localhost ~]# mkdir /jingxiang [root@localhost ~]# mount -o loop test.iso /jingxiang //挂载镜像文件
linux 使用shell脚本导出网络配置信息
#!/bin/bash
#此脚本是获取计算机当前的网络配置信息
#注意下面的'eth0'需要根据个人的网络适配器名称来进行修改
#1、获取ip地址
echo "获取当前的ip地址是:"
#第一种方法
ifconfig eth0 |grep "inet addr:" |sed 's/.*addr://g'|sed 's/Bcast.*$//g'
#第二种方法
#ifconfig eth0 |grep "inet addr:" |sed 's/.*addr://g' |awk '{print $1}'
#2、获取子网掩码
echo "获取当前的子网掩码:"
ifconfig eth0 |grep "inet addr" |awk 'BEGIN{FS=":"}{print $4}'
#3、获取网关
echo "获取当前的网关:"
route -n |grep "UG" |awk '{print $2}'
#4、获取DNS
echo "获取当计算机的DNS地址:"
cat /etc/resolv.conf |grep "nameserver"|awk '{print $2}'
#5、获取MAC地址
echo "获取当前适配器的MAC地址:"
ifconfig |grep "^eth0" |awk '{print $5}'
Linux下网站备份脚本
#!/bin/bash
#backup database
mypw=CactiEZ
newtime=$(date +%Y%m%d)
if [ -d /var/www/backup/ ];then
mysqldump -u root -p$mypw DB > /var/www/backup/$newtime-Database.sql
else
mkdir /var/www/backup/
mysqldump -u root -p$mypw DB > /var/www/backup/$newtime-Database.sql
fi
tar -zcvf /var/www/backup/$newtime-www.tar.gz /var/www/
find /var/www/backup/ -mtime +4 -exec rm -rf {} \;
Linux下利用nc命令来监控检测服务器的端口使用情况
最近看到一个问题,前端用apache htttpd进行发布(80端口),通过双机负载均衡转发到后端的两个tomcat进行处理(8081和8082端口),现在需要随时监控这三个端口的情况,一旦down掉需要能够立即告警处理。批量的系统监控比较好的是用nagios软件来实现,小项目专门装一个nagios软件,有点繁琐,可以用nc(NetCat)命令来实现。
NetCat 官方地址:http://netcat.sourceforge.net/
参考:http://my.oschina.net/jccpp/blog/123430
http://www.cnblogs.com/wenbiao/p/3375811.html
[root@server ~]# yum install -y nc [root@server ~]# rpm -qa nc nc-1.84-22.el6.x86_64
一、nc命令检测端口的用法
-s<来源地址> 设置本地主机送出数据包的IP地址。
-u 使用UDP传输协议。
-v 显示指令执行过程。
-w<超时秒数> 设置等待连线的时间。
-z 使用0输入/输出模式,只在扫描通信端口时使用。
例1:扫描指定的8080端口
# nc -v -w 10 -z 192.168.0.100 8080
Connection to 192.168.0.100 8080 port [tcp/http] succeeded!
例2:扫描20到25的端口范围,并详细输出。
# nc -v -w 2 -z 192.168.0.100 20-25
例3:扫描1到65535的端口范围,只输出打开的端口(去掉-v参数即可)
# nc -w 1 -z 192.168.0.100 1-65535
二、批量检测服务器指定端口开放情况:
1、假如我们要监控一堆指定的IP和端口,可新建一个文件(第1列服务器IP,第2列要监控的端口)。
# vim /scripts/ip-ports.txt
192.168.0.100 80 192.168.0.100 8081 192.168.0.101 8082 192.168.1.100 21
2、我们可以写这样一个脚本来批量检测端口是否开放:
# vim /scripts/ncports.sh
#!/bin/bash #检测服务器端口是否开放,成功会返回0值显示ok,失败会返回1值显示fail cat /scripts/ip-ports.txt | while read line do nc -w 10 -z $line > /dev/null 2>&1 if [ $? -eq 0 ] then echo $line:ok else echo $line:fail echo "服务器 $line 端口不通,请尽快处理!" | mutt -s "【机房监控】服务器$line端口不通" [email protected] fi done
3、执行脚本查看运行结果如下:
# chmod a+x /scripts/ncports.sh
# /scripts/ncports.sh
192.168.0.100 80:ok
192.168.0.100 8081:ok
192.168.0.101 8082:ok
192.168.1.100 21:fail
三、端口不通时设置邮件告警:
1、 邮件告警:
(1) 先安装linux下面的邮件发送程序mutt
(2) 如果上面的接收邮箱设置为移动139邮箱,并开启接收邮件短信告知,即可实现“短信告警”的功能。
(3) 端口不通时发送邮件
# vim /scripts/ncports.sh
#!/bin/bash #检测服务器端口是否开放,成功会返回0值,打不开会返回1值 cat /scripts/ip-ports.txt | while read line do nc -w 10 -z $line > /dev/null 2>&1 if [ $? -eq 0 ] then echo $line:ok else echo $line:fail echo "服务器 $line 端口不通,请尽快处理!" | mutt -s "【机房监控】服务器$line端口不通" [email protected] fi done
2、加入任务计划每2分钟执行一次
# crontab -e
*/2 * * * * /scripts/ncports.sh > /dev/null 2>&1
# service crond restart
linux 流量监控脚本
vim /root/network-check.sh
#!/bin/bash
# Date
# 2014.03.13
# Author fengxxxx
# Function 实时检查系统的网络流量的大小
function networkdownup(){
local nic=$1
R1=`cat /sys/class/net/$nic/statistics/rx_bytes`
T1=`cat /sys/class/net/$nic/statistics/tx_bytes`
sleep 1
R2=`cat /sys/class/net/$nic/statistics/rx_bytes`
T2=`cat /sys/class/net/$nic/statistics/tx_bytes`
TBPS=`expr $T2 - $T1`
RBPS=`expr $R2 - $R1`
TKBPS=`expr $TBPS / 1024`
RKBPS=`expr $RBPS / 1024`
echo "上传速率 $nic: $TKBPS kb/s 下载速率 $nic: $RKBPS kb/s at $(date +%Y%m%d%H:%M:%S)"
}
# run : 指定运行的检测次数,如果输入的次数为空,测默认检测10次
function run(){
#num count default value = 10
num=${1:-10} ;
local nic=$2 ;
while [ $num -gt 0 ]
do
networkdownup $nic;
num="$((num-1))"
done
}
#检测一下字符是否是数学
# 如是是,就返回1 ;如是不是,就返回0
# use echo to pass retval
function checkInt(){
local foo=$1
if [[ $foo != *[!0-9]* ]]; then
# echo "'$foo' is strictly numeric"
echo 1
else
#echo "'$foo' has a non-digit somewhere in it"
echo 0
fi
}
### use return to pass retval
function checkInt2(){
local foo=$1
if [[ $foo != *[!0-9]* ]]; then
# echo "'$foo' is strictly numeric"
return 1
else
#echo "'$foo' has a non-digit somewhere in it"
return 0
fi
}
####################### shell exec #####################
# method 1
#retval=$(checkInt $1)
# method 2
time=${1:-10}
checkInt2 $time
retval=$?
if [ $retval -eq 0 ] ;then
echo -e "检测的时间为数字(s),比如: sh network.sh [seconds] [nic] \ndefalut is sh network.sh 10 eth0 "
exit 1
fi
nic=${2:-"eth0"}
falg_nic=0
### check the nic is exist ??
for var in `ls /sys/class/net/ -F | grep "@"`
do
[ "$nic" == "${var%@}" ] && nic="${var%@}" && falg_nic=1
done
if [ $falg_nic -eq 1 ];then
run $time $nic
else
echo "Sorry ,$nic don't exist ."
fi
#chmod +x /root/network-check.sh
#/root/network-check.sh 5 eth0
上传速率 eth0: 0 kb/s 下载速率 eth0: 0 kb/s at 2014052818:11:48 上传速率 eth0: 0 kb/s 下载速率 eth0: 0 kb/s at 2014052818:11:49 上传速率 eth0: 0 kb/s 下载速率 eth0: 0 kb/s at 2014052818:11:50 上传速率 eth0: 0 kb/s 下载速率 eth0: 0 kb/s at 2014052818:11:51 上传速率 eth0: 0 kb/s 下载速率 eth0: 0 kb/s at 2014052818:11:52
可以添加到计划任务中
crontab -e
*/30 * * * * /root/network-check.sh > /dev/null 2>&1
start crond start
系统初始化脚本
#!/bin/bash # author: gm100861 # mail: [email protected] # blog: http://www.gm100861.com # date: 2013-06-25 if [ $(id -u) != 0 ];then echo "Must be root can do this." exit 9 fi # set privileges chmod 600 /etc/passwd chmod 600 /etc/shadow chmod 600 /etc/group chmod 600 /etc/gshadow echo "Set important files privileges sucessfully" # yum repo add cat > /etc/yum.repos.d/thrid-repository.repo <<EOF [epel] name=Extra Packages for Enterprise Linux 6 - $basearch baseurl=http://epel.mirror.ucloud.cn/epel/6/$basearch failovermethod=priority enabled=1 gpgcheck=1 gpgkey=file:///etc/pki/rpm-gpg/RPM-GPG-KEY-EPEL-6 [remi] name=Les RPM de remi pour Enterprise Linux $releasever - $basearch baseurl=http://remi.mirror.ucloud.cn enabled=0 gpgcheck=0 gpgkey=file:///etc/pki/rpm-gpg/RPM-GPG-KEY-remi [rpmforge] name = RHEL - RPMforge.net - dag baseurl = http://rpmforge.mirror.ucloud.cn/redhat/el6/en/$basearch/rpmforge enabled = 1 protect = 0 gpgkey = file:///etc/pki/rpm-gpg/RPM-GPG-KEY-rpmforge-dag gpgcheck = 0 [rpmforge-extras] name = RHEL - RPMforge.net - extras baseurl = http://rpmforge.mirror.ucloud.cn/redhat/el6/en/$basearch/extras enabled = 1 protect = 0 gpgkey = file:///etc/pki/rpm-gpg/RPM-GPG-KEY-rpmforge-dag gpgcheck = 0 EOF yum clean all &>/dev/null yum makecache &>/dev/null echo "add thired repository sucessfully" # Turn off unnecessary services service=($(ls /etc/init.d/)) for i in ${service[@]}; do case $i in sshd|network|syslog|iptables|crond) chkconfig $i on;; *) chkconfig $i off;; esac done #set ulimit cat >> /etc/security/limits.conf << EOF * soft nofile 65535 * hard nofile 65535 EOF # set sysctl cat > /etc/sysctl.conf << EOF net.ipv4.ip_forward = 0 net.ipv4.conf.default.rp_filter = 1 net.ipv4.conf.default.accept_source_route = 0 kernel.sysrq = 0 kernel.core_uses_pid = 1 kernel.msgmnb = 65536 kernel.msgmax = 65536 kernel.shmmax = 68719476736 kernel.shmall = 4294967296 net.ipv4.tcp_max_tw_buckets = 6000 net.ipv4.tcp_sack = 1 net.ipv4.tcp_window_scaling = 1 net.ipv4.tcp_rmem = 4096 87380 4194304 net.ipv4.tcp_wmem = 4096 16384 4194304 net.core.wmem_default = 8388608 net.core.rmem_default = 8388608 net.core.rmem_max = 16777216 net.core.wmem_max = 16777216 net.core.netdev_max_backlog = 262144 net.core.somaxconn = 262144 net.ipv4.tcp_max_orphans = 3276800 net.ipv4.tcp_syncookies = 1 net.ipv4.tcp_max_syn_backlog = 262144 net.ipv4.tcp_timestamps = 0 net.ipv4.tcp_synack_retries = 1 net.ipv4.tcp_syn_retries = 1 net.ipv4.tcp_tw_recycle = 1 net.ipv4.tcp_tw_reuse = 1 net.ipv4.tcp_mem = 94500000 915000000 927000000 net.ipv4.tcp_fin_timeout = 1 net.ipv4.tcp_keepalive_time = 1200 net.ipv4.ip_local_port_range = 1024 65535 vm.swappiness = 0 EOF echo "0 0 * * * /usr/sbin/ntpdate cn.pool.ntp.org &>/dev/null" >>/var/spool/cron/root # set iptables iptables -F iptables -X iptables -Z iptables -I INPUT -i lo -j ACCEPT iptables -A INPUT -p tcp --dport 22 -j ACCEPT iptables -A INPUT -p tcp --dport 80 -j ACCEPT iptables -A INPUT -p tcp --dport 443 -j ACCEPT iptables -A INPUT -p icmp --icmp-type 0 -m limit --limit 3/second --limit-burst 5 -j ACCEPT iptables -A INPUT -p icmp --icmp-type 8 -m limit --limit 3/second --limit-burst 5 -j ACCEPT iptables -A INPUT -p udp --sport 53 -j ACCEPT iptables -A INPUT -p tcp --sport 53 -j ACCEPT iptables -P INPUT DROP #iptables -P FORWARD DROP #iptables -P OUTPUT DROP /etc/init.d/iptables save echo "All things is init ok! "
一个防止暴力破解sshd的小脚本
#!/bin/bash
#denyhost ip
cat /var/log/secure|egrep -i -o "[0-9]{1,3}\.[0-9]{1,3}\.[0-9]{1,3}\.[0-9]{1,3}" | sort |uniq -c |sort -n > /root/dropip
ORIGIN="150"
cat /root/dropip | while read LINE
do
host=`echo $LINE|awk '{print $2}'`
num=`echo $LINE |awk '{print $1}'`
if [ $num -gt $ORIGIN ];then
grep $host /etc/hosts.deny &> /dev/null
if [ $? -gt 0 ];then
echo "ALL:$host" >> /etc/hosts.deny
fi
fi
done
linux系统服务rsync启动脚本
http://alanwake.blog.51cto.com/6881848/1421188
http://jishuweiwang.blog.51cto.com/6977090/1421184
关于Linux网卡***能调优之:RPS (Receive Packet Steering)
参考:http://navyaijm.blog.51cto.com/4647068/1334671
现如今服务器的CPU越来越强劲,RPS起初是谷歌为了发挥多CPU系统下网卡***能而给Linux打的补丁。RPS在系统层给网卡模块更多队列,更有效发挥网卡和CPU的协作能力。如今新版Kernel已默认采用了。
在定位LVS调度均衡***问题时,最终确定是 persistence_timeout 参数会使用IP哈希。目的是为了保证长连接,即一定时间内访问到的是同一台机器。但一般内部系统,由于出口IP相对单一,所以总会被哈希到相同的RealServer。
CentOS 6.1就开始支持RPS了
简单来讲,RPS就是让网卡使用多核CPU的。传统方法就是网卡多队列(RSS,需要硬件和驱动支持),RPS则是在系统层实现了分发和均衡。献上修改设置的脚本一例:
1、Broadcom的网卡建议关闭GRO功能
ethtool -K eth0 gro off ethtool -K eth1 gro off
2、关闭irqbalance服务并手动分配网卡中断
service irqbalance stop
chkconfig irqbalance off
# 查看网卡中断号
grep ethx /proc/interrupts
$ grep em1 /proc/interrupts
72: 62922 0 0 0 IR-PCI-MSI-edge em1-0
73: 12024 0 0 0 IR-PCI-MSI-edge em1-1
74: 2470 0 0 0 IR-PCI-MSI-edge em1-2
75: 99071 0 0 0 IR-PCI-MSI-edge em1-3
76: 1350 0 0 0 IR-PCI-MSI-edge em1-4
$ grep em2 /proc/interrupts
77: 8 0 0 0 IR-PCI-MSI-edge em2-0
78: 52607 0 0 0 IR-PCI-MSI-edge em2-1
79: 2471 0 0 0 IR-PCI-MSI-edge em2-2
80: 440 0 0 0 IR-PCI-MSI-edge em2-3
81: 670 0 0 0 IR-PCI-MSI-edge em2-4
# 分配到每颗颗CPU核上
cat /proc/irq/{72,73,74,75,76,77,78,79,80,81}/smp_affinity
PS:smp_affinity的值可以用下面脚本算
#!/bin/bash
#
echo "统计cpu的16进制"
[ $# -ne 1 ] && echo ‘$1 is Cpu core number’ && exit 1
CCN=$1
echo “Print eth0 affinity”
for((i=0; i<${CCN}; i++))
do
echo ==============================
echo "Cpu Core $i is affinity"
((affinity=(1<<i)))
echo "obase=16;${affinity}" | bc
done
使用方法:sh 脚本名字 空格 cpu核数
###例如我的cpu是4核心的,统计出下面情况。
sh smp-affinity.sh 4
统计cpu的16进制
“Print eth0 affinity”
==============================
Cpu Core 0 is affinity
1
==============================
Cpu Core 1 is affinity
2
==============================
Cpu Core 2 is affinity
4
==============================
Cpu Core 3 is affinity
8
echo 1 > /proc/irq/72/smp_affinity
echo 2 > /proc/irq/73/smp_affinity
echo 4 > /proc/irq/74/smp_affinity
echo 8 > /proc/irq/75/smp_affinity
echo 10 > /proc/irq/76/smp_affinity
echo 20 > /proc/irq/77/smp_affinity
echo 40 > /proc/irq/78/smp_affinity
echo 80 > /proc/irq/79/smp_affinity
echo 100 > /proc/irq/80/smp_affinity
echo 200 > /proc/irq/81/smp_affinity
3、开启网卡的RPS功能 (Linux内核2.6.38或以上版本支持)
#!/bin/bash
# Enable RPS (Receive Packet Steering)
rfc=4096
cc=$(grep -c processor /proc/cpuinfo)
rsfe=$(echo $cc*$rfc | bc)
sysctl -w net.core.rps_sock_flow_entries=$rsfe
for fileRps in $(ls /sys/class/net/eth*/queues/rx-*/rps_cpus)
do
echo fff > $fileRps
done
for fileRfc in $(ls /sys/class/net/eth*/queues/rx-*/rps_flow_cnt)
do
echo $rfc > $fileRfc
done
tail /sys/class/net/eth*/queues/rx-*/{rps_cpus,rps_flow_cnt}
补充一些知识:
Linux运维常见系统服务介绍:http://www.tiejiang.org/996.html
irabalance服务主要是可以合理调配使用各个CPU核心,把压力分配到各个CPU核心上面,提升***能,降低能耗。它自动收集系统数据分析使用模式,将工作状态置于performance mode和power-save mode二种模式。
一般精简操作系统没有安装irabalance服务,
安装和开启irbalance
yum -y install irqbalance service irqbalance start chkconfig irqbalance on mpstat -P ALL 1 10观察前后实际CPU使用运行情况
检查操作系统***诵懈鞲錾璞�IPO是不是启用了IRQBALANCE,通过下面命令可以看到
cat /proc/interrupts CPU0 CPU1 CPU2 CPU3 0: 133 0 0 0 IR-IO-APIC-edge timer 3: 1 0 0 0 IR-IO-APIC-edge 4: 1 0 0 0 IR-IO-APIC-edge 8: 1 0 0 0 IR-IO-APIC-edge rtc0 9: 0 0 0 0 IR-IO-APIC-fasteoi acpi 10: 248 0 0 0 IR-IO-APIC-edge ipmi_si 22: 3574 0 0 0 IR-IO-APIC-fasteoi ehci_hcd:usb2 23: 66835 0 0 0 IR-IO-APIC-fasteoi ehci_hcd:usb1 56: 0 0 0 0 DMAR_MSI-edge dmar0 57: 496 0 0 0 IR-HPET_MSI-edge hpet2 58: 0 0 0 0 IR-HPET_MSI-edge hpet3 59: 0 0 0 0 IR-HPET_MSI-edge hpet4 60: 0 0 0 0 IR-HPET_MSI-edge hpet5 70: 126234 0 0 0 IR-PCI-MSI-edge megasas 71: 1043467 0 0 0 IR-PCI-MSI-edge ahci 72: 62249 0 0 0 IR-PCI-MSI-edge em1-0 73: 11391 0 0 0 IR-PCI-MSI-edge em1-1 74: 2443 0 0 0 IR-PCI-MSI-edge em1-2 75: 98906 0 0 0 IR-PCI-MSI-edge em1-3 76: 1323 0 0 0 IR-PCI-MSI-edge em1-4 77: 8 0 0 0 IR-PCI-MSI-edge em2-0 78: 51597 0 0 0 IR-PCI-MSI-edge em2-1 79: 2423 0 0 0 IR-PCI-MSI-edge em2-2 80: 430 0 0 0 IR-PCI-MSI-edge em2-3 81: 658 0 0 0 IR-PCI-MSI-edge em2-4
从上面输出内容可以看出,网卡1(em0)和网卡2(em1)的IO并没有工作在负载均衡调度模式下面,所
有数据传输到cpu的第一个核里面去了,其它核处于空闲状态.
Linux下,普通用户如何临时获取root权限,来满足工作需要。
在实际工作中,公司不会将root用户直接给员工使用,而是通过员工自己的账号临时获得系统的root权限。
1.我现在测试的环境是:centos6.4-x64
2.创建两个普通用户,分别为kongzhong,xcg ;并设置密码
3.赋予root权限,有三种方式,如下:
在修改时,我们发现此文件只读,所以,我们需要在root用户下,将权限改成可修改的权限,修改完后,记得将权限改为原来的440
[root@rhel1 ~]# cd /etc/ [root@rhel1 etc]# ll sudoers -r--r-----. 1 root root 4002 Mar 2 2012 sudoers [root@rhel1 etc]# chmod 755 sudoers [root@rhel1 etc]# ll sudoers -rwxr-xr-x. 1 root root 4002 Mar 2 2012 sudoers [root@rhel1 etc]# chmod 440 sudoers # 此步,在修改好/etc/sudoers里面的内容后,将权限还原
(1).方法一:修改 /etc/sudoers 文件,找到下面一行,在root下面添加两行,如下所示:
[root@rhel1 ~]# vim /etc/sudoers root ALL=(ALL) ALL xcg ALL=(ALL) ALL # 这个在切换时,是需要输入密码的,密码是当前普通用户的密码 kongzhong ALL=(ALL) NOPASSWD:ALL # 这个在切换时,不需要输入密码 修改完毕,用xcg,kongzhong帐号登录, 然后,执行sudo 命令,即可执行相应的命令; 或者 执行sudo su ,临时切换到root用户下,获取root权限。
(2).方法二:修改 /etc/sudoers 文件,去除下面这一行的注释,然后修改普通用户默认组为wheel
[root@rhel1 ~]# vim /etc/sudoers %wheel ALL=(ALL) ALL 然后,修改普通用户,使其属于wheel 组,命令如下: [root@rhel1 etc]# usermod -g wheel kongzhong1 修改完毕,用kongzhong1帐号登录; 然后,执行 sudo 命令,即可执行相应的命令; 或者 执行sudo su ,临时切换到root用户下,获取root权限
(3).方法三:修改 /etc/passwd 文件,找到如下行,把用户ID修改为 0 ,如下所示:
[root@rhel1 ~]# vim /etc/passwd kongzhong2:x:504:504:kongzhong2:/home/kongzhong2:/bin/bash 修改后如下 kongzhong2:x:0:500:kongzhong2:/home/kongzhong2:/bin/bash 保存,用kongzhong2账户登录后,直接获取的就是root帐号的权限。
以上三种方法,建议使用 第一种,第三种强烈不建议使用,企业也不会去使用。