Linux PXE+DHCP+NFS+Kickstart无人值守安装 (1) 网络装机
PXE网络装机
注释:我们要安装的是 rhel-server-5.9_x86_64
下载地址是:地址晚一点给大家。
linux PXE远程安装介绍:
PXE是由Intel设计的协议,它可以使计算机通过网络启动。协议分为client和server两端,PXE client在网卡的ROM中,当计算机引导时,BIOS把PXE client调入内存执行,并显示出命令菜单,经用户选择后,PXE client将放置在远端的操作系统通过网络下载到本地运行,无盘工作站就是通过PXE来进行启动的。PXE协议的成功运行需要解决以下两个问题:
1.IP地址的分配:
可以用DHCP server来给PXE client分配一个IP地址,DHCP Server是用来给DHCP Client动态分配IP地址的协议,不过由于这里是给PXE Client分配IP地址,所以在配置DHCP Server时,需要增加相应的PXE特有配置。
2.下载Linux内核和根文件系统:
PXE client所在的ROM中,已经存在了TFTP Client。PXE Client使用TFTP Client,通过TFTP协议到TFTP Server上下载所需的文件。
3.工作原理:
PXE client是需要安装Linux的计算机,TFTP Server和DHCP Server运行在另外一台Linux Server上。Bootstrap文件、配置文件、Linux内核以及Linux根文件系统都放置在Linux Server上TFTP服务器的根目录下。PXE client在工作过程中,需要三个二进制文件:bootstrap、Linux 内核和Linux根文件系统。Bootstrap文件是可执行程序,它向用户提供简单的控制界面,并根据用户的选择,下载合适的Linux内核以及Linux根文件系统。
4.什么是Kickstart:
Kickstart是一种无人值守的安装方式。它的工作原理是在安装过程中记录典型的需要人工干预填写的各种参数,并生成一个名为 ks.cfg的文件。如果在安装过程中(不只局限于生成Kickstart安装文件的机器)出现要填写参数的情况,安装程序首先会去查找 Kickstart生成的文件,如果找到合适的参数,就采用所找到的参数;如果没有找到合适的参数,便需要安装者手工干预了。所以,如果Kickstart文件涵盖了安装过程中可能出现的所有需要填写的参数,那么安装者完全可以只告诉安装程序从何处取ks.cfg文件,然后就去忙自己的事情。等安装完毕,安装程序会根据ks.cfg中的设置重启系统,并结束安装。
服务器批量部署:
规模化 :同时装配多台主机
自动化 :装系统,配置各种服务
远程实现:不需要关盘,U盘等物理安装介质
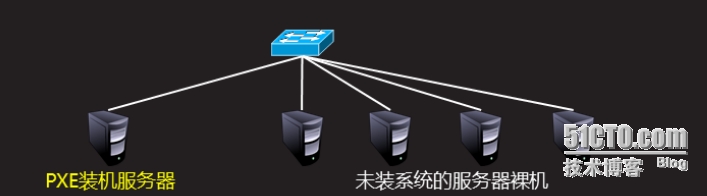
配置PXE服务器:
基本部署思路:
- 1,准备RHEL 5.9安装源(YUM库或NFS共享)
- 2,启动DNS服务(可选)
- 3,启动DHCP服务
- 4,启用TFTP服务,并提供内核,引导程序
- 5,为PXE安装配置启动菜单
注释首先要关闭防火墙和SELinux方法如下:
[root@localhost ~]# /etc/init.d/iptables stop
[root@localhost ~]# setenforce 0
1。给服务器配置固定的“IP”地址然后在重新启动网卡:修改网卡配置文件。
[root@localhost ~]# vim /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eth0
# Intel Corporation 82545EM Gigabit Ethernet Controller (Copper)
DEVICE=eth0
BOOTPROTO=static
ONBOOT=yes
IPADDR=192.168.0.252
NETMASK=255.255.255.0
[root@localhost ~]# /etc/init.d/network restart
正在关闭接口 eth0: [确定]
关闭环回接口: [确定]
弹出环回接口: [确定]
弹出界面 eth0: [确定]
在配置“YUM”的时候首先我们要把光盘挂载在到虚拟机上,方法如下。首先点击“虚拟机--然后看到里面有一个“设置”点击。就会出现下面的这个图” 配置“YUM”源,他的作用是提供软件包。
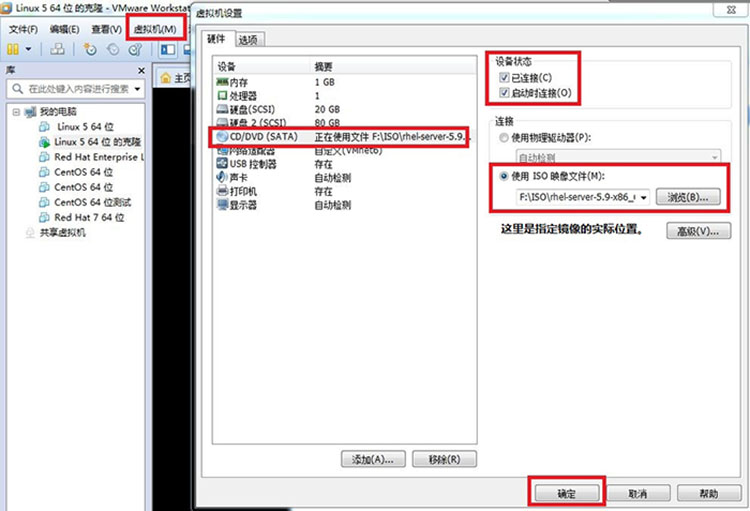
[root@localhost ~]# vim /etc/yum.repos.d/rhel-debuginfo.repo
[rhel-debuginfo]
name=Red Hat Enterprise Linux $releasever - $basearch - Debug
baseurl=file:///misc/cd/Server
enabled=1
gpgcheck=0
#gpgkey=file:///etc/pki/rpm-gpg/RPM-GPG-KEY-redhat-release
[root@localhost ~]# yum repolist
Loaded plugins: product-id, security, subscription-manager
This system is not registered to Red Hat Subscription Management. You can use subscription-manager to register.
rhel-debuginfo | 1.5 kB 00:00
repo id repo name status
rhel-debuginfo Red Hat Enterprise Linux 5Server - x86_64 - Debug 3,335
repolist: 3,335
[root@localhost ~]# yum clean all
Loaded plugins: product-id, security, subscription-manager
This system is not registered to Red Hat Subscription Management. You can use subscription-manager to register.
Cleaning up Everything
现在开始配置 配置相关的服务:
1,TFTP配置如下:
[root@localhost ~]# yum -y install tftp-server
[root@localhost ~]# rpm -q tftp-server
tftp-server-0.49-2
[root@localhost ~]# vim /etc/xinetd.d/tftp
# default: off
# description: The tftp server serves files using the trivial file transfer \
# protocol. The tftp protocol is often used to boot diskless \
# workstations, download configuration files to network-aware printers, \
# and to start the installation process for some operating systems.
service tftp
{
socket_type = dgram
protocol = udp
wait = yes
user = root
server = /usr/sbin/in.tftpd
server_args = -s /tftpboot
disable = yes ---------》把这里的“yes”改成“no”
per_source = 11
cps = 100 2
flags = IPv4
}
1.现在针对“ /tftpboot/”目录做一些相关的操作。具体步骤如下:
1)进入“TFTP”服务服务主目录然后查看一下目有哪些文件或者目录:
[root@localhost ~]# cd /tftpboot/
[root@localhost tftpboot]# ls
linux-install
将linux网卡引导文件“pxelinux.0”与linux安装光盘“initrd.img”、linux内核“vmlinuz”放到该目录下:
2)“pxelinux.0”的这个文件默认路径在“/usr/share/syslinux/”下我们可以直接把这个文件考到“/tftpboot/”这个目录里,我们使用“find”命令查找。
[root@localhost tftpboot]# find / -name pxelinux.0
/tftpboot/linux-install/pxelinux.0
/usr/share/syslinux/pxelinux.0
[root@localhost ~]# cp /usr/share/syslinux/pxelinux.0 /tftpboot/
3)“initrd.img”和“vmlinuz”这两个文件在光盘里的“isolinux/”目录下。
[root@localhost ~]# cd /misc/cd/
[root@localhost cd]# pwd
/misc/cd
[root@localhost cd]# cd isolinux/
[root@localhost isolinux]# ls
boot.cat general.msg isolinux.bin memtest param.msg splash.lss vmlinuz
boot.msg initrd.img isolinux.cfg options.msg rescue.msg TRANS.TBL
[root@localhost isolinux]# cp initrd.img vmlinuz /tftpboot/
[root@localhost isolinux]# ls /tftpboot/
initrd.img linux-install vmlinuz pxelinux.0
4)新建目录“pxelinux.cfg”这个目录要建到“/tftpboot”目录下才可以。
[root@localhost isolinux]# mkdir /tftpboot/pxelinux.cfg
[root@localhost tftpboot]# ls
initrd.img linux-install pxelinux.0 pxelinux.cfg vmlinuz
5)我们把“isolinux.cfg”这个文件复制到“/tftpboot/pxelinux.cfg”目录下在改名成“default”
在使用"ls -l"查看一下是否成功了。
[root@localhost isolinux]# cp isolinux.cfg /tftpboot/pxelinux.cfg/default
[root@localhost isolinux]# ls -l /tftpboot/pxelinux.cfg/default
-r-xr-xr-x 1 root root 364 07-09 00:37 /tftpboot/pxelinux.cfg/default
6)配置完成以后我们要把服务加入开机启动,方法如下:
[root@localhost ~]# /etc/init.d/xinetd restart
停止 xinetd: [确定]
启动 xinetd: [确定]
[root@localhost ~]# chkconfig xinetd on
[root@localhost ~]# chkconfig --list xinetd
xinetd 0:关闭 1:关闭 2:启用 3:启用 4:启用 5:启用 6:关闭
2.配置“DHCP”服务,步骤如下 :
[root@localhost ~]# yum -y install dhcp
[root@localhost ~]# rpm -q dhcp
dhcp-3.0.5-31.el5_8.1
1)在配置“DHCP”服务的时候首先要复制一份模板到这个目录下“/etc/dhcpd.conf”覆盖这个文件里的所有内容。
[root@localhost ~]# cp /usr/share/doc/dhcp*/dhcpd.conf.sample /etc/dhcpd.conf
cp:是否覆盖“/etc/dhcpd.conf”? y ----》这里是询问你。是否覆盖这个文件里的内容。我们打“y”确定覆盖就是了。
2)配置主配置文件“/etc/dhcpd.conf”:
[root@localhost ~]# vim /etc/dhcpd.conf
ddns-update-style interim;
ignore client-updates;
subnet 192.168.0.0 netmask 255.255.255.0 {
option routers 192.168.0.252;
option subnet-mask 255.255.255.0;
filename "pxelinux.0";
next-server 192.168.0.252;
option nis-domain "domain.org";
option domain-name "domain.org";
option domain-name-servers 192.168.0.252;
option time-offset -18000; # Eastern Standard Time
range dynamic-bootp 192.168.0.10 192.168.0.100;
default-lease-time 21600;
max-lease-time 43200;
}
1)设置“DHCP”服务为开机启动,以及把刚配置好的服务启动一下。
[root@localhost ~]# /etc/init.d/dhcpd restart
启动 dhcpd: [确定]
[root@localhost ~]# /etc/init.d/dhcpd restart
关闭 dhcpd: [确定]
启动 dhcpd: [确定]
[root@localhost ~]# chkconfig dhcpd on
[root@localhost ~]# chkconfig --list dhcpd
dhcpd 0:关闭 1:关闭 2:启用 3:启用 4:启用 5:启用 6:关闭
3.现在配置“NFS”服务:
1)首先要安装“nfs-utils ”“ nfs-utils-lib”这两个软件包。然后在查看一下是否安装成功。
[root@localhost ~]# yum -y install nfs-utils
[root@localhost ~]# yum -y install nfs-utils-lib
[root@localhost ~]# rpm -q nfs-utils
nfs-utils-1.0.9-66.el5
[root@localhost ~]# rpm -q nfs-utils-lib
nfs-utils-lib-1.0.8-7.9.el5
nfs-utils-lib-1.0.8-7.9.el5
2)现在来配置“nfs”的主配置文件:
[root@localhost ~]# vim /etc/exports
/misc/cd/ *(ro)
/ks *(ro)
3)设置“NFS”配置为开机启动。不要看,到启动服务的时候有几个失败的提示,不要怕这是正常的,因为这个服务是没有启动,所以我们在重新启动的这个服务的时候这个服务是没有启动的状态。下面“portmap”这个服务也要启动。
[root@localhost ~]# /etc/init.d/nfs restart
关闭 NFS mountd: [失败]
关闭 NFS 守护进程: [失败]
关闭 NFS quotas: [失败]
启动 NFS 服务: [确定]
关掉 NFS 配额: [确定]
启动 NFS 守护进程: [确定]
启动 NFS mountd: [确定]
Stopping RPC idmapd: [确定]
正在启动 RPC idmapd: [确定]
[root@localhost ~]# /etc/init.d/portmap restart
停止 portmap: [确定]
启动 portmap: [确定]
4)现在我们把“NFS”服务加入开机启动项:
[root@localhost ~]# chkconfig nfs on
[root@localhost ~]# chkconfig --list nfs
nfs 0:关闭 1:关闭 2:启用 3:启用 4:启用 5:启用 6:关闭
[root@localhost ~]# chkconfig portmap on
[root@localhost ~]# chkconfig --list portmap
portmap 0:关闭 1:关闭 2:启用 3:启用 4:启用 5:启用 6:关闭
4.现在安装自动应答文件的软件包“system-config-kickstart”
注意:我们要先创建一个“/ks”的目录,是为了放我们下面新建的自动应答文件。
[root@localhost ~]# yum -y install system-config-kickstart
[root@localhost ~]# rpm -q system-config-kickstart
system-config-kickstart-2.6.19.9-2.el5
1)现在配置自动应答文件的内容:
[root@localhost ~]# system-config-kickstart
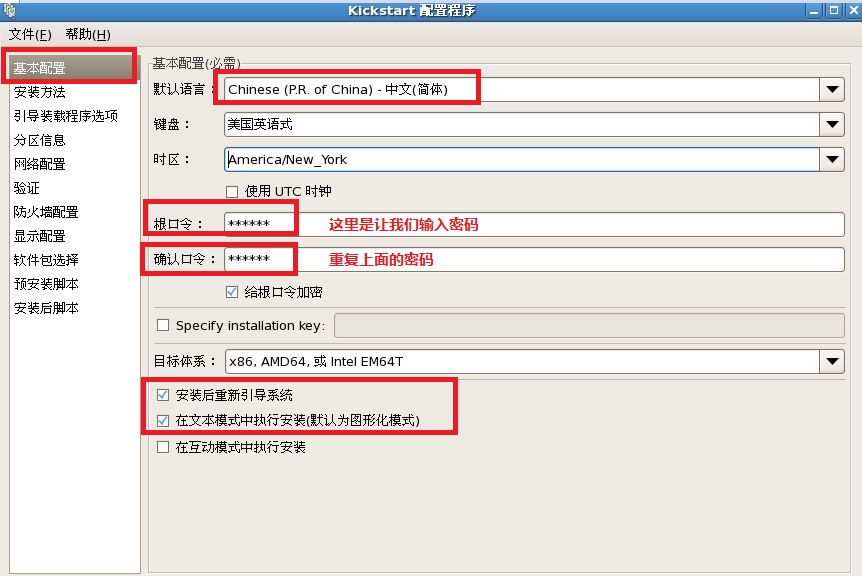
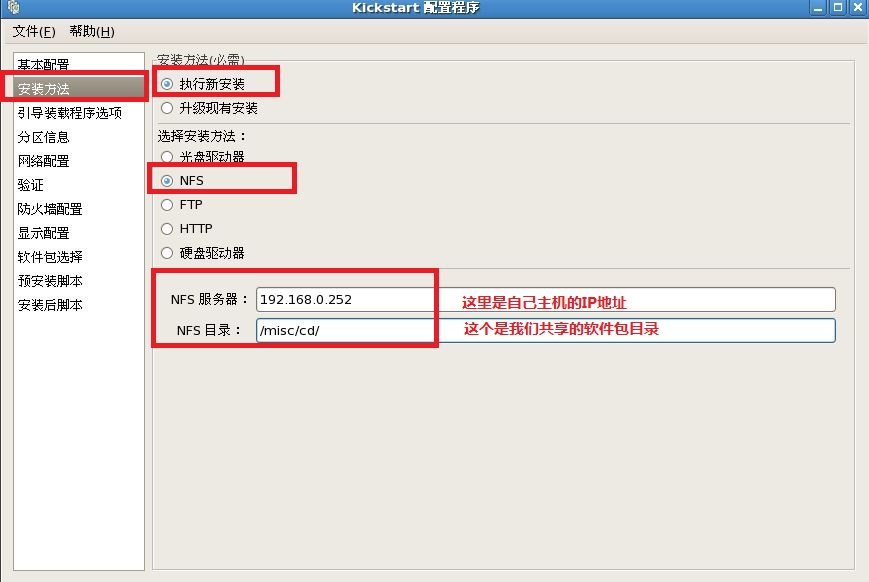
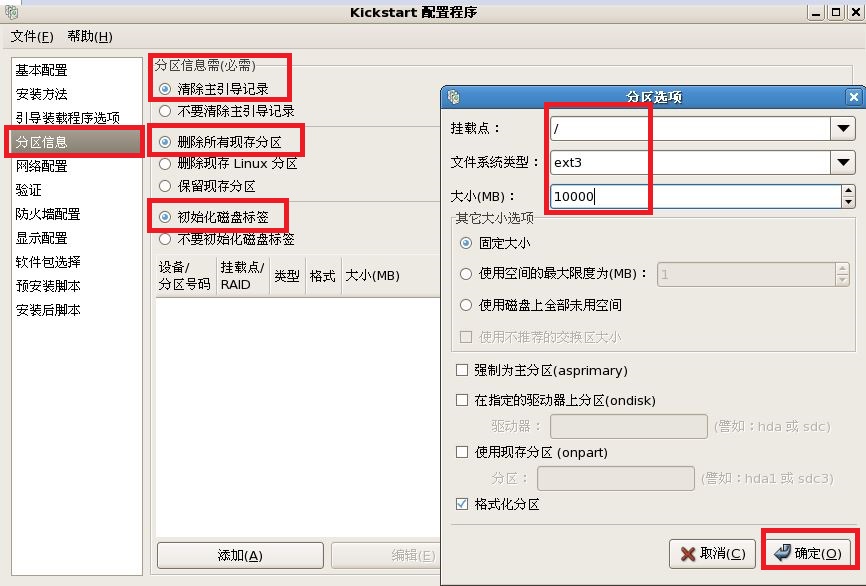
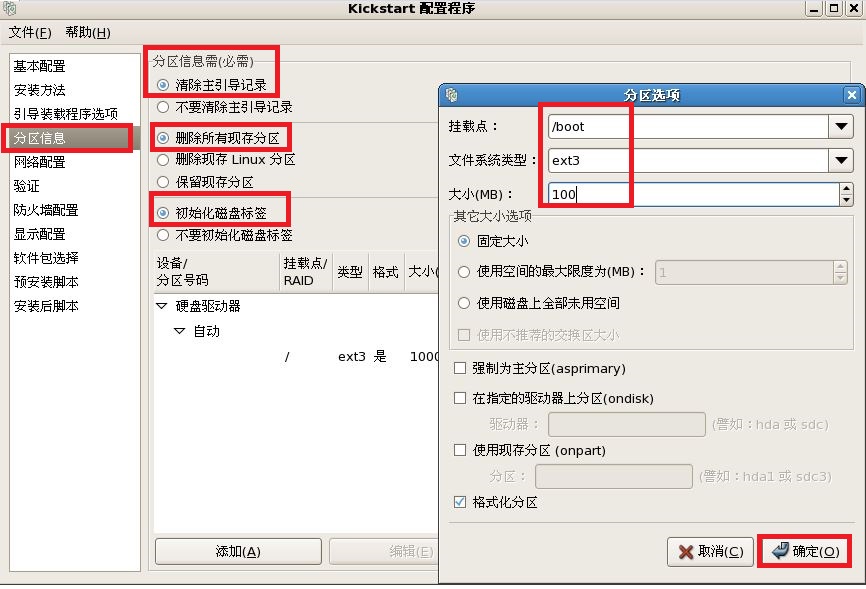
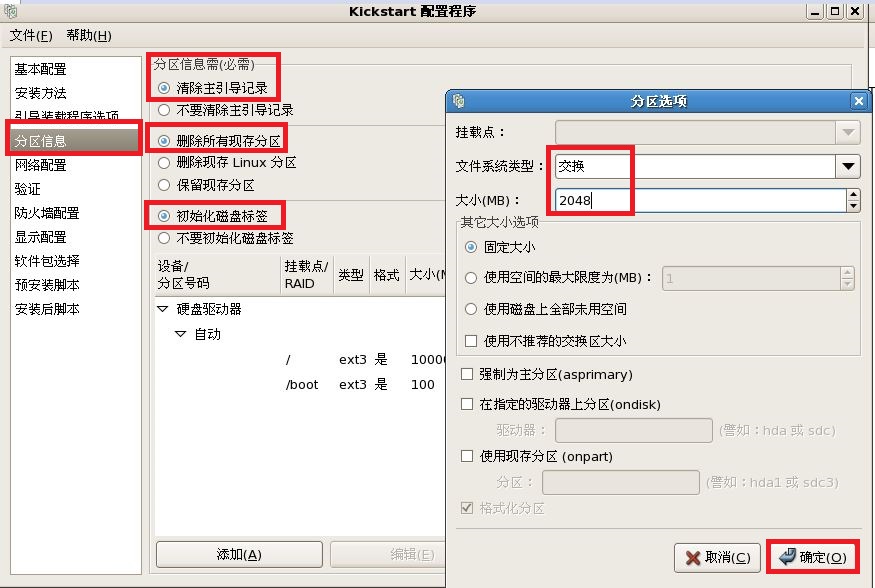
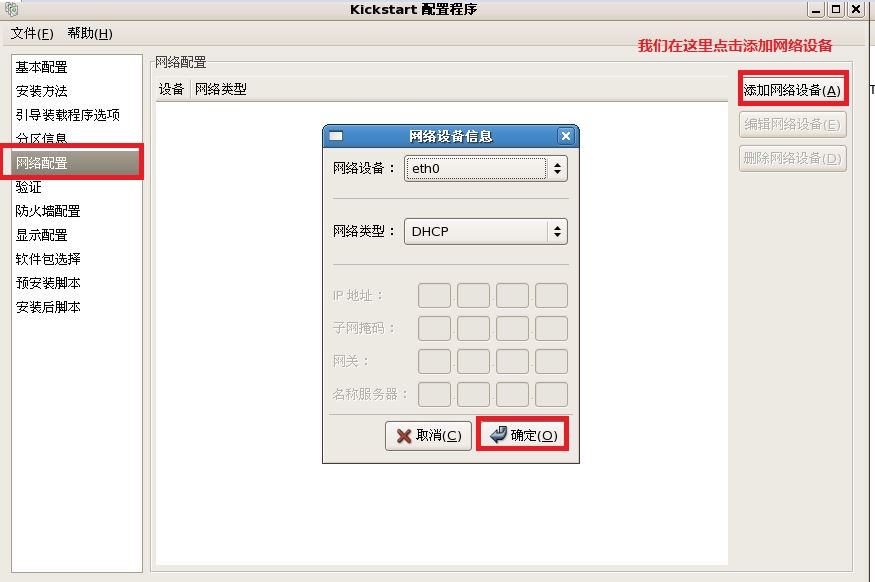
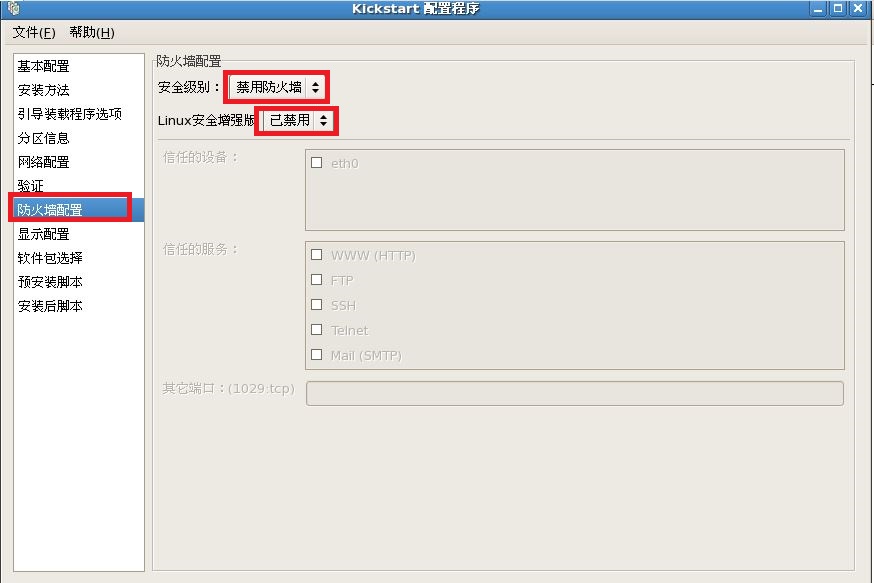
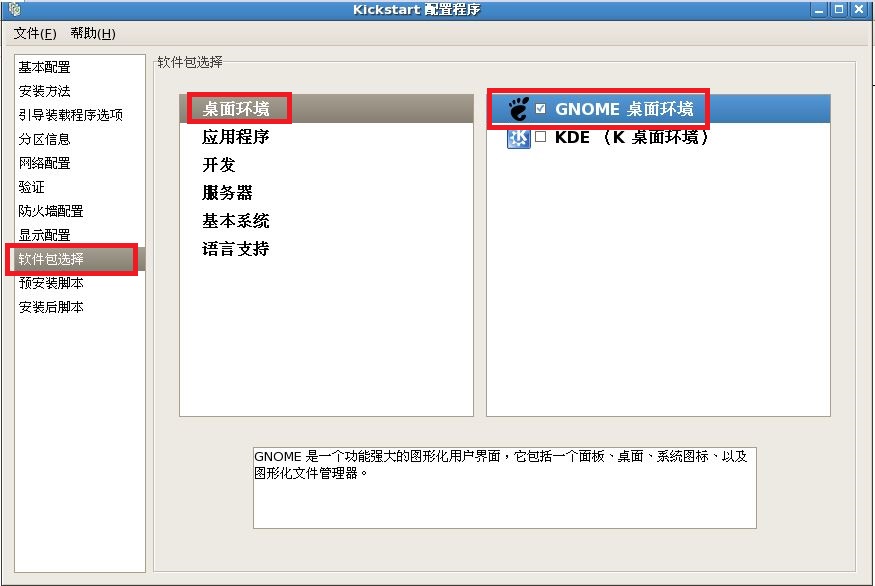
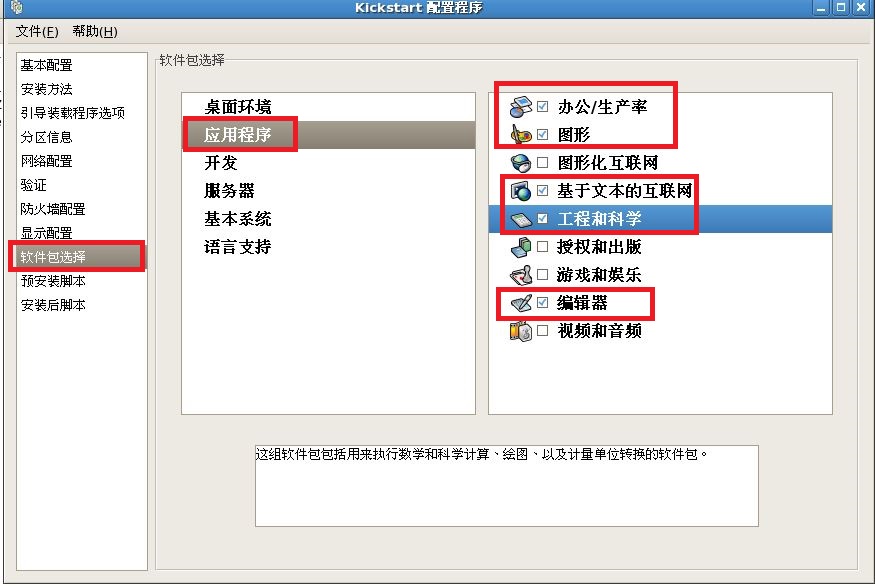
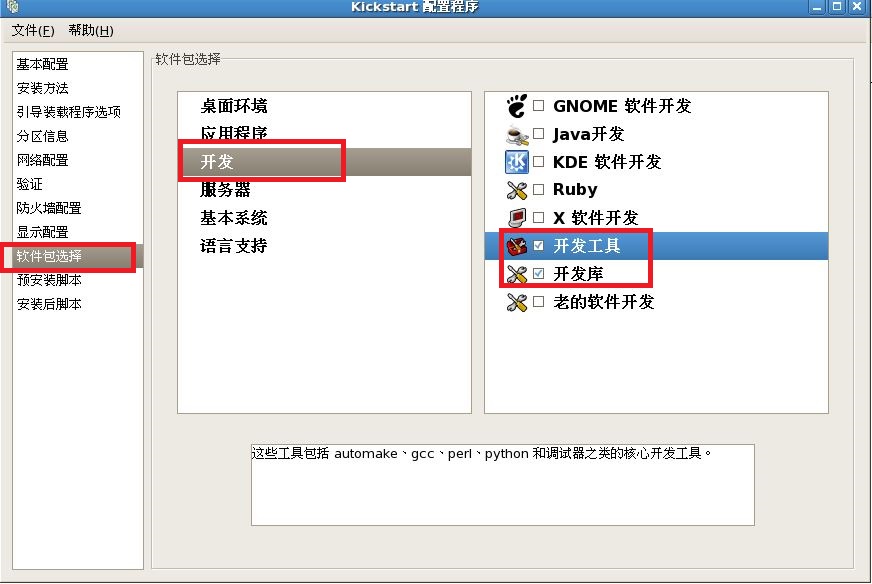
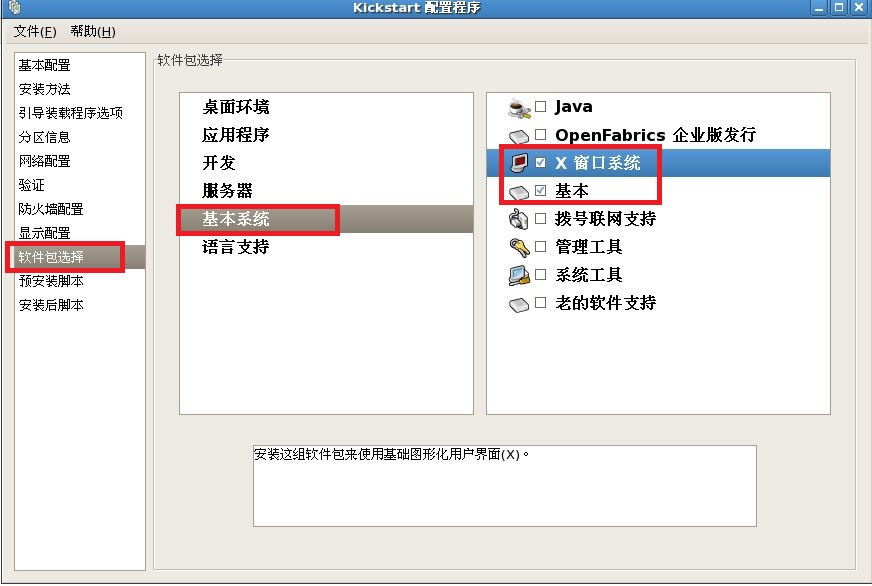
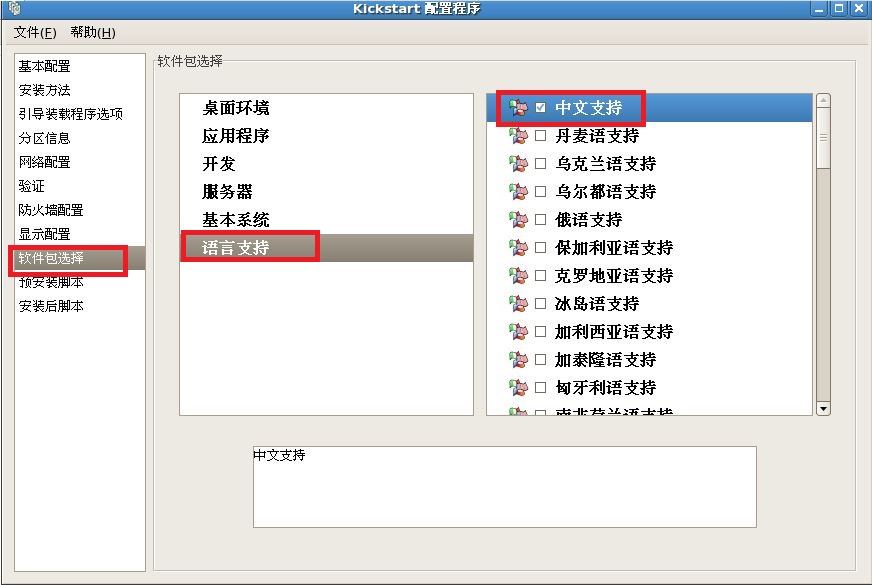
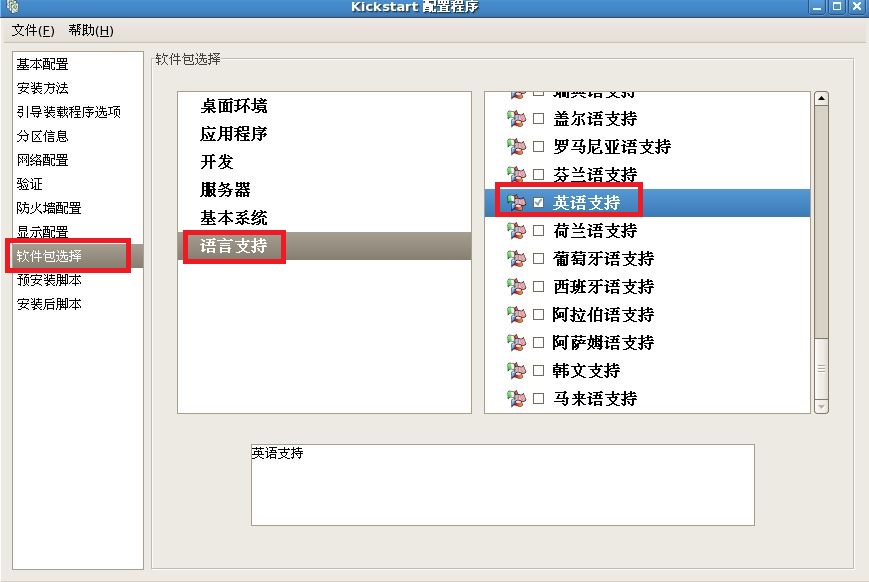
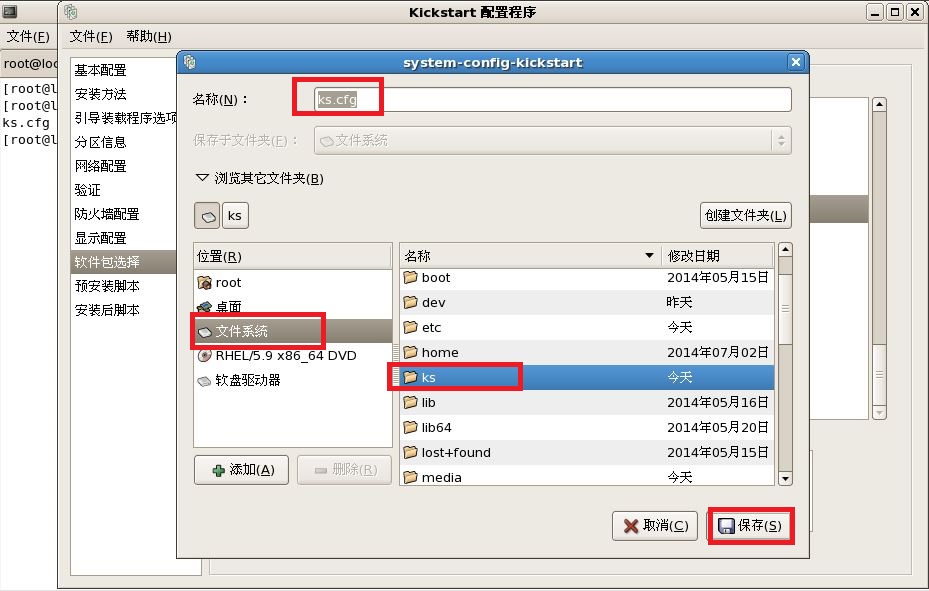
注释:最后把我们配置好的文件保存到,我们新见建的“/ks”目录下。
2)我们配置好文件以后,稍微修改一下,我们在这个文件里加入“key --skip”这个选项是为了,跳过序列号的验证。
[root@localhost ~]# cd /ks/
[root@localhost ks]# vim ks.cfg
[root@localhost ks]# cat ks.cfg
#platform=x86, AMD64, 或 Intel EM64T
# System authorization information
auth --useshadow --enablemd5
# System bootloader configuration
key --skip
bootloader --location=mbr
# Clear the Master Boot Record
zerombr
# Partition clearing information
clearpart --all --initlabel
# Use text mode install
text
# Firewall configuration
firewall --disabled
# Run the Setup Agent on first boot
firstboot --disable
# System keyboard
keyboard us
# System language
lang zh_CN
# Installation logging level
logging --level=info
# Use NFS installation media
nfs --server=192.168.0.252 --dir=/misc/cd/
# Network information
network --bootproto=dhcp --device=eth0 --onboot=on
# Reboot after installation
reboot
#Root password
rootpw --iscrypted $1$KMXm8XiE$EtJ0gOteQS3RSN/BUozSt/
# SELinux configuration
selinux --disabled
# System timezone
timezone America/New_York
# Install OS instead of upgrade
install
# X Window System configuration information
xconfig --defaultdesktop=GNOME --depth=8 --resolution=640x480
# Disk partitioning information
part / --bytes-per-inode=4096 --fstype="ext3" --size=10000
part /boot --bytes-per-inode=4096 --fstype="ext3" --size=100
part swap --bytes-per-inode=4096 --fstype="swap" --size=2048
%packages
@development-libs
@gnome-desktop
@base
@development-tools
@base-x
@graphics
@office
@chinese-support
@text-internet
@editors
@engineering-and-scientific
2)现在我们在稍微修改一下“/tftpboot/pxelinux.cfg/default”这个配置文件。因为这个文件是一个引导文件。
注意这个文件是只读的,如果修改完了以后保存的时候要加上“!”的意思是代表强制保存。
[root@localhost ~]# vim /tftpboot/pxelinux.cfg/default
default linux
prompt 1
timeout 600
display boot.msg
F1 boot.msg
F2 options.msg
F3 general.msg
F4 param.msg
F5 rescue.msg
label linux
kernel vmlinuz
append initrd=initrd.img ks=nfs:192.68.0.252:/ks/ks.cfg
label text
kernel vmlinuz
append initrd=initrd.img text
label ks
kernel vmlinuz
append ks initrd=initrd.img
label local
localboot 1
label memtest86
kernel memtest
append -
5.现在重启什么有的服务:
[root@localhost ~]# /etc/init.d/dhcpd restart
关闭 dhcpd: [确定]
启动 dhcpd: [确定]
[root@localhost ~]# /etc/init.d/portmap restart
停止 portmap: [确定]
启动 portmap: [确定]
[root@localhost ~]# /etc/init.d/xinetd restart
停止 xinetd: [确定]
启动 xinetd: [确定]
[root@localhost ~]# /etc/init.d/nfs restart
关闭 NFS mountd: [确定]
关闭 NFS 守护进程: [确定]
关闭 NFS quotas: [确定]
关闭 NFS 服务: [确定]
启动 NFS 服务: [确定]
关掉 NFS 配额: [确定]
启动 NFS 守护进程: [确定]
启动 NFS mountd: [确定]
Stopping RPC idmapd: [确定]
正在启动 RPC idmapd: [确定]
6,这样我们就可以再客户机上测试了:
注意事项:
1,新建一个虚拟机。
2,把新建好的虚拟机的网络调试到和服务器一个网络上
3,我们在把客户机设置成网络启动
步骤我就不说了。我想大家都会把。